Ch 18: Preoperative Care Medical Surgical Nursing TEXT + Lecture notes – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
surgery

answer
art and science of treating diseases, injuries, and deformities by operation and instrumentation. -involves open and dynamic interactive among the patient, anesthesia care provider (ACP), and nurse
question
Purposes of surgery
answer
-diagnosis (ex: biopsy) -cure (ex. appendectomy) -palliation (ex. debulking tumors) -prevention (ex. preventative mastectomy) -exploration (ex. laparotomy, laparoscopy) -cosmetic improvement
question
elective surgery
answer
-A surgical procedure that may be scheduled in advance, is not an emergency, and is discretionary on the part of the physician and patient. -Can be delayed without catastrophe. -Can be a carefully planned event
question
emergency surgery
answer
-must be performed immediately to save life or preserve function of body part. Ex: control of hemorrhage, appendectomy, repair of traumatic amputation -unexpected urgency
question
ambulatory surgery
answer
-Scheduled outpatient procedures provided for clients who do not remain overnight in a hospital. -majority of surgical procedures -usually minimally invasive -may be conducted in emergency departments, endoscopy clinics, physicians' offices, freestanding surgical clinics, outpatient surgery units in hospitals, etc. -performed using general, regional or local anesthetic -operating time of less than 2 hours -involves minimal laboratory tests, requires fewer preoperative and postoperative medications, and reduces patient's susceptibility to hospital-acquired infections -cost is usually less for both patient and the insurer -patients usually prefer because of the convenience of recovering at home -physicians prefer the flexibility in scheduling
question
surgical settings
answer
-elective or emergency -majority of surgery is ambulatory or same-day -emergency rooms -physician's office -freestanding surgical centre -surgical units in hospitals
question
patient interview
answer
-obtain patient's health information- usually done by a hospital nurse up to a few weeks before procedure -provide and clarify information about the surgery- preop teaching, patient can ask questions -assess patient's emotional state and readiness for surgery
question
subjective information
answer
-psychosocial assessment -past health history -medications (incl. herbals and OTC) -allergies -review of systems -functional health patterns (smoking, eating, exercise)
question
Gordon's Functional Health Patterns
answer
Health Perception Health Management Pattern Nutritional Metabolic Pattern Elimination Pattern Activity Exercise Pattern Sleep Rest Pattern Cognitive-Perceptual Pattern Self-Perception-Self-Concept Pattern Role-Relationship Pattern Sexuality-Reproductive Coping-Stress Tolerance Pattern Value-Belief Pattern
question
functional health pattern questions
answer
do you smoke? do you have any chronic illnesses? do you experience constipation? what is your height and weight? do you have problems chewing and swallowing? do you wear glasses or hearing aid? what have you found to be effective for pain relief? how do you feel about this surgery? do you have the support you need after surgery?
question
objective information
answer
-lab and diagnostic testing -physical exam
question
common preoperative laboratory and diagnostic tests
answer
-ABG's & pulse oximetry to asses ventilatory and metabolic function; oxygenation status -GLU- metabolic status, DM -BUN,CREAT- renal fxn -Chest XRAY- pulmonary disorders, cardiac enlargement, heart failure -CBC- anemia, immune status, infection -ECG - cardiac disease, dysrhythmias, electrolyte abnormalities -LYTES- metabolic status, renal function, diuretic side effects -hCG- pregnancy -LFTs- liver status -PT,PTT,INR, PLT- coag status -Pulmonary function studies- pulmonary status -ALB- nutritional status -Type & XM- blood availability for replacement (elective surgery patients may have own blood available) UR- renal status, hydration, UTI
question
psychosocial assessment
answer
-anxiety -common fears (recovery, death, mutilation/scars, waking during surgery, lack of control) -hope (anticipating positive outcome) -situational changes, concerns with the unknown, concerns with body image, past experiences, knowledge deficit)
question
past health history
answer
-previous medical and surgical problems -current health problems -menstrual and OB history including LMP (pregnancy) -family hx of cardiac or endocrine problems -family hx of problems with anesthesia (malignant hyperthermia) -Fig 18-3 Health History p 341
question
medications
answer
-current routine and intermittent medications -prescription, OTC and herbal/supplement -many patients believe that herbal supplements are "natural" and therefore do not pose a surgical risk, so make sure to ask. -assess compliance (ask when last taken) -recreational drug use, tobacco, alcohol (open ended questions, worry about alcohol withdrawal post surgery) -be frank about recreational substances- stress that their use may affect the type and amount of anesthesia that will be needed. -in many ambulatory surgery centres patients are asked to bring medications with them when reporting for surgery to facilitate accurate assessment and documentation of both the name and dosage of current meds.
question
medication interactions
answer
-tranquilizers may potentiate effect of opioids and anesthesia -antihypertensive meds may predispose to shock -insulin or oral diabetes meds may require adjustment -aspirin and NSAIDS may increase bleeding -ginger, feverfew, gingko biloba, garlic may increase bleeding -st johns wort may prolong effects of anesthesia -echinacea may cause inflammation of liver if used with other medications
question
allergies
answer
- distinguish: allergies vs idiosyncratic effects vs side effects -true drug allergy: produces hives, and/or anaphylaxis -non-drug allergies: latex, pollen, animals -latex screening: risk factors, contact dermatitis, contact uriticaria, aerosol reactions, hx of reactions that suggest allergy -risk factor: long-term, multiple exposures can cause latex allergy -food allergy to tropical fruits predisposes to latex allergy -pt with history of any allergic reactions has a greater potential for demonstrating hypersensitivity reaction to drugs administered during anesthesia
question
review of systems+physical exam
answer
CV, resp, neuro, GU, hepatic system, integumentary, musculoskeletal,endocrine, immune, fluid and electrolyte status, nutritional status -any acute or chronic problems
question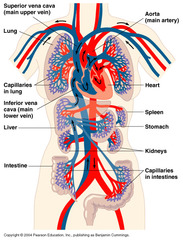
cardiovascular

answer
-prosthetic heart valves, pacemakers (left upper chest (sometimes right)), implanted defibrillators -inspect and evaluate edema -neck vein distension -obtain bilateral baseline BP -evaluate bilateral peripheral pulses -heart valve replacement (increases risk for bacterial endocarditis) -increased BP -arrythmias -heart failure -angina -myocardial infarction -patients at high risk for VTE (postoperative venous thromboembolism) are hx of previous thrombosis, blood-clotting disorders, cancer, varicosities, obesity, smoking, heart failure, or COPD
question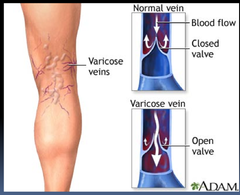
varicosities

answer
Varicose veins, visibly prominent, dilated & twisted veins, usually in lower extremities, but also in esophagus & anus. Usually the saphenous vein is affected in the leg.
question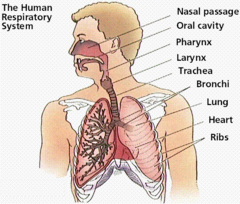
respiratory system

answer
-hx of smoking (O2 transport)- should stop 6 weeks prior to surgery. the greater the pack-years of smoking teh greater potential for pulmonary complications during or after surgery. -baseline resp rate and pattern -auscultate for normal and adventitious lung sounds -recent or chronic respiratory disease or infections -upper airway infection may result in cancellation or postponement of surgery because existing infection may increase risk of bronchospasm, laryngospasm, decreased O2 sat, problems with resp secretions -hx of dyspnea at rest or with exertion -coughing -hemoptysis (coughing blood) -hx of asthma (ask about meds) and COPD- at risk for hypoxemia, and atelectasis - sleep apnea, obesity, spinal/chest/airway deformities should also be noted
question
atelectasis
answer
Airlessness of the lungs due to failure of expansion or reabsorption of air from the alveoli.
question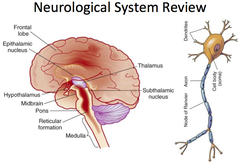
neurological system

answer
-ability to respond to questions, follow commands and maintain orderly though patterns -determine orientation to PPT&S -ability to pay attention, concentrate, and respond appropriately in preop phase must be documented to establish an accurate baseline for post op comparison. -cognitive function for completing preop preparation and post op care -hx of strokes, TIAs, spinal cord injury -myasthenia gravis, Parkinson's, MS (and treatments!)
question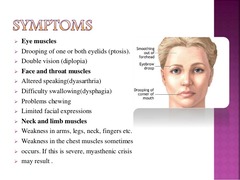
myasthenia gravis

answer
A disease in which acetylcholine receptors on muscle cells are destroyed so that muscles can no longer respond to the acetylcholine signal to contract. Symptoms include muscular weakness and progressively more common bouts of fatigue. The disease's cause is unknown but is more common in females than in males; it usually strikes between the ages of 20 and 50.
question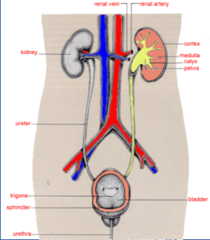
genitourinary system

answer
-hx of renal or urinary tract diseases -glomerulonephritis, CKD, repeated UTIs -renal dysfunction: fluid+electrolyte imbalances, coagulopathies, increased risk for infection, impaired wound healing. -colour, amount, characteristics of urine -UPT -many drugs are metabolized and excreted by the kidneys -decrease in renal function: latered response to drugs and unpredictable drug elmination -problems voiding
question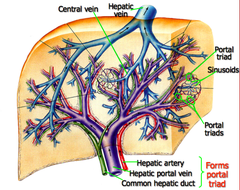
hepatic system

answer
-liver: glucose homeostasis, fat metabolism, protein synthesis, drug and hormone metabolism, bilirubin formation and excretion. detoxifies many anesthetics and adjunctive drugs -review hx of substance abuse -inspect skin colour and sclera for signs of jaundice -hepatic dysfunction may have increase perioperative risk for clotting abnormalities and adverse responses to medications. -hx of jaundice, hepatitis, alcohol abuse, obesity
question
integumentary system

answer
-hx of skin problems : rash, eczema, boils, lesions --esp around surgical site (may affect post op healing) -hx of pressure ulcers: may require extra padding during surgery -note dry skin, bruising, breaks. -assess skin turgor, mm for dehydration, skin moisture and temperature
question
muskuloskeletal system
answer
-hx of arthritis- note all affected joints -mobility restrictions may influence intraoperative and postoperative positioning and ambulation -spinal anesthesia may be difficult if the pt cannot flex his or her lumbar spine adequately to allow easy needle insertion -if neck is affected: intubation and airway management may be difficult -note any mobility aids: should be brought with patient on day of surgery -post op pain can be due to chronic muskuloskeletal pain and positioning during surgery -examine skin over pressure points -assess ROM, strength, gait, mobility, balance
question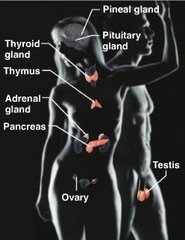
endocrine system

answer
-hx of diabetes: at risk for adverse effects of anesthesia and surgery -perioperative complications: hypoglycemia, hyperglycemia, ketosis, CV alterations, delayed wound healing, infection -glucose levels should be taken morning of surgery to establish baseline level. regardless of result, glucose levels will be assessed periodically and managed if necessary with short-acting, rapid-onset insulin -surgeon or ACP will determine if patient should take insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents on day of surgery -hx of thyroid dysfunction: surgical risk because of alterations in metabolic rate -hx of Addison's: crisis or shock can occur if pt abruptly stops taking replacement corticosteroids, and the stress of surgery may require additional IV corticosteroid therapy.
question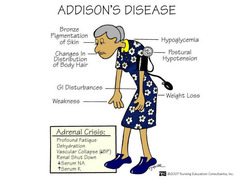
addison's

answer
occurs when the adrenal glands do not produce enough of the hormones cortisol or aldosterone
question
immune system

answer
-hx of compromised immune system or taking immunosuppressive drugs -corticosteroids used in immunosuppressive doses may be tapered down before surgery -impairment of the immune system may lead to delayed wound healing, and increased risk for post op infections. -HIV, AIDS, TB, Hep B, Hep C
question
fluid and electrolyte status
answer
-vomiting, diarrhea, pre op bowel preps -diuretic use -restricted fluid intake pre op instructions -especially critical for older adult because of reduced adaptive capacity (narrow margin of safety between overhydration and underhydration)
question
nutritional status
answer
-predictor of wound healing -very thin: provide more padding during surgery -morbidly obese: may need extra equipment for care of patients (longer instruments, etc) -obesity: stresses cardiac and pulmonary systems, can make it difficult to access surgery site, predisposes patient to wound dehiscence, wound infection and incisional herniation. adipose is less vascular so pt may be slower to recover because inhalation anesthetic is absorbed and stored by adipose tissue
question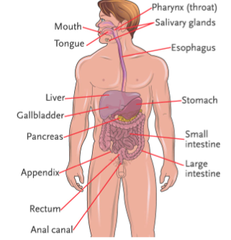
gastrointestinal system

answer
-recent weight gain/loss -intake pattern -date of last bowel movement and usual pattern -assess for presence of dentures or teeth that might be dislodged during intubation -weigh patient
question
pre-op teaching
answer
sensory: noisy, many people in room, narrow bed, cold, monitors and machines procedural information: fluid and food restrictions, what to wear and what to bring, bowel or skin prep, pain control options, turn-cough-deep breathe, mark surgical site process information: admission area, holding, or and recovery area, monitors and lines that may be present on awakening, when caregivers can see patient
question
day of surgery prep
answer
-informed consent -final teaching, assessment, communication with team -have pt in gown, no cosmetics -no jewelry -glasses and hearing aids off at last min, return ASAP -void before preop meds -transport to OR
question
Pre op meds
answer
-antibiotics (prevent post op infection) -anticholinergics (decrease oral and respiratory secretions) -antidiabetics (stablize blood glucose) -antiemetics (increase gastric emptying, prevent N/V) -benzodiazepines (decrease anxiety, induce sedation, amnesic effects) -beta blockers (manage hypertension) -histamine receptor antagonists (decrease HCl secretion, increase pH, decrease gastric volume) -opioids (releive pain during preop procedures)



