examination of skin, hair, nails
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion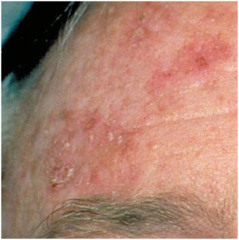
Actinic Keratosis

answer
superficial, flattened papules covered by dry scale; often multiple, can be round or irregular; pink, tan, or greyish; benign, though 1 of every 1000 per year develop into squamous cell carcinoma
question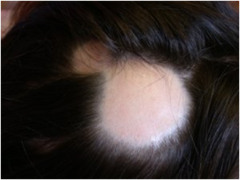
Alopecia Areata

answer
sudden, rapid, patchy loss of hair; affected skin smooth, normal appearing; usually on scalp or face may be from emotional disturbances, infections, chemotherapy
question
Alopecia Areata

answer
sudden, rapid, patchy loss of hair; affected skin smooth, normal appearing; usually on scalp or face may be from emotional disturbances, infections, chemotherapy
question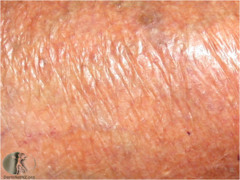
atrophy

answer
thinning of skin surface & loss of normal skin markings; skin translucent, paper like; examples: striae, aged skin, chronic steroid use
question
Basal cell carcinoma
answer
most common form on skin cancer slow growing & rarely metastasizes usually appears on face fair skin & sun exposure risk factors Telangiectatic vessels often visible
question
Basal cell carcinoma
answer
most common form on skin cancer slow growing & rarely metastasizes usually appears on face fair skin & sun exposure risk factors Telangiectatic vessels often visible
question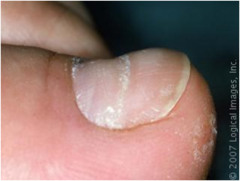
Beau's lines

answer
transverse grooving in nails associated with acute severe illness lines emerge from under proximal nail weeks later ; gradually grow out with the nails
question
Beau's lines

answer
transverse grooving in nails associated with acute severe illness lines emerge from under proximal nail weeks later & gradually grow out with the nails
question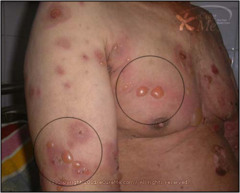
Bulla

answer
vesicle greater than 1 cm examples: blisters, pemphigus vulgaris, bullous erythema multiforme
question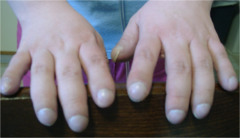
clubbing

answer
Distal phalanx of each finger becomes rounded & bulbous; nail plate more convex angle between the plate & the proximal nail fold increases to 180 degrees or more; causes: chronic hypoxia from variety of respiratory DO's (COPD, lung Ca), cardiac DO's (CHF), chirrhosis
question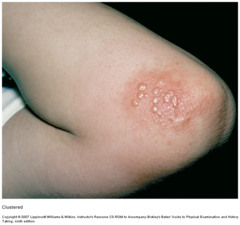
clustered pattern

answer
seen in herpes & poison ivy
question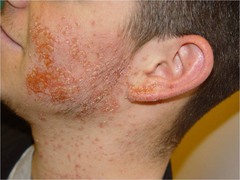
crust

answer
dried residue on skin of serum, blood or pus; Slightly elevated, varies in size & color; examples: scabs (eschars), eczema, impetigo
question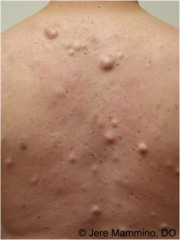
cysts

answer
elevated, encapsulated lesion in dermis or subcutaneous tissues filled with liquid or semi solid material (purulent or sebaceous) examples: sebaceous cysts, cystic acne, inclusion cysts
question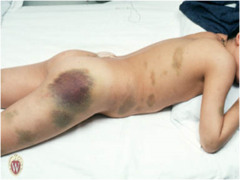
Ecchymoses

answer
Purple or purplish-blue (fades to green, yellow, brown with times) 'bruise' variable size, nonblanching causes: trauma, bleeding disorders
question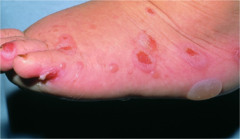
Erosion

answer
loss of superficial epidermis depressed, moist, glistening follows rupture of vesicle or bulla; does not bleed examples: apthous stomatitis, area after ruptured vesicle
question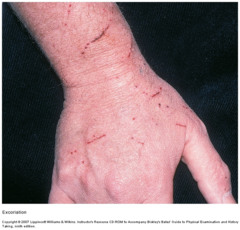
Excoriation

answer
linear or punctate hollowed out crusted areas examples: scratch, abrasion
question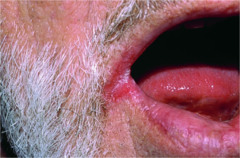
Fissure

answer
linear crack or break in the skin often due to excessive dry skin Examples: athlete's feet (tinea pedis), cheilosis (cracking at the angle of the mouth)
question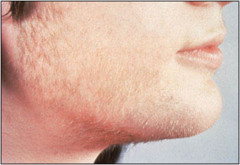
Hirsuitism

answer
Growth of hair in women in the male distribution pattern(face, body, pubic areas) symptom not disease causes: Cushing's disease, insulin resistance, adrenal hyperplasia, polycystic ovary syndrome
question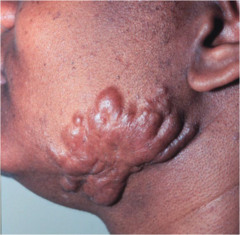
Keloid

answer
irregularly shaped, hypertrophic elevated scar grows beyond the boundaries of the wound caused by excessive collagen formation during healing
question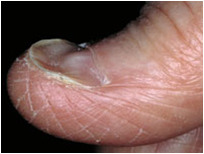
Koilonychia

answer
central depression of the nail with lateral elevation of the nail plate produces concave curvature associated with: Fe deficiency anemia Syphilis fungal Dermatosis Hypothyroidism
question
Koilonychia

answer
central depression of the nail with lateral elevation of the nail plate produces concave curvature associated with: Fe deficiency anemia Syphilis fungal Dermatosis Hypothyroidism
question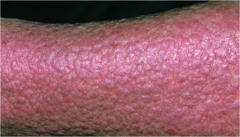
Lichenification

answer
Rough, thickening epidermis increased visibility of normal skin furrows Often due to chronic rubbing (flexor surfaces), itching, skin irritation
question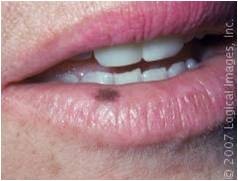
Macule

answer
small, flat, circumscribed area that is changed color if skin less than 1 cm examples: moles (nevi), freckles, measles, drug reactions
question
Macule

answer
small, flat, circumscribed area that is changed color if skin less than 1 cm examples: moles (nevi), freckles, measles, drug reactions
question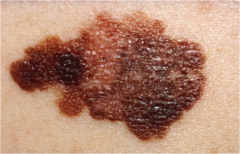
Melanoma

answer
Asymmetry Irregular Borders variation in Color--mixtures of black, blue, red Diameter--greater than 6mm Elevation--may also be flat changing in nevi of concern--new swelling, redness, scalling, oozing, bleeding, itching/bumping/pain
question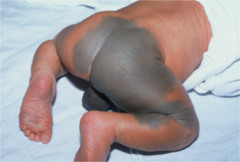
Mongolian spots

answer
flat, nonpalpable, irregularly shaped macule greater than 1 cm in diameter congenital birthmark--more common in Mongolain area of the world; tend to fade w/ age
question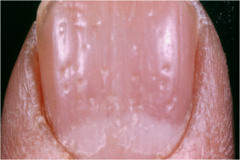
nail pitting

answer
small depressions on the nail surface causes: psoriasis, lichen planus, eczema, alopecia areata, idiopathic
question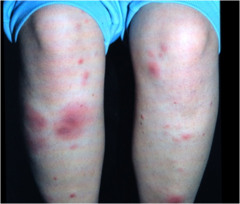
Nodule

answer
Elevated, firm, marble-like lesion deeper than papule (in dermis) generally 0.5-2cm (if >2cm=tumor) examples: erythema nodosum, dermatofibroma, lipomas
question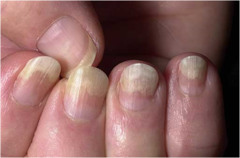
Onycholysis

answer
painless separations of the nail plate from the nail bed; start distally often multiple nails included Causes: hyperthyroidism, psoriasis, eczema, mycotic diseases of nails
question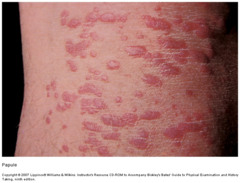
Papule

answer
raised, firm, circumscribed area less than 1 cm examples: verruca (wart), raised moles, lichen planus
question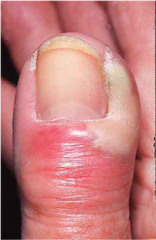
Paronychia

answer
infection of nailbed often related to trauma
question
Paronychia

answer
infection of nailbed often related to trauma
question
Patch (Vitiligo)

answer
flat, nonpapule, irregular shaped macule greater than 1 cm in diameter
question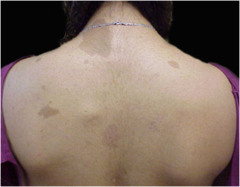
Patch (cafe au lait spots)

answer
develop as people age; first indication of neurofibromatosis flat, nonpalpable, irregularly shaped macule greater than 1cm in diameter
question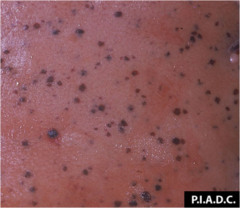
Petechiae

answer
red-purple nonblanching discoloration (blood outside vessels) 1-3mm diameter Causes: intravascular defects (thrombocytopenia, increased INR), endocarditis, vasculitis
question
Port wine stain

answer
type of patch
question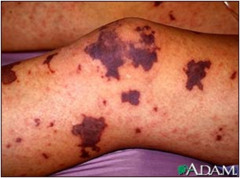
Purpura

answer
larger petechie may be palpable (vascultis) meningiococcal--******** producing bacterium
question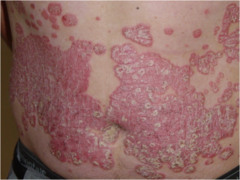
Plaque

answer
elevated, superficial, firm lesion with flat top surface greater than 1 cm in diameter Examples: psoriasis (velvety texture), actinic & seborrheic keratosis
question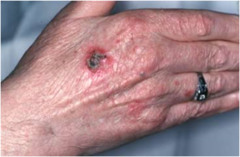
Squamous Cell Carcinoma

answer
most commonly in sun-exposed areas, particularly scalp, back of hands, lower lip & ear lesions are soft, elevated w/ surface scale, base of lesion may be inflamed may develop actinic keratosis usually grow more quickly, are firmer, and redder
question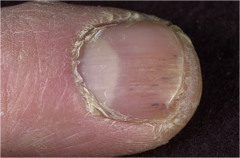
Splinter hemorrhages

answer
linear hemorrhages in the nail bed common in people who perform manual labor (more distal) also seen in endocarditis (more proxmial)
question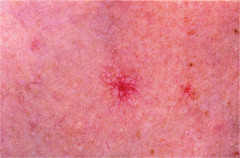
Spider Angioma

answer
Fiery red, central body (sometimes raised) surrounded by erythema + radiating 'legs' up to 2 cm common on face, neck, arms, trunk; almost never below waist causes: liver disease, pregnancy, vitamin B deficiency, normal variant in some people
question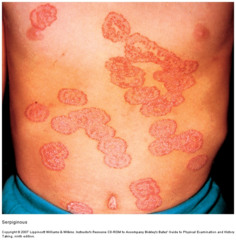
Serpiginous

answer
worm-like
question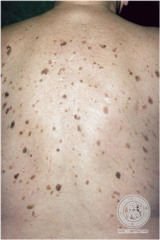
Seborrheic Keratosis

answer
common, benign yellowish to brown raised lesions slightly velvety, greasy, warty--have 'stuck on' appearance typically multiple, symmetrically distributed
question
Seborrheic keratosis

answer
common, benign yellowish to brown raised lesions slightly velvety, greasy, warty--have 'stuck on' appearance typically multiple, symmetrically distributed
question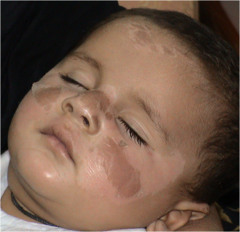
Scale

answer
thin flake of dead, exfoliated epidermis irregular, thick or thin, varies in size examples: seborrheic dermatitis, dry skin, cellulitis
question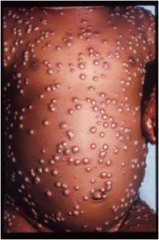
Pustule

answer
similar to vesicle except filled with purulent material less than 1 cm Examples: acne, impetigo, smallpox
question
Pustule

answer
similar to vesicle except filled with purulent material less than 1 cm Examples: acne, impetigo, smallpox
question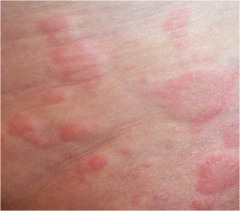
Wheal

answer
Elevated, irregularly shaped area of cutaneous edema; classic hive variable diameter, solid, transient Examples: insect bite, urticaria, allergic reactions
question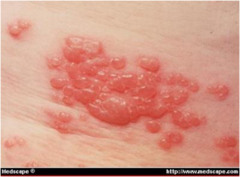
Vesicle

answer
Elevated, circumscribed, superficial (not into dermis) Filled with serous fluid (yellowish, viscous fluid; typical ascites) less than 1 cm Examples: varicella (chicken pox), shingles, HSV
question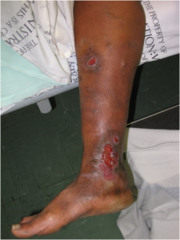
Ulcer

answer
deep loss of epidermis & dermis examples: decubiti, vascular ulcers
question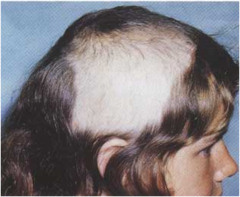
Trichotillomania

answer
loss of scalp hair due to physical manipulation usually an unconscious habit affected area has irregular border, hair density is greatly reduced, but site is not totally bald
question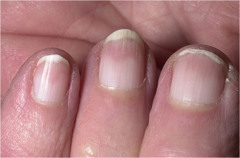
Terry's nails

answer
nails mostly whitish with a distal band of reddish brown lunulae may not be visible seen with aging ; with chronic diseases (cirrhosis, CHF, DM)
question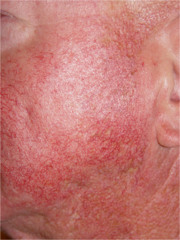
Telangiectasia

answer
fine, irregular red lines (0.5-1mm) caused by dilation of capillaries--blanch when palpated causes: hereditary, pregnancy, liver disease, CREST syndrome
question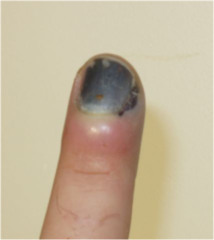
Subungual hematoma

answer
collection of blood under nail due to trauma
question
Squamous cell carcinoma

answer
most commonly in sun-exposed areas, particularly scalp, back of hands, lower lip ; ear lesions are soft, elevated w/ surface scale, base of lesion may be inflamed may develop actinic keratosis usually grow more quickly, are firmer, and redder
question
Impetigo
answer
honey colored crusts



