OPENSTAX A&P chapter 1
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
anatomy
answer
study of bodily structures (section 1.1)
question
gross anatomy
answer
study of body's larger structures example ? study of the brain (as opposed to neurons) (section 1.1)
question
microscopic anatomy
answer
study of bodily structures that can only be observed with the use of a microscope or other magnification devices example ? study of the neuron (as opposed to the brain) (section 1.1)
question
regional anatomy
answer
study of the interrelationships of all the structures in a specific body region example ? study of structures within the abdominal region (section 1.1)
question
systemic anatomy
answer
study of the structures that make up specific body system example ? study of the nervous system (study 1.1)
question
homeostasis
answer
state of steady internal conditions maintained by living things (section 1.1)
question
cell
answer
smallest independently functioning unit of a living organism (section 1.2)
question
organelles
answer
tiny functioning units within a cell (section 1.2)
question
tissue
answer
group of many similar cells that work together to perform a specific function (section 1.2)
question
organ
answer
anatomically distinct structure of the body composed of two or more tissue types each organ performs one or more physiological function withing the body (section 1.2)
question
organ system
answer
group of organs that work together to perform major functions or meet physiological needs of the body (section 1.2)
question
organism
answer
living being that has a cellular structure and that can independently perform all physiologic functions necessary for life (section 1.2)
question
anabolism
answer
assembly of more complex molecules from simpler molecules _________ consumes energy (section 1.3)
question
catabolism
answer
breakdown of more complex molecules into simpler ones __________ releases energy (section 1.3)
question
metabolism
answer
sum of chemical (anabolic and catabolic) reactions that take place in the body (section 1.3
question
adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
answer
chemical compound that is the energy currency of cells (section 1.3)
question
responsiveness
answer
ability of an organism to adjust to changes in its internal and external environments (section 1.3)
question
development
answer
chronological sequence of changes that a body undergoes includes processes of ? differentiation ? growth ? reproduction (section 1.3)
question
differentiation
answer
process by which unspecialized cells become specialized in structure and function (section 1.3)
question
growth
answer
process of increase in size (section 1.3)
question
reproduction
answer
formation of a new organism from parent organism(s) (section 1.3)
question
requirements of life
answer
? oxygen ? nutrients (water, macro-, micro-) ? narrow range of temperature (within few degrees of 37°C or 98.6°F) ? narrow range of atmospheric pressure (section 1.4)
question
nutrient
answer
chemical obtained from foods and beverages that is critical to human survival examples ? water ? macronutrients: energy-yielding (carbohydrates, lipids) and body-building (proteins) nutrients ? micronutrients: vitamins and minerals (section 1.4)
question
sweating
answer
bodily response to high temperatures that causes water to be secreted through the skin and evaporated removing some thermal energy from the body (section 1.4)
question
shiverring
answer
random muscle movement that generates heat (section 1.4)
question
pressure
answer
force exerted by a substance that is in contact with another substance (section 1.4)
question
atmospheric pressure
answer
pressure exerted by the mixture of gasses (primarily N and O) on the Earth's atmosphere (section 1.4)
question
respiration
answer
taking on of oxygen and release of carbon dioxide (section 1.4)
question
decompression sickness (DCS)
answer
condition in which gasses dissolved in the blood or in other body tissues are no longer dissolved following a reduction in the pressure on the body gasses dissolved in blood (primarily nitrogen) come rapidly out of solution, forming bubbles in the blood and in other bodily tissues treatment includes hyperbaric chamber and oxygen therapies (section 1.4)
question
set point
answer
physiological value around which the normal range fluctuates example ? body temperature of 98.6°F (section 1.5)
question
normal range
answer
restricted set of values that is optimally healthful and stable (section 1.5)
question
negative feedback
answer
mechanism that prevents a physiological response from going beyond the normal range by reversing the action once the normal range is exceeded 3 basic components ? sensor (receptor) ? control center ? effector (section 1.5)
question
sensor
answer
component of a feedback system that monitors a physiological value example ? (sweat response) nerve cells in skin and brain (section 1.5)
question
control center
answer
component in a feedback system that compares the value to the normal range example ? (sweat response) temperature-regulating hypothalamus (section 1.5)
question
effector
answer
component in a feedback system that cause a change in a value example ? (sweat response) sweat glands (section 1.5)
question
positive feedback
answer
process that intensifies a change in the body's physiological condition rather than reversing it results in changes in status of body, rather than its homeostasis (section 1.5)
question
anatomical position
answer
position of the body whereby it is ? upright ? feet shoulder width apart and parallel ? toes forward (section 1.6)
question
prone
answer
oriented face-down (section 1.6)
question
supine
answer
oriented face-up (section 1.6)
question
anterior
answer
describes the front or direction toward the front of the body a.k.a. "ventral" example ? toes are ________ to the foot (section 1.6)
question
posterior
answer
describes the back or direction toward the back of the body a.k.a. "dorsal" example ? popliteus is _________ to the patella (section 1.6)
question
superior
answer
describes a position above or higher than another part of the body proper a.k.a. "cranial" example ? orbits are ________ to the oris (section 1.6)
question
inferior
answer
describes a below, or lower than, another part of the body proper a.k.a. caudal example ? pelvis is ________ to the abdomen (section 1.6)
question
lateral
answer
describes the side or direction toward the side of the body example ? thumb (pollex) is _______ to the digits (section 1.6)
question
medial
answer
describes the middle or direction toward the middle of the body example ? hallux is the ______ toe (section 1.6)
question
proximal
answer
describes a position in a limb that is nearer to the point of attachment or the trunk of the body example ? brachium is ________ to the femur (section 1.6)
question
distal
answer
describes a position in a limb that is farther from the point of attachment or the trunk of the body example ? the crus is ______ to the femur (section 1.6)
question
superficial
answer
describes a position closer to the surface of the body example ? skin is ___________ to the bones (section 1.6)
question
deep
answer
describes a position farther from the surface of the body example ?brain is ____ to the skull
question
section
answer
two-dimensional surface of a three-dimensional structure that has been cut (section 1.6)
question
plane
answer
imaginary two-dimensional surface that passes through the body (section 1.6)
question
sagittal plane
answer
plane that divides the body or an organ vertically into right and left sides (section 1.6)
question
midsagittal plane
answer
plane that runs directly down the middle of the body dividing it into equal right and left sides a.k.a. "median plane" (section 1.6)
question
parasagittal plane
answer
plane that divides the body into unequal right and left sides a.k.a. "longitudinal section" (section 1.6)
question
frontal plane
answer
plane that divides the body or an organ into an anterior (front) portion and a posterior (rear) portion a.k.a. coronal plane (section 1.6)
question
transverse plane
answer
plane that divides the body or organ horizontally into superior (upper) and inferior (lower) portions produces images referred to as cross-sections (section 1.6)
question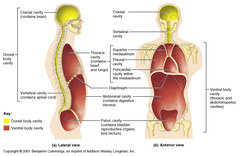
dorsal cavity

answer
posterior body cavity that houses the brain and the spinal cord a.k.a. "posterior cavity"
question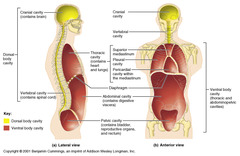
ventral cavity

answer
larger body cavity located anterior to the posterior (dorsal) body cavity includes the serous membrane-lined pleural cavities for the lungs, pericardial cavity for the heart, and the peritoneal cavity for the abdominal and pelvic organs a.k.a. "anterior cavity" (section 1.6)
question
cranial cavity

answer
division of the posterior (dorsal) cavity that houses the brain (section 1.6)
question
spinal cavity
answer
division of the dorsal cavity that houses the spinal cord a.k.a. "vertebral cavity" (section 1.6)
question
thoracic cavity
answer
division of the anterior (ventral) cavity that houses the heart, lungs, esophagus, and trachea (section 1.6)
question
abdominopelvic cavity
answer
division of the anterior (ventral) cavity that houses the abdominal and pelvic viscera (section 1.6)
question
serous membrane
answer
membrane that covers organs and reduces friction a.k.a. "serosa" (section 1.6)
question
pleura
answer
serous membrane that lines the pleural cavity and covers the lungs (section 1.6)
question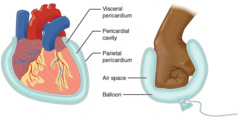
pericardium

answer
serous membrane that surrounds the heart in the pericardial cavity (section 1.6)
question
x-ray
answer
a form of high energy electromagnetic radiation with a short wavelength capable of penetrating solids and ionizing gases used in medicine as a diagnostic aid to visualize body structures such as bones (section 1.7)
question
computed tomography (CT)
answer
noninvasive imaging technique that uses computers to analyze several cross-sectional X-rays in order to reveal minute details about structures of the body invented in the 1970s operates on the principle that as X-rays pass through the body, they are absorbed or reflected at different levels (section 1.7)
question
magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
answer
medical imaging technique in which a device generates a magnetic field to obtain detailed sectional images of the internal structures of the body based on a phenomenon of nuclear physics discovered in the 1930s in which matter exposed to magnetic fields and radio waves was found to emit radio signals (section 1.7)
question
positron emission tomography (PET)
answer
medical imaging technique in which radiopharmaceuticals are traced to reveal metabolic and physiological functions in tissues (section 1.7)
question
ultrasonography
answer
application of ultrasonic waves to visualize subcutaneous body structures such as tendons and organs (section 1.7)
question
renewal
answer
process by which worn-out cells are replaced



