Anti-Cancer Rx – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Recall: Cell Cycle
answer
• G1 Phase: Preparation for DNA synthesis. Synthesis of substrates (ribo and deoxyribo nucleotides) and enzymes necessary for DNA formation. • S Phase: DNA replication • G2 Phase: Proof reading of synthesized DNA & correction of any mismatch, protein synthesis for cell division. • M Phase: Separation of chromatids and division of cell into 2 daughter cell. • G0 Phase: Differentiation of cell into mature cell
question
Anticancer Rx can cause killing of rapidly dividing normal cells. Name some of these cells and their clinical consequences
answer
Bone marrow: neutropenia, thrombocytopenia GI mucosa: mucositis & blsitsers Hair follicles: alopecia Gonads: infertility Most anticancer drugs are carcinogenic (DNA damage).
question
Major toxicity of some Rx:
answer
*Cyclophosphamide & Ifofamide*: Hemorrhagic cystitis *Bleomycin*: Pulmonary fibrosis *Cisplatin*: Nephrotoxicity & Deafness *Doxorubicin & Daunorubicin*: Dilated cardiomyopathy *Vincristine*: Peripheral neuropathy *Etoposide, Methotrexate & Vinblastine*: Bonemarrow suppression *L-Asparaginase*: Pancreatitis and bleeding
question
What can be used to prevent some of the common drug-induced damages?
answer
Hemorrhagic cystitis by cyclophosphamide & ifosfamide: *MESNA* Cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity: *Good hydration and amifostine* Doxorubicin & daunorubicin induced dilated cardiomyopathy: *Dexrazoxane* Bonemarrow suppression by various drugs: *Filgrastim (GM-CSF)* Methotrexate induced bonemarrow suppression: *Leucovorin (Tetrahydrofolic acid)*
question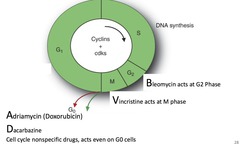
What is the ABVD regimen and what does it Tx?

answer
Adriamycin (Doxorubicin) Bleomycin Vincristine Dacarbazine Tx: *Hodgkin's Lymphoma*
question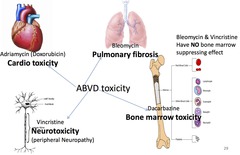
ABVD - toxicity profile

answer
Adriamycin/Doxorubicin - cardiotoxicity Vincristine - neurotoxicity (peripheral neuropathy) Bleomycin - pulmonary fibrosis Dacarbazine - bone marrow toxicity
question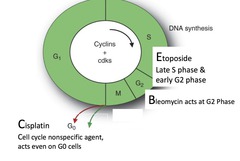
What is the BEP regimen and what does it Tx?

answer
Bleomycin Etoposide Platinum (Cisplatin) Tx: *Testicular Cancer*
question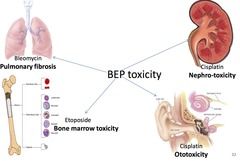
What is the BEP regimen toxicity profile?

answer
Bleomycin - PF Etoposide - BM toxicity Cisplatin - Ototoxicity, Nephrotoxicity
question
Define: Adjuvant chemotherapy
answer
Chemotherapy in addition to surgery or radiotherapy
question
Define: Neo-adjuvant chemotherapy
answer
Chemotherapy given before surgery to decrease the size of the tumor
question
Define: Induction chemotherapy
answer
Chemo given to obtain complete remission from tumor, usually blood cancers.
question
Define: Maintenance chemotherapy
answer
Chemo given to maintain remission from the cancer
question
What are the classifications of Anti-Cancer Rx?
answer
Antimetabolites, Antitumor Antibiotics, Epipodophyllotoxins, Vinca Alkaloids, Taxanes, Camptothecins Alkylating Agents: - Nitrogen mustards - Alkyl sulfonates (Busulfan) - Nitrosoureas - Triazenes (Dacarbazine) - Methylhydrazines (procarbazine) - Platinum Complexes Hormonal Agents - Glucocorticoids - Estrogens - Estrogen Inhibitors - Progestins - Androgens - Anrogen Inhibitors - Androgen Receptor Blockers (Flutamide) Signal Transduction Inhibitors Miscellaneous
question
Alkylating Agents - MOA
answer
- Alkylation at *N7 position of guanine *in DNA - Miscoding through *abnormal base pairing with thymine* or in depurination by *excision of guanine* residues, leading to *strand breakage* - Cross-linking of DNA and ring cleavage may occur
question
Alkylating Agents - basic properties
answer
*Cell cycle nonspecific* agents Mutagenic, carcinogenic Cyclophosphamide - most common
question
Name the nitrogen mustards
answer
Cyclophosphamide Ifosfamide Mechlorethamine Melphalan Chlorambucil
question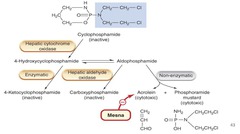
Cyclophosphamide - MOA

answer
Needs to be* activated by hepatic enzymes* ? *acrolein* (toxic)
question
Cyclophosphamide - use
answer
Neoplastic Disease, in combo: - Adrenal cortex cancer - Bladder cancer - Bone cancer - Cervical cancer - Endometrial cancer - Lung cancer - Non-hodgkins lymphoma
question
Cyclophosphamide - AE
answer
• Bone marrow suppression • Immunosuppression • Hemorrhagic cystitis • Nausea and vomiting • Alopecia • Gonadal failure: amenorrhea ; sterility • SIADH
question
Why is MESNA used with cyclophosphamide?
answer
To prevent irritation of the bladder by acrolein ? hemorrhagic cystitis Also recommended to maintain urine output ; 3L/day
question
Ifosfamide - details
answer
MOA ; AE similar to cyclophosphamide *More potent* than cyclo. More potential to cause *hemorrhagic cystitis* *Prior admin of MESNA is a must for each dose*
question
Mechlorethamine - use, AE
answer
Tx: Nonhodgkin's Lymphoma Highly *vesicant*
question
Mephalan - use
answer
Tx: Multiple myeloma
question
Chlorambucil - use
answer
Tx: CLL
question
What is the name of the alkylsulfonate?
answer
Busulfan
question
Busulfan - use, AE
answer
Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) AE: adrenal insufficiency, *pulmonary fibrosis*, skin pigmentation
question
Name the Nitrosoureas
answer
Carmustine (BCNU) Lomustine (CCNU) Semustine
question
Carmustine Lomustine Semustine - MOA
answer
Chloroethyl moiety of nitrosoureas ? alkylates nucleic acids & proteins ? single-strand breaks & inter-strand cross-linkage of DNA *Cross BBB*
question
Carmustine Lomustine - use, AE
answer
Highly lipophilic ? BBB *Used as adjuncts in Tx of brain tumors* AE: GI distress, delayed myelosuppression, CNS dysfunction
question
Name the triazene
answer
Dacarbazine (DTIC)
question
Dacarbazine - details
answer
• Synthetic drug; requires *activation by liver microsomal system* • Tx: *Hodgkin's disease, soft tissue sarcoma and melanoma* • AE: Myelosuppression, nausea ; vomiting
question
Name the methylhydrazine
answer
Procarbazine
question
Procarbazine - details
answer
Combo Tx: Hodgkin's Disease Teratogenic, mutagenic, *leukemogenic* AE: n/v, myelosuppresion, hemolytic anemia, pulmonary effects, peripheral sensory neuropathy, disulfiram-like reaction
question
Name the platinum compounds
answer
Cisplatin Carboplatin Oxaliplatin
question
Cisplatin Carboplatin Oxaliplatin - basic properties
answer
Cell cycle *nonspecific* agents Minimal bone marrow suppression
question
Cisplatin Carboplatin Oxaliplatin - MOA, use
answer
*Alkylates N7 position of guanine in DNA* Tx: Wide range of solid tumors like germ cell tumors, ovarian cancer, non small cell lung cancer, etc.
question
Cisplatin Carboplatin Oxaliplatin - AE
answer
- *Severe nausea and vomiting* due to intense stimulation of CTZ (Chemoreceptor Trigger Zone) - *Neurotoxicity*- peripheral neuropathy and deafness (cochlear nerve damage) - *Nephrotoxicity*- leads to electrolyte imbalance
question
How to combat Cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity?
answer
• Osmotic diuresis with *mannitol* • Forced chloride diuresis with 0.1% NaCl •* Amifostine* -cytoprotective agent which gives Thiol (-SH) compound on activation inactivates free radicals generated by cisplatin
question
What drug is commonly co-admin with cisplatin to reduce AE?
answer
*Amifostine* It ? frequency of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity, ototoxicity, neurotoxicity, and myelosuppression. FDA-approved to ? cumulative renal toxicity in pts receiving repeated doses of cisplatin for advanced ovarian cancer and non-small- cell lung cancer
question
Compare contrast cisplatin with other platinum compounds
answer
Carboplatin & oxaliplatin: • Has more acceptable toxicity profile than cisplatin- less nephrotoxic, less neurotoxic & less emetogenic. • More myelosuppression than cisplatin.
question
Antimetabolites - basic properties
answer
• Structurally similar to natural substances like vitamins, nucleosides, nucleotides or amino acids. • Block important biosynthetic pathway by *competing with natural substances*. • Are incorporated, instead of natural substances. • Cell cycle specific drugs, acting mostly on *S phase*
question
Name the antimetabolites:
answer
Folate antagonist: Methotrexate Purine antagonists: 6-Mercaptopurine, 6-Thioguanine Pyrimidine antagonists: 5-Fluorouracil, Capecitabine, Cytarabine, Gemcitabine
question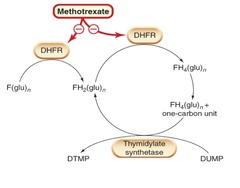
Methotrexate - MOA

answer
Inhibits the enzyme *dihydrofolate reductase*, which converts dihydrofolic acid to tetrahydrofolic acid
question
Methotrexate - uses
answer
• Choriocarcinoma • Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) • Burkitt's lymphoma • Osteosarcoma • Breast cancer
question
Methotrexate - AE
answer
Common: BM suppression, immune-suppression, mucositis, alopecia Renal damage: due to crystal deposits in kidney tubules (good hydration prevents this) Pulmonary toxicity: esp in kids Hepatic fibrosis: LT Tx
question
What is the Leucovorin rescue? Why is it given?
answer
*Leucovorin or Folinic acid* • Used in cases of OD or in high-dose methotrexate protocols. • Leucovorin provides cells a source of reduced folate, thereby overcoming blockade by methotrexate.
question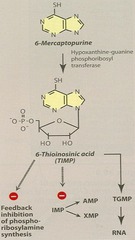
6-Mercaptopurine (6-MP) - MOA

answer
*Purine Antagonists* 6-MP ? 6 thioinosinic acid (TIMP) ? inhibits de novo purine synthesis TIMP ? blocks formation AMP, GMP
question
6-Mercaptopurine (6-MP) - coadmin with allopurinol?
answer
6-MP metabolized to thiouric acid by xanthine oxidase Allopurinol (xanthine oxidase inhibitor) is used to reduce uric acid synthesis *Dose of 6-MP must be reduced if co-admin with allopurinol*
question
6-Mercaptopurine (6-MP) - use, AE
answer
Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia (ALL) AE: BM suppression, hepatotoxicity, n/v
question
6- Thioguanine- details
answer
MOA:* inhibits DNA ; RNA synthesis by ? intracellular [GMP]* Use: Tx acute lymphoid leukemia (ALL). *No drug interaction with allopurinol* AE: BM suppression, Hepatotoxicity, n/v
question
5-Flurouracil Capecitabine Cytarabine Gemcitabine
answer
*Pyramidine antagonists*
question
5-Flurouracil (5-FU) - MOA
answer
5-FU ? deoxyribonucleotide ? *inhibits thymidylate synthase* ? thymidine deficiency ? inhibits DNA synthesis 5-FU also incorporated into RNA
question
Coadmin of 5-FU with leucorvorin - what happens
answer
Supplementing leucovorin (folinic acid) along with 5-FU leads to incorporation of more 5-FU metabolite into RNA- generation of more nonfunctional RNA. *Addition of leucovorin increases the cytotoxic effects of 5-FU*
question
5-FU - Use, AE
answer
Systemic use: Adenocarcinomas Topical use: Skin cancer AE: - Myelosuppression - Mucositis - *Hand-foot syndrome* (skin exfoliation on palm, feet) - Alopecia
question
Capecitabine - details
answer
*Oral prodrug of 5-FU* • Converted into 5-FU by *thymine phosphorylase* inside the tumor cells. • Use: *metastatic breast cancer ; colorectal cancer* • Adverse effects: similar to 5-FU
question
Gemcitabine - MOA
answer
*Pyrimidine analog* Incorporated into DNA, inhibits chain elongation - Competes with cytidine
question
Gemcitabine - AE, use
answer
Use: *Pancreatic cancer*, non-small cell lung cancer, ovarian cancer AE: myelosuppression, alopecia, flu-like Sx, ? liver enzymes
question
Cytarabine (ara-C) - details
answer
• MOA: *S phase*-specific antimetabolite. • Biotransformed to active forms: Ara-CTP *competitively inhibits the enzyme DNA polymerase*. • Use: AML for induction ; CML in blast crisis • Adverse effects: Myelosuppression (common) ; ataxia
question
Vincristine Vinblastine Vinrelbine - class
answer
Vinca Alkaloids, natural products
question
Vincristine Vinblastine Vinrelbine - origin, MOA
answer
Derived from plant vinca rosea MOA: Bind to ?-tubulin and *prevents formation of microtubules* "Mitotic spindle poisons" *Cells arrested
question
Vincristine - use, AE
answer
Use: Hodgkin's lymphoma AE: *Neuropathy* (myelosuppression is minimal, considered a *bone marrow-sparing drug*)
question
Vinblastine - use, AE
answer
Use: Testicular cancers AE: myelosuppression
question
Vinrelbine - Use, AE
answer
Use: Non-small cell lung cancer AE: Granulocytopenia
question
Paclitaxel Docetaxel - class
answer
Taxanes Derivative of Western Yew
question
Paclitaxel Docetaxel - MOA
answer
Enhances tubulin polymerization and *stabilizes microtubules in polymerized state* Cell is *Arrested in metaphase (M phase)*
question
Paclitaxel Docetaxel - Use
answer
Use: Ovarian, breast cancer
question
Paclitaxel - AE
answer
Severe allergic reaction attribute to cremophor vehicle, neutropenia, alopecia
question
Docetaxel - AE
answer
Skin toxicity and fluid retention leading to pleural and peritoneal effusions
question
Etoposide Tenoposide - class
answer
Epipodophyllotoxins
question
Etoposide Tenoposide - MOA
answer
*Topoisomerase II inhibition*, prevents re-ligation of DNA strand breaks Acts at *late S and early G2* phases of cell cycle
question
Etoposide Tenoposide - Use, AE
answer
Use: Germ cell tumor, AML, lung cancer AE: myelosuppression Association between etoposide use and leukemia (in survivors)
question
Topotecan Irinotecan - class
answer
Camptothecins
question
Topotecan Irinotecan - MOA
answer
Topoisomerase I inhibition
question
Topotecan - Use, AE
answer
Metastatic ovarian cancer (cisplatin-resistant) AE: Neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, anemia
question
Irinotecan - use, AE
answer
Colon and rectal cancer AE: severe diarrhea, myelosuppression (caution in patients with *Gilbert's syndrome*)
question
What are the antitumor antibiotics?
answer
Bleomycin Anthracyclines - Doxorubicin - Daunorubicin Dactinomycin
question
Bleomycin - basic properties
answer
Cell cycle specific agent: *G? Phase* PK: eliminated by kidney Inactivated by cellular metabolism via enzyme: *bleomycin hydrolase*
question
Bleomycin - MOA
answer
Induces free radical-mediated DNA strand breaks Reduced iron mediates the reduction of molecular oxygen into damaging free radicals
question
Bleomycin - Use, toxicity
answer
Use: Hodgkin's lymphoma, testicular cancer, kaposi sarcoma Toxicity: seen in tissues low in enzyme bleomycin hydrolase: - *Pneumonitis followed by pulmonary fibrosis* - Skin reaction - Raynauld's phenomenon - Retroperitoneal fibrosis No significant effect on BM (*Bone marrow sparing drug*)
question
Doxorubicin Daunorubicin - class
answer
*Anthracyclines * Derived from streptomyces fungi
question
Doxorubicin Daunorubicin - MOA
answer
Inhibition of *topoisomerase II* ? DNA breaks Formation of highly reactive oxygen free radical species which damages DNA, cell membrane, proteins, etc Alters membrane fluidity, and ion transport
question
Doxorubicin Daunorubicin - use, AE
answer
Broad anti-tumor activity: Breast cancer, AML, lymphomas, sarcomas, etc AE: *Cardiotoxicity*, myelosuppression, n/v, alopecia, mucositis, erythema at sites of prior radiation "Radiation recall reaction", highly vesicant
question
Doxorubicin Daunorubicin - Cardiotoxicity Tx
answer
Free radical damage Heart vulnerable because limited capacity to neutralize free radicals *Dexrazoxane* - iron chelating agent, ? free radical damage
question
What is Dexrazoxane?
answer
Iron chelating agent, ? free radical damage
question
Dactinomycin - details
answer
Cell cycle *nonspecific* agent MOA: binds to DNA *noncovalently* Use: *Wilm's tumor, sarcomas* AE: - Highly vesicant (extravasation ? tissue necrosis) - Erythema at sites of prior radiation (Radiation recall reaction)
question
Dexamethasone Hydrocortisone Prednisone Prednisolone - class
answer
Glucocorticoids used to Tx Cancer
question
Dexamethasone Hydrocortisone Prednisone Prednisolone - MOA
answer
Bind to intra-cytoplasmic receptor ? steroid-receptor complex binds to nuclear receptor ? modulates protein expression
question
Dexamethasone Hydrocortisone Prednisone Prednisolone - AE
answer
Immunosuppression ?? infections, mood swings, osteoporosis, hyperglycemia, poor wound healing
question
Dexamethasone Hydrocortisone Prednisone Prednisolone - Use in Cancer Tx
answer
• Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia, Hodgkins lymphoma, non-hodgkins lymphoma, multiple myeloma, etc. • Palliative care to improve feeling of well being. • Used in spinal cord compression due to metastasis to relieve edema. • Management of autoimmune anemia and thrombocytopenia.
question
Diethylstilbestrol Ethinylestradiol - class
answer
Estrogens
question
Diethylstilbestrol Ethinylestradiol - MOA
answer
Bind to intra-cytoplasmic receptor ? steroid-receptor complex binds to nuclear receptor ? modulates protein expression
question
Diethylstilbestrol Ethinylestradiol - AE
answer
? risk thromboembolism, migraine, cholestasis, mood changes - Gynecomastia and impotence in men
question
Diethylstilbestrol Ethinylestradiol - Use in Cancer, contraindications
answer
*Prostate cancer* Contraindicated in pts with breast & endometrial cancers
question
Tamoxifen Raloxifene - class
answer
*Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulator* Exhibit agonistic action in some tissue and antagonistic action in others
question
Tamoxifen Raloxifene - AE
answer
Hot flushes, thrombosis Fluid retention *Risk of endometrial cancer* with LT use
question
Tamoxifen - E modulation
answer
Antagonist @ breast Agonist @ endometrium, bone
question
Raloxifene - E modulation
answer
Antagonist @ breast, endometrium Agonist @ bone
question
Tamoxifen - Use
answer
*Primary therapy for metastatic breast cancer* in both men & postmenopausal women Decreases incidence of breast cancer in women who are at high risk for developing the disease
question
Aromatase
answer
After menopause, E produced by peripheral conversion of androstenedione ? estriol by aromatase in adipose tissue
question
Types of Aromatase inhibitors
answer
Competitive or reversible: - Steroidal: Aminogluthethimide - Non-steroidal: anastrozole, letrozole Steroidal irreversible inhibitors: - Exemestane, Formestane
question
Aminogluthethimide - MOA
answer
• Inhibitor of adrenal steroid synthesis at the first step, conversion of cholesterol to pregnenolone • Inhibits the extra-adrenal synthesis of estrone and estradiol. • Inhibits the enzyme aromatase that converts androstenedione to estrone.
question
Aminogluthethimide - Use, AE
answer
*ER+ metastatic breast cancer* AE: - Adrenal insufficiency - Dizziness - Lethargy - Visual blurring - Rash
question
Anastrozole Letrozole - use, AE
answer
*Selective non-steroidal inhibitor of aromatase enzyme* Use: Tx advanced ER+ breast cancer that is *resistant to tamoxifen* AE: Hot flushes & headache
question
Exemestane Formestane - use, AE
answer
*Steroidal irreversible inhibitors* Use: Advanced ER+ cancer AE: Mood changes, acne and hair growth.
question
Hydroxyprogesterone Megestrole - class
answer
Progestins used in Cancer Tx
question
Hydroxyprogesterone Megestrole - use, AE
answer
Use: endometrial cancer; palliative care (? appetite in terminally ill cancer patients) AE: Weight gain, Depression, Edema, acne, ?HDL
question
Fluoxymesterone Testosterone - class, use
answer
Androgens used in Cancer Tx Use: palliative care to improve feeling of well being and appetite
question
Leuprolide Goserelin - class
answer
Antiandrogens: Gonadotropin-releasing analogues
question
Leuprolide Goserelin - MOA
answer
Continuous dose (not pulsatile) will produce reversible medical castration ? ? release of LH & FSH Initial flare-up of androgen dependent cancer may occur
question
Leuprolide Goserelin - Use, AE
answer
Prostate cancer, sometimes for uterine fibroids AE: ? bone mass, hot flushes, initial tumor flare up, impotence
question
Flutamine - class, MOA, use
answer
Androgen Receptor Blocker Antagonizes androgenic effects Approved for *prostate cancer* Tx Given with GnRH agonists to prevent initial tumor flare-up
question
Flutamine - AE
answer
Gynecomastia, GI distress
question
Hydroxyurea - MOA
answer
Urea analog *Inhibits ribonucleotide reducase* ? ? deoxynucleoside triphosphate pools ? inhibiting DNA synthesis *S phase specific agent*
question
Hydroxyurea - use
answer
Tx: Melanoma, chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), sickle cell disease to ?HbF
question
Hydroxyurea - AE
answer
Leukopenia (reversible upon discontinuation of drug) Mild GI toxicity Mild dermatologic changes with prolonged therapy
question
L-Asparaginase - MOA
answer
Enzyme isolated from bacteria Causes catabolic depletion of serum asparagine ? aspartic acid & ammonia ? ?blood glutamine levels ? inhibits protein synthesis *Neoplastic cells require external source of asparagine*
question
L-Asparaginase - Use, AE
answer
*Childhood acute leukemia* Hypersensitivity rxns (shock), hemorrhage, hyperglycemia, headache, pancreatitis
question
Arsenic trioxide - Use
answer
Tx: Acute pro-myelocytic leukemia In PML/RAR-? positive AML, arsenic trioxide causes differentiation of leukemic cells
question
Arsenic trioxide - AE
answer
headache, cardiac arrhythmias, fluid retention, increases risk of skin cancers
question
Interferon - MOA
answer
Produced by recombinant DNA technology MOA not clearly understood INF-? stimulates NK cells ? expression of HLA molecules on tumor cells
question
Interferon - Use
answer
INF-2?: CML, hairy cell leukemia, kaposi sarcoma INF-2?: Melanoma, follicular lymphoma, AIDS related Kaposi sarcoma
question
Interferon - AE
answer
Fever, myalgia, headache, loss of appetite, depression
question
How do signal transduction inhibitors work to Tx cancer?
answer
• Specifically act on tumor cells hence usually* lack non specific toxicities like bone marrow suppression, alopecia, mucositis, etc.* • Over-expression of one particular pathway in tumor is targeted.
question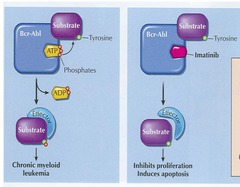
Imatinib - MOA

answer
Inhibits tumor *tyrosine kinase* activity
question
Imatinib - Use
answer
Tx* BCR-ABL+ CML*, ALL, & GIST
question
Imatinib - AE
answer
Fluid retention, edema, hepatotoxicity, thrombocytopenia
question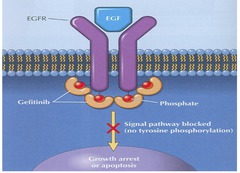
Gefitinib - MOA

answer
Inhibits *epidermal growth factor receptor* signal transduction
question
Gefitinib - Use, AE
answer
Tx: non-small cell lung cancer AE: Acne-like skin lesions, nausea, diarrhea
question
Cetuximab - MOA, use, AE
answer
Inhibits EGFR signaling Colorectal cancer, head and neck cancer AE: Infusion reaction, skin rash, fatigue
question
Trastuzumab - MOA, use, AE
answer
Epidermal growth factor receptor protein 2 Breast cancer AE: CHF, infusion reaction
question
Bortezomib - MOA, Use, AE
answer
Inhibits *proteosome* which has chymotrypsin-like activity MM, mantle cell lymphoma AE: Thrombocytopenia, neuropathy
question
Sunitinib - MOA, use, AE
answer
Multiple receptor kinase inhibition, like VEGF-1, 2, 3; PDGFR Renal cell cancer, GIST AE: skin rash, bleeding
question
Erlotinib Lapatinib - MOA, use, AE
answer
EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor Non-small cell lung cancer, pancreatic cancer AE: skin rash, interstitial lung disease
question
Sorsfenib - MOA, use, AE
answer
Multiple receptor kinase inhibition like VEGF-2, 3; PDGFR Renal cell cancer, hepatocellular cancer AE: skin rash, fatigue
question
Which anticancer drugs are bone marrow sparing? Which cause minimal BM suppression?
answer
Vincristine Bleomycin Signal transduction inhibitors (Bortezomib, Cetuximab, Erlotinib, Gefitinib, Imatinib, Lapatinib, Sorafenib, Sunitinib, Trastuzumab) Minimal bone marrow suppression: Platinum compounds (cisplatin, carboplatin, oxaliplatin)
question
Which anticancer drug causes "hand-foot syndrome"?
answer
5-Flurouracil (5-FU) Skin exfoliation on palms, feet
question
Which anticancer drugs cause Radiation Recall reaction, and what is that?
answer
Erythema at sites of prior radiation Caused by: anthracyclines (doxorubicin, daunorubicin) & Dactinomycin
question
Which anticancer drugs are highly vesicant?
answer
Mechlorethamine Anthracyclines (doxorubicin, Daunorubicin) Dactinomycin



