Biochemistry – Carbohydrates Test Questions – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
monosaccharide
answer
simple sugars
question
disaccharide
answer
two monosaccharide units
question
oligosaccharide
answer
short chains of saccharides connected by glycosidic bonds
question
polysaccharide
answer
sugar polymers (>20 units)
question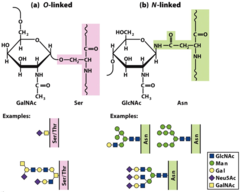
glycoconjugate

answer
carbohydrates COVALENTLY linked with other chemical species such as proteins, peptides, lipids and saccharides. Formed via glycosylation
question
carbohydrate functions (3)
answer
energy source and energy storage structural component of cell walls and exoskeletons informational molecules in cell-cell signaling
question
Aldose vs ketose
answer
aldose - aldehyde functionality (double-bonded O on last carbon in chain form) ketose - ketone functionality (double-bonded O on second-to-last carbon)
question
Enantiomer
answer
Stereoisomers that are nonsuperimposable mirror images
question
Diastereomer
answer
stereoisomers that are not mirror images different physical properties
question
Epimers
answer
two sugars that differ only in the configuration around one carbon atom
question
Ribose
answer
standard five-carbon sugar
question
Glucose
answer
standard six-carbon sugar
question
pyranoses
answer
Six-membered oxygen-containing rings
question
furanoses
answer
Five-membered oxygen-containing rings
question
What's a reducing sugar? How is it reduced? Ex?
answer
any sugar that is capable of acting as a reducing agent because it has a free aldehyde group or a free ketone group only linear chain the carbonyl group is oxidized (usually by Cu 2+) to a carboxyl group
question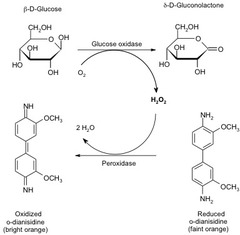
Colorimetric analysis (3)

answer
The enzyme glucose oxidase catalyzes the conversion of glucose to glucono--lactone and hydrogen peroxide Hydrogen peroxide oxidizes organic molecules into highly colored compounds Concentrations of such compounds is measured colorimetrically
question
Key structural features of sugars
answer
-aldose (carbonyl group at end) or ketose (carbonyl group in any other position) -sterchemistry of hydroxyl groups -number of chiral carbons -cyclic
question
Significance of stereoisomers (w/r to enzymes)
answer
Enzymes that act on sugars prefer certain stereoisomers because of binding site specificity
question
Ring form sugar (how? cis trans)
answer
carbonyl group forms covalent bond with hydroxyl oxygen creates new chiral center and therefore creates a more stereo-chemically complex molecule if anomeric hydroxyl group is trans to CH2OH group = alpha; cis = beta
question
Open chain (structure, D and L)
answer
carbonyl group at one end hydroxyl group at other - if hydroxyl group furthest from carbonyl carbon is on left = L configuration; if right = D configuration
question
# of stereoisomers equation
answer
= 2^(# of chiral centers)
question
What configuration of isomer is hexose most found as?
answer
D isomers
question
hemiacetal
answer
product of first addition of alcohol group to carbonyl carbon (aldehyde) alcohol group, hydrogen, r group, or group
question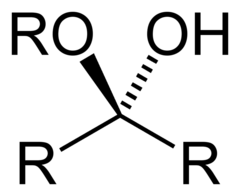
hemiketal

answer
product of first addition of alcohol group to carbonyl carbon (ketone) 2 r groups, or group, alcohol group
question
acetal
answer
product of second addition of alcohol group to carbonyl carbon (aldehyde) two or groups, hydrogen, r group
question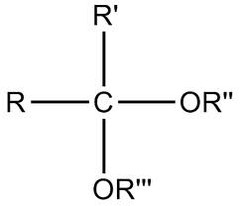
ketal (how formed, structure)

answer
product of second addition of alcohol group to carbonyl carbon (ketone) 2 r groups, 2 or groups
question
mutarotation
answer
the process of decycilization and recycilization to switch alpha to beta or vice versa
question
How are disaccharides joined? (O and N bond)
answer
O-glycosidic bond from anomeric carbon to hydroxyl group N-glycosyl bond from anomeric carbon to nitrogen atom in glycoproteins
question
Non reducing sugar
answer
When anomeric carbon is in glycosidic bond (full acetal or ketal), the linear formation is prevented, making the carbonyl carbon unable to undergo reducing
question
Functions of polysaccharides (homopolysaccharides ; heteropolysaccharides)
answer
homo - storage forms of fuel (ex starch and glycogen) hetero - structural elements (ex chitin, cellulose, peptidoglycan)
question
Structure and composition of Starch
answer
contains two types of glucose polymer, amylose and amylopectin hydrated (lots of hydroxyl groups)
question
Amylose and Amylopectin
answer
Found in starch lose - consists of long, unbranched chains of D-glucose residues connected by (1 to 4) linkages pectin - highly branched. The glycosidic linkages joining glucose residues in amylopectin chains are (1 to 4); the branch points (occurring every 24 to 30 residues) (1 to 6)
question
Glycogen
answer
polymer of (1 to 4)-linked subunits of glucose, with (1 to 6)-linked branches glycogen is more extensively branched (on average, every 8 to 12 residues) branches nonreducing
question
Dextrans
answer
bacterial and yeast polysaccharides made up of (1 to 6)-linked poly-D-glucose have branches source of glucose for bacterial metabolism adhesive used by plaque bacteria
question
Cellulose (structure, what sugar, orientation, why strong?)
answer
linear unbranched homopolysaccharide containing D- glucose In contrast with amylose: beta 1 to 4 linkages chairs 180 degrees relative to neighbor; all OH groups exposed for bonding with neighboring chains Very strong due to folding major component in tree trunks etc
question
Chitin (linkage, type sugar, diff. cellulose, found?)
answer
linear homopolysaccharide composed of N-acetylglucosamine residues in (beta 1 to 4) linkage only chemical difference from cellulose is the replacement of the hydroxyl group at C-2 with an acetylated amino group found in exoskeletons
question
Structure of polysaccharides. Ie glycogen and starch
answer
exposed hydroxyl groups participate in hydrogen bonding which create 3D structure limited by steric hindrance, broken down into angles glycogen and starch form coiled helices, 6 per turn with hydrogen bonds between the hydroxyl groups
question
Test for amylose
answer
Iodine = blue I- fits into helix core
question
Peptidoglycan
answer
heteropolymer N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylmuramic acid linked by short peptide chains lysozyme hydrolyzes glycosidic bonds penicillin prevents peptide chains from forming which inhibits bacteria from stopping osmotic lysis
question
Agar
answer
sulfated heteropolysaccharides made up of D-galactose and an L-galactose derivative ether-linked between C-3 and C-6
question
Agarose
answer
the agar component with the fewest charged groups (sulfates, pyruvates) double helix
question
Glycosaminoglycans
answer
linear polymers composed of repeating disaccharide units N-acetylglucosamine or N-acetylgalactosamine; the other is in most cases a uronic acid extended conformation due to negative charge provide viscosity, adhesiveness, and tensile strength to the extracellular matrix
question
Functions of glycoconjugates
answer
communication between cells and their extracellular surroundings label proteins for transport to and localization in specific organelles recognition sites for extracellular signal molecules
question
Proteoglycans (function, structure)
answer
tissue organizers, and they influence various cellular activities, such as growth factor activation and adhesion consists of a "core protein" with covalently attached glycosaminoglycan(s) -Ser-Gly-X-Gly- (where X = any amino acid)
question
Glycoproteins (what, where, describe function procedure)
answer
one or several oligosaccharides of varying complexity joined covalently to a protein usually found on the outer face of the plasma membrane, in the extracellular matrix, in the blood, and in specific organelles highly specific sites for recognition and high affinity binding by carbohydrate-binding proteins called lectins
question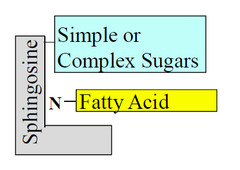
Glycosphingolipids

answer
plasma membrane components in which the hydrophilic head groups are oligosaccharides oligosaccharides act as specific sites for recognition by lectins signal transduction in cells and nerve conduction
question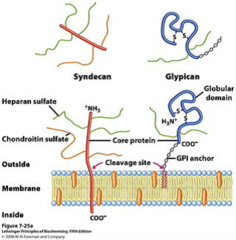
Syndecan and Glypican

answer
membrane heparan sulfate proteoglycans Syn - single transmembrane domain and an extracellular domain bearing three to five chains of heparan sulfate gly - attached to the membrane by a lipid anchor
question
Proteoglycan aggregates
answer
enormous supramolecular assemblies of many core proteins all bound to a single molecule of hyaluronan
question
Sugar code
answer
There is an enormous amount of information in each molecule due to the diversity of glycans. Read by proteins
question
Lectins
answer
proteins that bind carbohydrates with high specificity and with moderate to high affinity cell-cell recognition, signaling, and adhesion processes and in intracellular targeting of newly synthesized proteins govern the rate of degradation of certain peptide hormones, circulating proteins, and blood cells
question
Selectins
answer
a form of membrane bound lectin that mediate cell to cell recognition and adhesion selectin binds to oligosaccharide of the surface of glycoproteins on leukocytes
question
Lectin binding (function, how function, increase binding how?)
answer
Binds with carbohydrate binding affinity is increased by multiple carbohydrate-binding domains for oligosaccharides polar side of sugar hydrogen bonds with lectin while less polar side interacts with non polar amino acid residues
question
Mass spectrometry and high-resolution NMR spectroscopy
answer
yield essential information about sequence, configuration at anomeric and other carbons, and positions of glycosidic bonds
question
Analysis of carbs structure
answer
specific enzymatic hydrolysis to determine stereochemistry at the glycosidic bond and to produce smaller fragments for further analysis; methylation to locate glycosidic bonds; and stepwise degradation to determine sequence and configuration of anomeric carbons
question
Microarrays

answer
useful in determining the specificity and affinity of lectin binding to specific oligosaccharides.
question
Solid-phase synthetic methods yield
answer
yield defined oligosaccharides that are of great value in exploring lectin-oligosaccharide interactions and may prove clinically useful.



