Cardiovascular System Vet. Anatomy and Physiology – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Heart
answer
Muscular hollow organ with four chambers
question
Base
answer
wide top portion where the atria are found and the major vessels enter and exit the heart
question
Apex
answer
pointed end of the heart that is where the left and right ventricle are found
question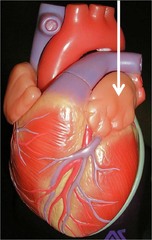
Auricles

answer
ear shaped appendages of either atrium of the heart
question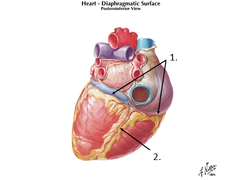
Intraventricular sulci

answer
the borders of the ventricles; can be seen on the surface of the heart; contain fat and blood vessels
question
Atria
answer
at the base of the heart; thin walls as they contain blood under low pressure
question
Ventricles
answer
thick walls as they eject blood under high pressure into arteries; right ventricular wall is smaller
question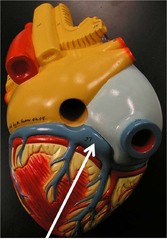
Coronary arteries

answer
Branch off of aorta immediately after leaving the left ventricle and course around the heart
question
Pericardium
answer
Fibrous connective tissue sac covering heart; Made of loose connective tissue covered by a layer of mesothelium
question
Epicardium
answer
Outermost layer of the heart
question
Endocardium
answer
Inner lining epithelium that lines the chambers and valves
question
Myocardium
answer
The muscular middle layer of the heart
question
Interventricular Septum
answer
Muscular structure that separates the left and right ventricles
question
Moderator band
answer
A band of tissue in the right ventricle that originates at the interventricular septum but does not attach to the flaps of the tricuspid valve; it connects to the outside wall of the right ventricle; gives the wall of the right ventricle structural support
question
Heart Valves
answer
Control the unidirectional blood flow in the heart as they can only open in one direction
question
Atrioventricular (AV) valves
answer
loose, overlapping flaps of tissue attached to papillary muscles on the inner wall of the heart by cordae tendineae ("heart strings")
question
Tricuspid (Right Valve)
answer
One-way flow from right atrium to right ventricle
question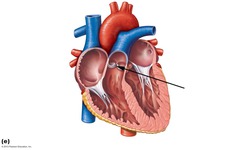
Pulmonary Valve (a semilunar valve)

answer
One-way flow out of right ventricle into pulmonary artery
question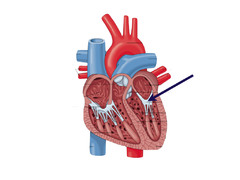
Mitral Valve (Left AV valve)

answer
One-way flow from left atrium into left ventricle
question
Aortic Valve (a semilunar valve)
answer
One-way flow from left ventricle into aorta
question
Coronary Veins
answer
Empty deoxygenated blood via the coronary sinus into the right atrium
question
Coronary Arteries

answer
Supply the muscle of the heart with oxygenated blood from the aorta
question
Pulmonary circulation
answer
Under low pressure, inside the thorax
question
Systemic circulation
answer
Blood circulation outside the thorax; Under high pressure and includes portal and peripheral circulation
question
Arteries
answer
Carry blood under high pressure away from the heart, has 3 layerts, inner smooth endothelium, middle smooth muscle, outter fibrous tissue
question
Aorta
answer
largest artery in the body
question
subclavian arteries
answer
supply the thoracic limb
question
Iliac arteries
answer
supply the pelvic limbs
question
Arterioles
answer
Small branches of arteries that lead to capillaries
question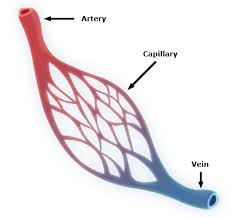
Capillaries

answer
Vessels with thin walls (no muscle in the walls); where oxygen and nutrients in the blood are exchanged for carbon dioxide and other waste products
question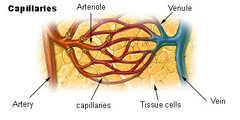
Venules

answer
Small veins that carries blood from capillaries to veins
question
Veins
answer
carry blood under low pressure to the heart, small and medium ones have vavles
question
Cranial Vena Cava
answer
carries blood from the left and right brachiocephalic veins to the heart
question
Caudal Vena Cava
answer
carries blood from the left and right iliac veins to the heart
question
Arterial system
answer
High pressure system, forcing blood to tissues
question
Venous system
answer
Low pressure system, returning blood by gravity and muscular pressure
question
Edema
answer
accumulation of fluid in tissues
question
Diastole
answer
First part of the cardiac cycle when the heart is relaxed and filling with blood (lower)
question
Systole
answer
Second part of cardiac cycle when the atria and ventricles of the heart are contracting and expelling blood into the vascular system and increasing vascular pressure (higher)
question
Hypovolemic shock
answer
blood loss
question
Anaphylactic shock and septicemic shock
answer
small blood vessels of the organs and tissues all dilate at the same time
question
Foramen ovale
answer
A hole between the cardiac atria that closes at birth; allows the blood to bypass the pulmonary circulation by passing from the right atrium to the left atrium
question
Ductus arteriosus
answer
Blood vessel that shunts blood from the pulmonary artery to the aorta in a fetus
question
Auscultation
answer
listening to the heart by using a stethoscope
question
1st heart sound
answer
Closure of atrioventricular valves (Tricuspid on right, Mitral on left)
question
2nd heart sound
answer
Closure of semilunar valves
question
3rd heart sound
answer
Rapid ventricular filling
question
4th heart sound
answer
Contraction of the atria
question
Cardiac Output
answer
the volume of blood that leaves the heart per minute
question
Stroke Volume
answer
the amount of blood ejected with each cardiac contraction
question
Heart Rate
answer
how often the heart contracts per minute
question
Formula for CO
answer
CO (Cardiac Output) = SV (Stroke Volume) X HR (Heart Rate)
question
Starling's Law
answer
Increased filling of the heart (increased preload) results in increased cardiac contraction
question
Inotrophy
answer
force of contraction
question
Chronotrophy
answer
rate of contraction
question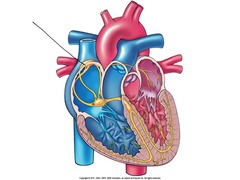
Sinoatrial (SA) Node

answer
Group of automatically depolarizing cells that are the heart's pacemaker located in the wall of the right atrium
question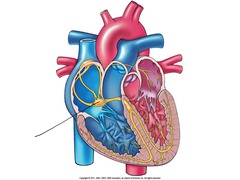
Atrioventricular (AV) Node

answer
A specialized cluster of connecting cells through which, in normal animals, the depolarization wave can reach the ventricles
question
The cardiac Cycle
answer
Impulse for depolarization travels through the SA node, the AV node, the bundle of His, and then the Purkinje Fibers, which causes ventricular contraction
question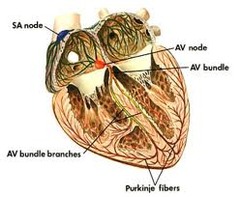
Purkinje Fibers

answer
Located in the left and right ventricular walls; Disseminate electrical impulses across the ventricles which cause the ventricles to contract
question
Resting state
answer
no activity, cell membrane ion pumps constantly move sodium out of, and move potassium into the cells to maintain cell's electrical potential under readiness to discharge an impulse or depolarize
question
Resting membrane potential
answer
the electrical charge of some cells at rest caused by differing concentrations of ions inside and outside of the cell membrane
question
Depolarization
answer
Sodium channels open upon stimulus; Sodium rushes into cells following electrical potential or attraction; Inside of cell goes from negative charge to positive charge
question
action potential
answer
Change in charge
question
Repolarization
answer
Sodium channels close and potassium channels open K+ rushes out of cells following electrical potential or attraction;Inside of cell goes from positive charge to negative charge; resting potential is re-established and cell is ready to depolarize again after refractory period; Sodium-potassium pump moves ions back across membrane to re-establish Na+ concentrations outside cell and K+ inside
question
Depolarization Threshold
answer
the required level of stimulation, or degree of change in cell's electrical potential, necessary to initiate an action potential
question
All-or-None Principle
answer
the way in which a neuron depolarizes completely or not at all in response to stimulation
question
Refractory Period
answer
period in the depolarization-repolarization cycle when the neuron cannot be stimulated to depolarize or can only be depolarized with a greater than normal stimulation
question
Dromotropic
answer
electrical conduction
question
P wave
answer
atrial depolarization (contraction)
question
QRS complex
answer
ventricular depolarization (systole)
question
T wave
answer
ventricular repolarization
question
Normal sinus rhythm
answer
P waves followed by QRS waves and T waves in the normal length of time and configuration
question
Arrhythmia
answer
abnormal pattern of electrical activity in the heart
question
Premature Ventricular Contraction (PVC)
answer
depolarization of the ventricles out of the normal sequence, causing the ventricles to contract prematurely
question
Paroxysm
answer
a short series of multiple PVCs
question
Ventricular Flutter
answer
longer series of PVCs
question
Ventricular Fibrillation
answer
severe conduction disturbance resulting in a ventricular contraction so uncoordinated that the heart simply quivers, a rapidly fatal condition
question
1st degree AV block
answer
prolonged PR interval
question
2nd degree AV block
answer
a P wave without a corresponding QRS complex (an intermittent missed beat on auscultation)
question
3rd degree AV block
answer
the ventricles beat independently of the atria
question
Sympathetic nerves
answer
stimulate the heart to beat faster and stronger under circumstances of fright or stress
question
Parasympathetic nerves
answer
inhibit the function of the heart beat by slowing it down and weakening the force of the beat
question
Nerve Origin SNS
answer
arise from T1-L5 spinal nerves
question
Nerve Origin PNS
answer
arise from brain (Cranial Nerves) and sacral vertebral spinal nerves
question
norepinephrine
answer
key neurotransmitter in the SNS
question
Adrenergic (sympathomimetic) Neurons
answer
release norepinephrine
question
Alpha1-adrenergic receptors
answer
associated with the sympathetic nervous system response; these receptors, when stimulated by catecholamines (dopamine, norepinephrine, epinephrine), tend to cause vasoconstriction
question
Beta1-adrenergic receptors
answer
Located on the heart; Associated with the sympathetic nervous system response; these receptors, when stimulated by catecholamines (dopamine, norepinephrine, epinephrine), tend to cause an increase in rate and force of contraction of the heart by increasing the permeability of the heart muscle to calcium
question
Beta-2 adrenergic receptors
answer
associated with the sympathetic nervous system response; these receptors, when stimulated by catecholamines (dopamine, norepinephrine, epinephrine), tend to cause bronchodilation and vasodilation of some blood vessels
question
Muscarinic Receptors for Acetylcholine (PNS)
answer
found on the target organs and tissues supplied by the postganglionic neuron of the parasympathetic nervous system
question
Nicotinic Receptors for Acetylcholine (PNS)
answer
found primarily on the postganglionic neurons of both the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system, as well as between motor neurons and muscle in the somatic (voluntary) motor system



