CFA Level II Portfolio Management – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Arbitrage Pricing Theory (APT) assumption
answer
1. a factor model describes asset returns,?expected market return 2. ?????there are many assets and investors can form well diversified portfolios to eliminate asset specific risk 3. ????? no arbitrage opportunities exist among well diversified portfolios
question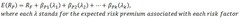
Arbitrage pricing theory formula
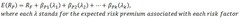
answer
beta- ????????????????GDP?inflation?? lumda-?????beta?????,?capm??Rm-Rf *APT model???????????????* ????risk premium???sensitivity beta??
question
????????????portfolio, ?expected return, sensitivity to inflation factor, sensitivity to GDP factor

answer
lumbda-???sensitivity factor???????????????Rm-Rf????
question
Carhart four factor model-?????predicted ???????

answer
small-capitalization stocks low price to book ratio stocks-momentum stocks stock whose prices have been rising-momentum stocks
question
???????Portfolio,expected return??beta,???well diversified,???????????????
answer
??well diversified portfolio,????????? lumda,????not diversified portfolio?beta??expected return,?????????????????????portfolio????????return?8%??????rentun?7.25%,?construct?short???portfolio (build from the combination of well diversified portfolios),???7.25%??????short??????portfolio,?8%??
question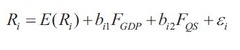
Multifactor model-Macroeconomic fatcor
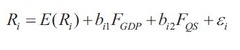
answer
??=???+factor return+firm specific risk F=surprise, beta-factor senstivity F(gdp) surprise in GDP rate,F(qs) surprise in credit quality spread (Actual value - predicted value) ---X ??Inflation-predicted inflation ????return???????GDP,credit quality spread surprises,regression??sensitivity-time series data Bi1,Bi2 are surprise sensitivity of assets error term-firm specific surprise which not be explained by model E(Ri)-expected return derived from the APT equation alpha epislon??????? beta i=(PE-PE average)/sigma PE
question
slope coefficients-Factor sensitivity
answer
measure of the response of return to each unit of increase in a factor holding all other factors constant
question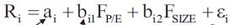
Multifactor model-Fundamental fatcor
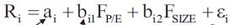
answer
bi1, bi2?x?standardized P/E or Size,?return, b1,b2???F(p/e),F(size) F(p/e),F(size)?additional return associated with one increase corresponding to b value Cross sectional data,???????????????return ?????????????????????????b???????F, surpris??
question
Security selection return
answer
Security selection return = active return - factor return active return(Rp-Rb)= factor return (?????????(beta-beta') lumada1) +security selection return (b0-b0')
question
Active Risk/Active return(Value added)/
answer
Active return-differences in returns between a managed portfolio and its benchmark Active risk-tracking error volatility Standard deviation of active returns S(Rp-Rb)
question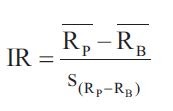
Information risk
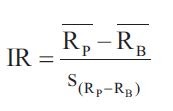
answer
evaluating mean active returns per unit of active risk ??????active risk???active return, information risk assess active return, sharp ratio assess total return Only active fund manager uses information risk
question
Active risk squared=
answer
active risk squared= active factor risk + Active specific risk Active factor risk-over weight a specific kind of stock/sector, eg. overweight tech stock in the portfolio Active specific risk-asset selection risk-overweight one specific stock in the sector, overweight microsoft in tech stocks
question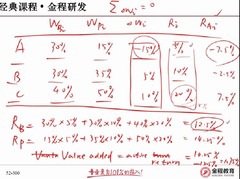
Value added -2

answer
Ra=sum of wi x Rai wi-???weight Rai-???????????? ?????????????????????
question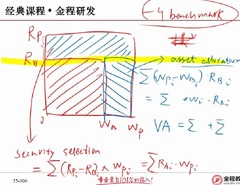
Value added -3

answer
????asset allocation??, rb rp?? Value added=Value added (asset allocation) + value added (security selection) ??? Asset allocation value added of one asset=asset allocation difference comparing to benchmark (%) * benchmark return Security selection =Actual asset allocation (%) * active return difference comparing to benchmark
question
Active return
answer
active return=security selection return+factor return ?multifactor model????? active return= security selction-expected return difference + factor return- (beta1-beta0)×lumda
question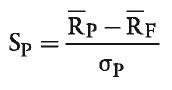
Sharp ratio?cash
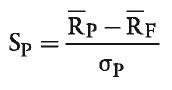
answer
Reward per unit of risk in absolute returns Risk free rate is the bench mark, thus it is unaffected by the addition of cash or leverage in a portfolio. Sharp ratio?cal?slope, ????risk free asset like cash,??????????????????
question
Information ratio??benchmark portfolio
answer
Measures reward per unit of risk in benchmark relative returns. Benchmark is benchmark portfolio,???sharp ratio ? benchmark ??risk free??benchmark portfolio, ?????benchmark portfolio,?sharp ratio???????????IR *UNAFFECTED BY AGGRESSIVENESS OF ACTIVE WEIGHTS* ?????benchmark portfolio???asset????investment return??????cash,ir??
question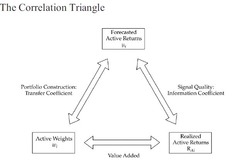
Correlation Triangle-new ??????

answer
signal quality: information coefficient-correlation between the foretasted active returns and realized active returns VA: Value added Portfolio construction:The transfer coefficient measures how well the anticipated (ex-ante), risk adjusted returns correlate with the risk-adjusted active weights. ???(0,1)??
question
Constructing Optimal Portfolios, level of active risk-new-?????

answer
Optimal portfolio-?????? 1.??active risk=IR/SRb*benchmark risk 2. total risk of actively managed portfolio is sum of benchmark return variance and active return variance
question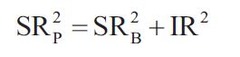
Constructing *optimal* portfolio-?????
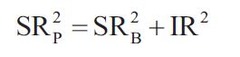
answer
Principal-finding the single risky asset portfolio with maximum sharp ratio Property in active management theory: squared sharp ratio of actively managed portfolio equal to squared sharpe ratio of benchmark plus the information ratio squared ?????? SRp=(SR(b)^2+IR^2)^1/2 Portfolio with highest information ratio will also have the highest sharp ratio
question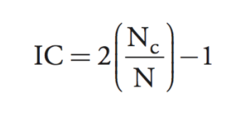
Information coefficient
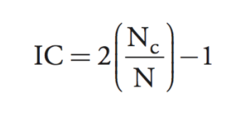
answer
Nc-?????? N-?????
question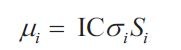
Grinold rule-?expected return
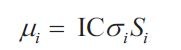
answer
???expected return IC-expected information coefficient Si-a set of standardized forecasts of expected returns across securities-scores Sigma-volatility
question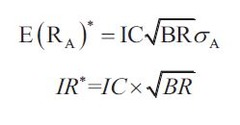
Basic fundamental law of active management
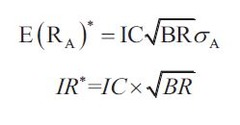
answer
Information ratio ????????????? Constraint-many investors are constrained to be long only
question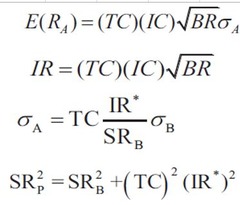
Full fundamental law of active management-??
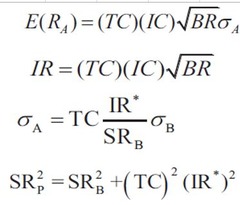
answer
??TC: cross sectional correlation between the foretasted active security return and actual active weights (?????return????
question
Discount rate ????
answer
1.real risk rate 2.inflation 3.Risk premium
question
Performance measurement

answer
expected value added conditional on the realized information coefficient ICr actual performance vary from expected value in a range determined by the benchmark tracking risk E(ra)=Ra+Noise, noise>0 noise ????1-tc^2,Ra ???? Tc^2
question
Present value model

answer
?? 1.real risk rate 2.inflation 3.Risk premium
question
Risk free rate-l
answer
Mt=Utility future/Utility Current=Ut/U0 <1 ????? Mt-inter-temporal rate of substitution-????? ????????????Mt??utility l=(Pt-P0)/P0=1/Mt - 1 P0=E(Mt) Mt=Ut/U0 GDP growth and volatility of GDP growth---????l
question
BR??

answer
row- correlation
question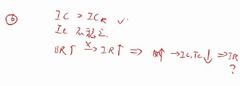
????
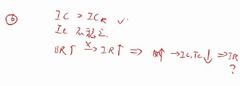
answer
??????BR??IR? BR???IC TC???IR??????
question
P0??????
answer
1. zero coupon 2. ?inflation 3. ?default ?? 4. payout??????
question
Real risk free rate ???utility, investor wealth, investor's future income expectation??
answer
1.??utility???real risk free rate ?? Mt??? P0???1/P0 - 1?? 2.???????real risk free rate?? ????utility???????ut,u0?? 3.????????????real risk free rate ?? Mt??,real risk free rate ??
question
Risk averse investor's covariance of the inter-temporal rate of substitution with asset price
answer
For risk-averse investors, when the expected future price of the investment is high (low), the marginal utility of future consumption relative to that of current consumption is low (high). Hence, the covariance of the inter-temporal rate of substitution with asset price is expected to be negative for risk-averse investors.
question
flight to quality
answer
???????? Good consumption hedge
question
GDP Growth and RFR
answer
if GDP growth ????GDP growth????Ut???Mt??????? RFR ?? ??: GDP??RFR?? GDPJ??RFR??
question
Risk free, ignore inflation, zero interest bond, risk seeking and risk aversion investor's co-variance between price and mt (inter temporal rate of substitution) and risk premium (+,-) covariance term??risk aversion
answer
P bond ?? *risk aversion* COV(p1,mt)0 (??????????premium????????? ?????covariance;0,????? interest rate???bond????
question
risk free rate and inter temporal rate of substitution
answer
inversely related the higher the return of investor, more important current consumption becomes relative to future consumption
question
real risk free rate and gdp growth and gdp volatility

answer
???
question
Inflation discount rate
answer
Inflation rate ?? ???? CF/(RFR+inflation rate+Risk Premium) Inflation rate??????? ?=expected inflation rate risk free rate + ? = nominal risk free free short term inflation=risk free rate + ? long term inflation = risk free rate + ? + ? (? is uncertainty of inflation)
question
Breadth
answer
BR, or breadth, conceptually equal to the number of independent decisions made per year by the investor in constructing the portfolio.
question
active return vs alpha
answer
RA = RP - RB, while ?P = RP - ?P × RB. alpha is actual return on portfolio - expected return
question
Taylor's rule

answer
?????0.5??target
question
? + ?
answer
? + ? = Breakeven inflation rate = yield of noninflation index bond - yield of inflation index bond *reading55 is new chapter this year, the test will be mostly from the book's exercise*
question
Risk premium and business cycle-contraction, scarcity and recession
answer
credit spread goes up default rate goes up and recovery goes down default rate (1- recovery rate)= expected loss%
question
real default free bond
answer
P0=Ut/U0
question
Discount rate of equity vs high risk bond
answer
equity:R+ ? + ?+?+? ?+?????equity premium bond: R+ ? + ?+? ?-credit risk premium ?-additional risk premium for equity comparing to high risk bond
question
economic ? P/E P/B???
answer
P/E P/B ??? ?????+? ???discount rate ??? equity price??
question
growth stock attributes
answer
growth stock high growth rate, small earning, dividend low growth stock?????????p/e?
question
Commercial real estate discount rate
answer
R+ ? + ?+?+?+? ?-illiquidity risk premium ????? ?+?-risk premium?????? 1. rent, tenet credit risk 2. sales, value uncertainty
question
portfolio management-identifying investor's objective and constraint
answer
planning -objective (RR: Risk and return)and constraint (TTLLU: tax, time horizon, legal, liquidity, unique circumstances) execution feedback -monitor balance -performance evaluation
question
cyclical?non cyclical sector?senstive?????
answer
The sensitivity of a corporate bond's spread to changes in the business cycle and the level of cyclicality tend to be positively correlated. The greater the level of cyclicality, the greater the sensitivity of the bond's spread to changes in the business cycle. During an economic downturn, the spreads of corporate bonds can be expected to widen, as the risk premium that investors demand on risky financial assets will increase. When spreads widen, the spreads on bonds issued by corporations with a low credit rating and that are part of the cyclical sector will tend to widen most. During recessions, cyclical companies are likely to experience sharp declines in earnings, more so than non-cyclical companies. In contrast, while coming out of a recession, cyclical companies are likely to generate higher earnings growth relative to non-cyclical companies.
question
bad consumption outcomes hedge
answer
depends on the relative certainty about the amount of consumption that the investor will be able to undertake with the payoff, which is short-dated, default-free government bonds
question
Risk-averse investors demanding a large equity risk premium are most likely expecting their future consumption outcomes and equity returns to be •uncorrelated. •positively correlated. •negatively correlated. ?
answer
B is correct. If investors demand high equity risk premiums, they are likely expecting their future consumption and equity returns to be positively correlated. The positive correlation indicates that equities will exhibit poor hedging properties, as equity returns will be high (e.g., pay off) during "good times" and will be low (e.g., not pay off) during "bad times". In other words, the covariance between risk-averse investors' inter-temporal rates of substitution and the expected future prices of equities is highly negative, resulting in a positive and large equity risk premium. This is the case because, in good times, when equity returns are high, the marginal value of consumption is low. Similarly, in bad times, when equity returns are low, the marginal value of consumption is high. Holding all else constant, the larger the magnitude of the negative covariance term, the larger the risk premium.
question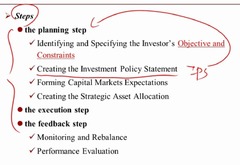
ips

answer
ips ?planning step



