A&P 2 -Respiratory and Lymphatic Systems – Behmer
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
What structural changes occur from primary bronchi to terminal bronchi?
answer
A) The mucous membrane changes from pseudo stratified ciliated columnar epithelium to non-ciliated simple cubodial epithelium C)The amount of smooth muscle increases D)Incomplete rings of cartilage disappear
question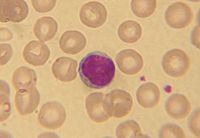
Lymphocyte

answer
Identify the large pink stained cell in the center.
question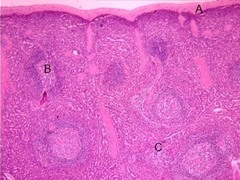
Spleen: A=connective tissue capsule, B=white pulp, C=red pulp

answer
identify the items labeled on this slide
question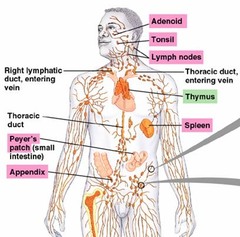
Lymphoid tissue

answer
tissues where antigens interact with cells of the immune system, Lymphocyte storage areas; examples: tonsils, spleen, appendix
question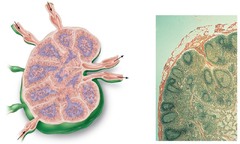
Lymph Node Structure

answer
White/red pump, Capsule Afferent lymphatic vessels-enter Efferent lymphatic vessels-exit
question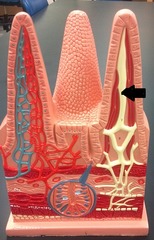
lacteal

answer
Identify.
question
cisterna chyli
answer
Identify A
question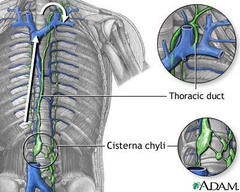
thoracic duct

answer
Identify B
question
A
answer
variable portion of an antibody; antigen binding site
question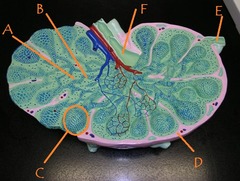
medullary cord

answer
Identify B
question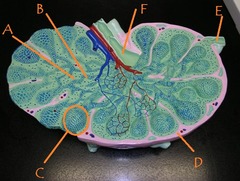
efferent lymphatic vessel

answer
Identify F
question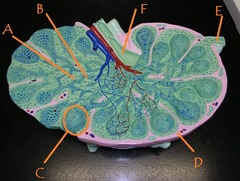
B lymphocytes

answer
What cells are found in high concentrations in C?
question
Lymph capillaries in intestinal villi involved in absorption of fat.
answer
lacteal
question
spleen
answer
An organ that is part of the lymphatic system; it produces lymphocytes, filters the blood, stores blood cells, and destroys old blood cells.
question
lymph node
answer
Bean-shaped filters that cluster along the lymphatic vessels of the body. They function as a cleanser of lymph as wells as a site of T and B cell activation
question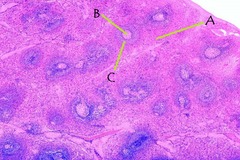
white pulp

answer
Identify C
question
antigen
answer
A protein or carbohydrate that, when introduced in the blood, triggers the production of an antibody
question
antibody
answer
A protein that acts against a specific antigen
question
antiserum
answer
Human or animal serum that contains antibodies to a particular antigen because of previous exposure to the disease or to a vaccine containing antigens from that infectious agent.
question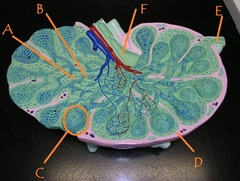
afferent lymphatic vessel

answer
Identify E
question
For inhalation to occur alveolar pressure must be greater than atmospheric pressure (T/F?)
answer
False
question
Determining O2 saturations in hemoglobin by measuring partial pressure of CO2 (T/F?)
answer
False
question
Parasympathetic activity causes bronchoconstriction (T/F?)
answer
True
question
Hyperventilation leads to respiratory acidosis (T/F?)
answer
False
question
Volume of Vital Capacity?
answer
Inspiratory volume+ tidal volume +expiratory reserve volume.
question
Inspiratory Reserve Volume?
answer
The additional inhaled air when taking a very deep breath
question
Dead Space is?
answer
30% of tidal volume that remains in conducting airways never reaching the respiratory zone.
question
Amospheric Pressure is
answer
760mm Hg
question
What stops continuous inhalation?
answer
Herring Brewer reflex
question
Cervical lymph nodes
answer
A
question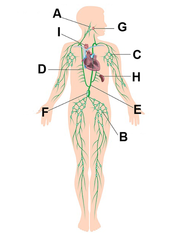
Inguinal lymph nodes

answer
B
question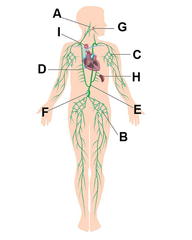
Axillary lymph nodes

answer
C
question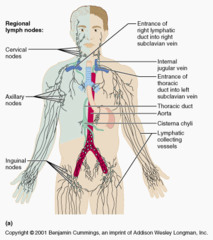
Right lymphatic duct

answer
D
question
Thoracic duct

answer
E
question
Cisterna chyli
answer
F
question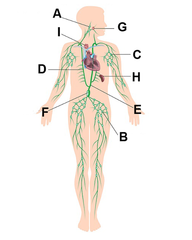
Palatine tonsils

answer
G
question
Spleen
answer
H
question
Thymus
answer
I
question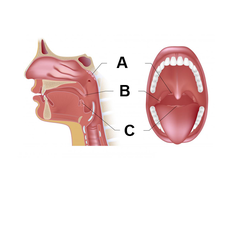
Pharyngeal tonsils

answer
A
question
Palatine tonsils

answer
B
question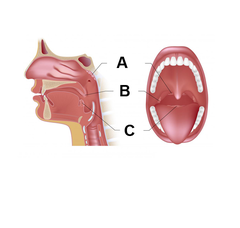
Lingual tonsils

answer
C
question
What effects do you think a pleural effusion (when pleural cavity fills with fluid) have on ventilation?
answer
Could result in a collapsed lung.
question
What kind of epithelium tissue is in the Alveoli?
answer
Simple Squamous - For diffusion.
question
Why are there more goblet cells in the upper respiratory passages than in the lower respiratory passages?
answer
Goblet cells make mucous in order to catch debris before it goes into the lower passages.
question
What is pulmonary ventilation?
answer
The physical movement of air in and out of the lungs.
question
What is Boyle's Law?
answer
P=1/v. Basically, when thoracic pressure is up, then the thoracic volume is down. and vice versa.
question
What is the difference between Restrictive and Obstructive diseases?
answer
Restrictive - Conditions that prevent lungs from fully expanding. Obstructive - Conditions preventing full exhalation of air out of lungs.
question
What is the Bicarbonate-carbonic acid buffer system?
answer
A homeostatic mechanism that regulates the body's pH level.
question
What is Respiratory Alkalosis?
answer
When an increased respiration rate elevates the pH level int he body higher than normal. (More Basic)
question
What is Respiratory Acidosis?
answer
When lungs can't remove all of the CO2 out of the body.
question
What is Tidal Volume (TV)?
answer
The amount of air exchanged with each breath during normal, quiet breathing.
question
What is Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV)?
answer
The volume of air that may be expired after a Tidal Volume.
question
What is Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV)?
answer
The amount of air that may be inspired after a tidal inspiration.
question
What is Residual Volume (RV)?
answer
The amount of air that remains in the lungs after maximal expiration.
question
What is Inspiratory Capacity (IC)?
answer
The amount of air that a person can maximally inspire after a tidal expiration. It's the difference between IRV and ERV. And CANNOT be measured by a spirometer.
question
What is Functional Residual Capacity (FRC)?
answer
The amount of air that is normally left in the lungs after a tidal expiration. It's the sum of the ERV and RV.
question
What is Vital Capacity (VC)?
answer
The total amount of exchangeable air that moves in and out of the lungs. VC= TV+IRV+ERV
question
What is Total Lung Capacity (TLC)?
answer
The total amount of exchangeable and nonexchangeable air in the lungs.
question
Why should a person breathe into a paper bag when he or she is hyperventilating abnormally?
answer
To increase CO2 intake. By breathing back in the CO2 that is exhaled, you can correct the body's pH balance.
question
What can happen if you remove the spleen?
answer
Your body won't be able to remove the Red Blood Cells and your immunity would be compromised.
question
Infants who have DiGeorge syndrome (where the thymus is absent or nonfunctioning), what can happen to him or her?
answer
T cells would not be functional, preventing the infant from fighting infections. There would be severe immunodeficiencies, which would lead to the infant's death.
question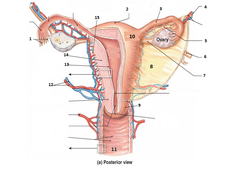
Fibrilae

answer
1?
question
Fundus
answer
2?
question
Uterine Tube
answer
3?
question
Ligaments of ovary??? (Double Check this)
answer
4?
question
Check....
answer
5?
question
Round Ligament? .... (Double Check)
answer
6?
question
Ovary ligament
answer
7?
question
Broad Ligament
answer
8?
question
Cervix
answer
9?
question
Uterus body
answer
10?
question
vagina
answer
11?
question
arteries/veins
answer
12?
question
Endometrium layer
answer
13?
question
Myometrium layer (Double Check)
answer
14?
question
Pericardium (it's wrong. Please check?
answer
15?
question
Vagina
answer
1?
question
??
answer
2?
question
??
answer
3?
question
Clitoris
answer
4?
question
??
answer
5?
question
Vestibular folds????
answer
6?
question
Ovary
answer
1?
question
Pre XXX
answer
2?
question
Primary XXXX
answer
3?
question
Secondary
answer
4?
question
Third one
answer
5?
question
???
answer
6?
question
Adipose tissue
answer
1?
question
???
answer
2?
question
Lobule
answer
3?
question
____ duct
answer
4?
question
Areola
answer
5?
question
Nipple
answer
6?
question
_____ sinus
answer
7?
question
Ureter
answer
1?
question
Urinary bladder
answer
2?
question
Seminal gland
answer
3?
question
Prostate Gland
answer
4?
question
Ejaculatory duct
answer
5?
question
Bullb___ gland
answer
6?
question
Anus
answer
7?
question
Prostetic duct???
answer
8?
question
Sponga Cavernosa???
answer
9?
question
Spongy XXXXX
answer
10?
question
Spongy urethra
answer
11?
question
Vans deferens
answer
12?
question
Penis
answer
13?
question
Epidydimis
answer
14?
question
Testes
answer
15?
question
External urethra orifice ??? (Check name)
answer
16?
question
What are they calling this?
answer
17?
question
Spermatic cord????
answer
1?
question
Prostate?
answer
2?
question
Teste vein ???
answer
3?
question
Pinipiform plexus (Check Spelling)
answer
4?
question
??? vein
answer
5?
question
Epidydimis
answer
6?
question
Teste
answer
7?
question
scrotum
answer
8?
question
Vans deferens
answer
9?
question
Cremaster muscle
answer
10
question
Inguinal vein
answer
11?
question
Inguinal artery
answer
12?
question
Penis
answer
13?
question
Ureter
answer
1?
question
_____ Gland
answer
2?
question
Prostate Gland
answer
3?



