Big Idea 1: Nuclear chemistry – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
radioactivity
answer
property of matter in which unstable nucleus spontaneously emits small particles to attain stability (radioactive decay)
question
radioactive isotope
answer
emit subatomic particles - electron (beta particle) - neutron - helium nucleus (alpha particle) - positron
question
after emitting subatomic particles
answer
the nuclear mass and nuclear charge of the atom changes one isotope converted to another with a different identity -energy released in form of x-rays/gamma rays
question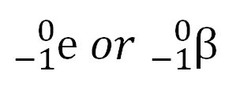
electrons/beta particles
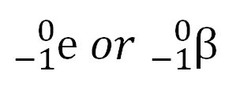
answer
collide less, usually do not penetrate skin
question
neutrons
answer
emitted in nuclear reactions, very penetrating -easily pass through because of zero charge, significant damage because of mass
question
helium nuclei/alpha particles
answer
travel few cm before colliding with air > lose KE > gain electrons > ordinary helium
question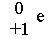
positrons
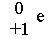
answer
positive equivalents to beta particles/electrons - unable to penetrate matter
question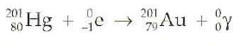
electron capture
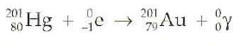
answer
proton + electron > neutron decreasing atomic number by 1
question
gamma rays
answer
produced when some radioactive decay event occur -nucleus has excess energy > energy lost as gamma ray -no charge or mass, penetrate easily
question
x rays
answer
highly penetrating electromagnetic radiation -penetrate body unless blocked by dense structure like bones
question
natural radioactive elements
answer
polonium Z = 84 to uranium Z = 92 and potassium 40, vanadium 50, lanthanum 138
question
transuranium elements
answer
92-118 artificial and radioactive
question
hazards
answer
radon-222: potential environmental hazard, decomposition of uranium radium-226: biological damage uranium-238: hazards of radon gas potassium-40: light radioactive elements, emit positron to form argon-40
question
half life
answer
half life of an isotope: 0.693/k fraction left: (1/2)^number of half-lives rate = KN K= constant N=number of radioactive nuclei Rate = number of nuclei that disintegrate per second ln (Nº/N†) = Kt Nº: original number of radioactive atoms N†: number of radioactive atoms left after t secs K: rate constant with units of s^-1 t: time in seconds from start of experiment



