FOB MARKETING – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Marketing is the activity, set of institutions, and processes for creating, communicating, delivering, and exchanging offerings that have value for customers, clients, partners, and society at large.
answer
marketing definition
question
Basic, simple marketing cycle

answer
Marketing and exchange
question
? In marketing Start with the customer, get customer insights Get customer insights through integrated marketing, how do you promote it? What do they want? What are they looing for? By delivering what the customer wants you create profits through delivering satisfaction ? In sales Start with the product "Shout about it and someone will come and get it" About shouting about products not Profits through Sales Volume
answer
• Difference between selling and marketing concepts
question
•CONSUMER/ MARKET DRIVEN BUSINESSES V SALES/INTERNALLY ORIENTATED BUSINESSES •Customer concern throughout business V •Convenience comes first •Know customer choice criteria and match with marketing mix V •Assume price and product performance are the key to most sales •Segment by customer differences V •Segment by product •Invest in market research and track market changes •Rely on anecdotes and received wisdom •Welcome change V •Cherish the status quo •Try to understand competition V •Ignore competition •Market spend regarded as an investment V •Marketing spend regarded as luxury •Reward innovation V •Innovation punished •Search for latent markets V •Stick with the same •Being fast V •Why rush? •Strive for competitive advantage •Happy to be me-too
answer
Difference between Consumer/Market driven businesses and sales/internally orientated businesses
question
• What is involved in marketing? ? As an organisation you market at Individuals households To do that, you have to know about consumer behaviour ? Marketing towards buyers within companies Business to business Industrial companies (massive units to buy cars, or all the equiptment for the oil industry) Institutions (hospitals, universities) Profit organisastions vs Non-profit organisations
answer
Marketing involves Individuals and Organisations
question
? Products Tangible that you can see or buy off a shelf FMCG: fast moving consumer goods, small scale, don't cost a lot of money for the end consumer Durables: washing machines, freezers, televisions ? Services Personal Business ? Ideas Education The Church ? Products or services?
answer
What are we marketing?
question
? First step for launching a new product is understanding your environment ? Can be done at a strategic level for an organization as a whole, or on a product level ? PEST: Political What's happening in gov't? What's happening at the gov't level that could influence your market? Economic ? Recissions? Credit Crunch? Deflation? Societal ? What are we doing different now that we didn't ten years ago? ? What are the new trends? Technological ? Are people using apps? Should we be getting into apps? Etc.
answer
Marketing Occurs in a Dynamic Environment
question
Needs to be constant and dynamic Create value for customers and build customer relationships ? Understand the marketplace and customer needs and wants ? Design a customer-driven marketing strateegy ? Constuct an integrate dmarketing program that delivers superior value ? Build profitable relationships and create customer delight and loyalty Create value from customers in return ? Capture value from customers to create profits and customer equity -Long term benefit and trust from the customer in you
answer
? Understanding the customers needs and wants within this environment
question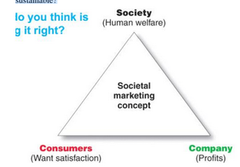
How do we maintain profit for our shareholders and company but still remain ethical and sustainable?

answer
• What's happening in marketing and where is it going?
question
Transactional becomes relational ? Importance of relationships ? Changing environment

answer
? Building relationships
question
• False wants and too much materialism -Social commentators have said that marketing urges too much interest in material possessions. People are judged by what they own and not who they are. - issues of trust, responsibility • Too few social goods -Overselling private goods at the expense of public goods. • Too much political power -Businesses lobby politicians to support their interests above the public interest.
answer
Ethical challenges in marketing
question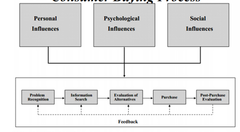
? Top part is consumer influences ? Bottom part is how the combination of influences creates a decision making process

answer
Possible influences on the consumer buying process
question
Cultural Social Personal Pyschological inflences
answer
influences that make up buyer
question
Cultural: major influence. Where you have grown up. Includes morals, language •Culture is the most basic cause of a person's wants and behavior. "..that complex whole which includes knowledge, beliefs, art, morals, custom and any other capabilities and habits acquired by man as a member of society" E.B. Taylor 187 Cultural issues: don't want to offend or stereotype- have to be sensitive to cultural differences. HSBC do It well: saying they are global and local: depending on which culture you grew up in will see rug differently. Within culture are sub-cultures: youth
answer
Cultural
question
SOCIAL INFLUENCES Roles and family: the toothpaste your family has bought for years likely to influence what you buy •2 or more people, related by birth, marriage or adoption •Roles: -Gatekeeper, buyer, decider, user, influencer.... -Family decision making, sibling influence, "family identity bundles" Epp A ; Price L (2008) " Family identity: A framework of identity interplay in consumption practices" Journal of Consumer Research Vol 35, Commuri ; Gentry (2000) Reference groups and social networks.... • normative-. • comparative- may compare yourself with others • aspirational- Aspire to luxury brands. • opinion leaders/co-creation- personalization of what consumer wants
answer
social
question
Personal Age- can you buy alc?, occupation, economic situation, lifestyle (and changes), self-concept- hight self asteem or low, life-stage
answer
Personal
question
Psychological Influences Personality - unique psychological characteristics (openness, conscientiousness, extraversion, agreeableness, neuroticism) - big 5 scale used to measure personality Perception and attitudes - brand - Burberry brand almost destroyed by chavs wearing iconic pattern. Motives Ability ; Knowledge
answer
Psychological
question
? Basic needs at the bottom, least necessary needs at the top Need to first satisfy basic needs: hunger. Move up the hierarchy: Marketing trying to help achieve these needs: e.g. phone for safety or for social needs: social media, or esteem needs: liking photos. Most successful products satisfying needs.

answer
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs- physcological
question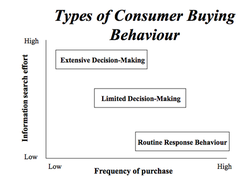
3 types of buying behaviour routine: always buy colgate toothpaste because mum did. Difficult to break limited: hungry: go into shop and pick snack spontaneously- branding is important extensive: structure of decision process

answer
Types of consumer buying behaviour
question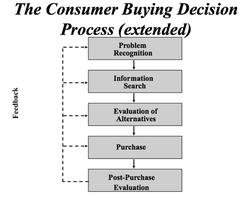
E.g. problem recognition: man needs to buy more family friendly car. Info search: need to find out about safety of cars etc. collecting info via car magazines, word of mouth etc Evaluation of alternatives: look at different options. Can be informal or formal. Important for marketers: need to know whats important for consumers and where they are finding info. Purchase: sales assistant not very helpful so may deter you from buying Post-purchase evaluation: how you feel socially/financially after purchase. Do you feel comfortable. Company may send flowers: makes you feel better- what is going to make consumer happy. Develops on going relationship. At each stage of decision process marketer needs to know about influences.

answer
The consumer buying decision process
question
Select customers to serve Breaks down audience into segments that want your product. Segmentation: divide total market into smaller segments. Targeting: select segment to enter- which one most cost effective. Decide on a value proposition Differentiation: differentiate the market offering to create superior customer value. Positioning: position the market offering in the minds of target customers. "A market segment is a group of individuals, groups or organisations that share one or more similar characteristics which make them have relatively similar product needs." Need to make sure segmemts are discreet and reachable
answer
Segmentation
question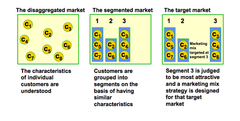

answer
The process of market segmentation and target marketing
question
• Geographic variables Country/region - Urban or rural area • Demographic variables sex - dove targets men and women v differently - age - stage in the family life cycle- face creams • Socio-economic variables income/occupation - education/social class •Psychographic variables - more difficult to target personality lifestyle attitudes •Product -related variables - Users v. non-users- tesco clubcard- knows what you have bought and can see what incentives e.g. discounts change your behaviour. -loyalty patterns benefits sought attitude to product
answer
Bases for Segmenting Consumer Markets
question
product place price promotion - analysed target market
answer
The marketing mix
question
? Anything received in an exchange ? Favourable and unfavourable ways to be perceived Combination of tangible and intangible attributes, including functional, social and psychological utilities or benefits ? ? Can be an idea, a service, a good, or any combination Anything that can be offered to a market for attention, acquisition, use or consumption that might satisfy a want or need
answer
Product
question
CONSUMER Convenience Shopping Speciality Unsought ? Annoying products ? House insurance, car insurance, taxes BUSINESS Raw materials Major equipment Accessory equipment Component parts Process materials Consumable supplies Business services
answer
Two classifications of products
question
? Product attributes What attributes are my consumers look for In supermarkets, where you position your price What is the product made up of, expecctation, how do we make our product different BRANDING What the customer thinks about you PACKAGING The way the design, logo, colours look Identifies product wihtin market Signifies quality, style, story LABELLING Way it looks and also legal requirements Food labeling Calorific value, etc. PRODUCT SUPPORT SERVICES What are we offering the ustomer over and above the product Reinforcing differentiation within market place
answer
Product and Service Decisions
question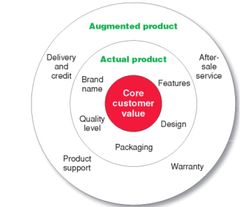

answer
Levels of products and services
question
?People: NOT CUSTOMERS; the appearance and behaviour of service dleiverers; staff and representatives ? Processes: how the service is actually delivered; back up systems ? Physical Evidence: layout, furniture, brochures, signs, etc, certificates, photos ? Idea generation NPD: New Product Development; backwards and forwards through various stages to ensure customer satisfaction ? New product planning ? Idea generation ? Screening and evaluation ? Technical development ? Market appraisal ? Launch
answer
The extended service mix
question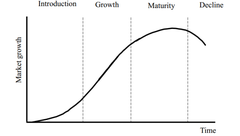
As a product moves through its life Faces different marketing conditions Different marketing objectives become important Different marketing strategies become applicable

answer
• PLC: Product Life-Cycle Concept
question
Introduction -Create product awareness and trial Growth -Maximise market share Maturity -Maximise profit while defending market share Decline -Reduce expenditure and milk the brand
answer
Marketing Objectives and strategies at different stages of the PLC
question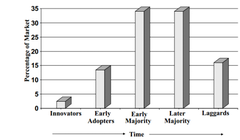

answer
Diffusion of Innovation
question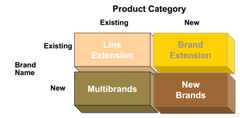
The power of a brand lies in what customers have learned, felt, seen and heard about the brand over time. In other words, the power of a brand resides in the minds of customers ? Four product brand strategies

answer
Branding a product or service
question
• Represents the costs involved in producing the product. • The revenue that can be generated from the sale of the product. • The profits and longterm survival of the firm. • The ability to respond quickly to market conditions.
answer
The nature and importance of price. To the seller
question
• Represents the value placed on what is exchanged. • Also represents the cost to the customer. • It can signify the quality of the product or provider. • It is affected by buying power.
answer
The nature and importance of price. To the buyer
question
? Organisational objectives ? Pricing objectives ? Costs ? Channel member expectations Supply chain to the customer ? Buyer's perceptions ? Competition ? Legal and regulator issues ? Other marketing mix variables
answer
Factors influencing general pricing decisions
question
•Profit oriented: -Target return objective - sets a specific level of profit, usually stated as a % of sales or investment. Also called the ROI. -Profit maximisation - • seeks to achieve as much profit as possible. 'To charge what the market will bear' •Sales oriented: -Sales growth objective - seeks some level of unit sales, pound sterling/dollar sales or share of market without referring to profit. •Market share objective: -gain some specific share (%) of a market or market share leadership. •Status Quo oriented: -Price stability - to meet the competition or even avoid competition. -Non-price competition - aggressive action on one or more of the Ps other than price. -Survival
answer
Pricing Objectives
question
• development of pricing objectives • assessment of target market's ability to purchase and evaluation of price • determination of demand • analysis of demand, cost and profit relationships • evaluation of competitors' prices • selection of a pricing policy • development of a pricing method • determining a specific price
answer
8 stages of price setting
question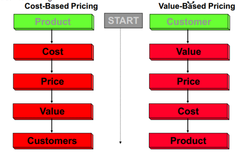

answer
Value based pricing
question
• Emphasises price as an issue. • Attempts to match or beat competitors' prices. • The firm needs to be a low cost producer to compete on price. • It is particularly evident in industries where product differentiation is difficult. • It enables the firm to react quickly to competition. • Can encourage customers to become price sensitive.
answer
Features of price based competition
question
• Competition focuses not on price but on some distinctive features of the product or service. • Firms need to be able to distinguish products or brands, obtain a unique brand image. • Distinctive features must be of value to the customer. • Works well when customers are less price sensitive. • Enables the firm to build customer loyalty.
answer
Features of value based Competition
question
• Charging an initial high price • Appeals to those who can afford and most desire the product. • Generates much needed cash flow. • Covers large R&D spend. • Helps keep demand consistent with production capabilities. • Competition may be attracted by high price.
answer
Pricing Policies for New Products price skimming
question
• Initial price set below competing brands. • Useful when demand is elastic. • Useful for low cost producers. • Less flexible than skimming • Can be useful if threat of entrants is high. • Can deter some competitors due to low unit profit.
answer
Pricing Policies for New Products penetration pricing
question
•Product line pricing •Optional-product pricing •Captive product pricing •By-product pricing •Product-bundle pricing
answer
Pricing tactics within the marketing mix
question
•Discounting •Segmentation •Psychological •Promotional •Geographical •Dynamic
answer
Tactical: Product adjustment strategies
question
• Despite the increased role of non-price factors in the modern marketing process, price remains an important element of the marketing mix both strategically and tactically •Many internal and external factors influence pricing decisions • Decisions on price can affect sales but can also adversely affect brand and long term future •In the end, the consumer decides whether the company has set the right price and they may differ in the values they assign to different product features
answer
Price summary
question
The groups of individuals and organisations which direct the flow of products from producers to consumers
answer
Distribution/Marketing Channel:
question
• Distribution (or "Place"): Activities that make the product availbale to target consumers • Distribution Channel: the means by which products are moved from producer to end consumer •Channel Intermediaries: someone who's helping you achieve the goal of delivering goods to end consumer •Wholesaler: will buy in bulk from one producer and then sell on to another part of the business, don't come in contact with consumers, wine wholesaler buys from france then distributes to wine shops • Retailer: deal directly with the end consumer • Facilitators perform some other function in the distribution of products, make it run smoothly • Many ways a marketing channel can be built:
answer
Key terms
question
closing the gap between functions
answer
Purpose of distribution channel =
question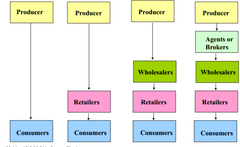

answer
Types of marketing channel...
question
?Organisational resources and objectives: what can you afford what are you trying to achieve ?Product features: some need more experts and specialists, so impacts whether you go direct or not ? Market characteristics ? Consumer behaviour: what are your consumers doing?, use of the internet for example ? Environmental forces: pestle analysis
answer
Factors Influencing Distribution Channel strategy
question
? Information gap: fulfills the information gap beetween what do people need/want ? Promotion gap: advertising ? Negotiation gap: negotiating with bulk buyers ? Ordering gap: efficiency in ordering ? Financing gap: take on responsibility for financing ? Risk-taking gap: utilizing experts on risk taking in your area ? Physical possession gap: chain becomes more fluid an cash is easier to come buy ? Payment gap: physical possession goes on, payment down the chain is smoother and quicker
answer
Functions of a distribution channel: closing the gaps
question
Sorting= classifying different supplies into groups of similar products. Accumulating= developing a stock of similar products Allocating= Breaking down stock into smaller units Assorting= Combining products into collections required by customers
answer
Functions of Intermediaries
question
If you have a trusted intermediary then you can deliver once to them and then they distribute, which is cost effective so long as they are experts
answer
Why use intermediaries
question
Producer to consumer is more common, a channel with no intermediaries Examples: Farm shops Distribution via sales representatives or party plan Internet sales direct from producer or service provider
answer
Channels with no intermediaries
question
provides the services interface to end consumer Producer -> retailer -> consumer Examples: White goods Furniture Electricals Books
answer
Channel with one intermediary
question
wholesalers take delivery of many limited, high volume lines, resell to retailers in mixed assortments convenient to end consumers • Producer -> wholesaler -> retailer -> consumer Examples: Groceries Pharmacies
answer
Channel with two intermediaries,
question
Producer -> agent -> wholesaler -> retailer -> consumer Channel with three intermediaries, agent acts on behalf of producer or wholesaler to make sale Example: Agricultural products
answer
Channel with three intermediaries, agent acts on behalf of producer or wholesaler o make sale
question
Short more direct customer feedback greater quality control greater price control Long greater geographical coverage greater efficiency more professionalism
answer
Relative advantages to producers of short and long channels?
question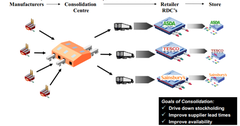
? All about how you maximize the efficiency, minimize the costs, etc.

answer
The shape of logistics networks
question
Intensive Using all possible outlets (e.g. Coke) Want all the possible outlets, want to be well placed, seen as the brand of choice, convenient and impulsive Benefits = convenience, impulse Selective Using proportion of outlets (e.g. make up) -Chanel, debenhams, harvey nichs: about being selective, may want to limitdistribution - Want to go somewhere where the sales staff can talk with the consumer -Resource efficiency, quality control, strategic positioning Benefits = resource efficient, quality control, Strategic positioning. Exclusive Using very restricted outlets (e.g. Ducati) - Experience going there Benefits = resource efficient, quality control, premium image
answer
• Levels of Distribution Intensity
question
In conventional marketing channels, intermediaries are autonomous firms - Producer -> wholesaler -> retailer -> consumer Advantages = specialisation, professionalism BUT Producers risk losing control/end customer contact Conflicts happen between channel members... ...adversarial negotiations over price (Bertini and Gourville, 2012) ... retailers add new lines, restricting space for original lines ...prdrs/wlrs/rtlrs disagree over responsibilities To retain advantages of long channels but overcome these problems, firms adopt channel integration activities... corporate, contractual and administered vertical marketing systems
answer
Channel Integration
question
Corporate Contractual Administered
answer
Vertical integration options
question
Where one firm in the channel owns or acquires other channel members E.g. Shell owns extraction, processing, storage, transport, retail functions Advantages = total channel control (with all benefits of price control, quality control) Risks = over-extension of expertise
answer
corporate
question
Where one firm in the channel contracts other channel members to perform their activities according to specified terms and conditions, in return for technical/marketing support E.g. licensing - Coca Cola contracts local enterprises to make up, bottle and distribute its soft drinks to retailers E.g. franchising - McDonalds/Ford contract local restaurateurs/car dealers to offer sales/services to end customers Advantages = Licensors/franchisors control terms with downstream intermediaries, L/Frs gain local knowledge/entrepreneurship Risks = over-supply, customer response issues
answer
Contractual vertical marketing systems
question
Where the size and power of one firm in the channel commands cooperation from other channel members e.g. large multiple grocery retailers Advantages = de facto control of channel members (without having to bear investment costs of acquisition or management costs of contracts) Risks = bad publicity and legal actions e.g. relating to employee welfare, supplier relations...
answer
Administered vertical marketing systems
question
Channel integration can bring cost, management and marketing advantages to firms (lower costs by agreeing terms of deal with channel members, eases management by allowing more control over what other members do, and can bring upstream firms closer to end consumers) BUT can also generate risks... Over-extension of channel members' expertise Transparency and customer response issues Accusations of market distorting behaviour
answer
Reflections on channel integration
question
Place - the silent, less sexy yet crucial element of the marketing mix ! Today we considered marketing/distribution channel selection, intensity and integration demonstrating the complex nature of channel management which must support customer requirements and marketing objectives in an increasingly complex and global world - not easy!
answer
summary place
question
Communication with target audiences. - ? Have a clear target audience. ? Understand as much as possible about them in order to communicate To inform and educate. To persuade and influence decisions. - Why my product over others To remind and stimulate repeat buying. To reassure before, during and after buying decisions.
answer
aims of promotion
question
• Promotion is the fourth P but promotion (sales) can also be a tool. • Therefore to avoid confusion, I will refer to Promotion - the P - as Marketing Communications....(which is often used in text books)
answer
confusion
question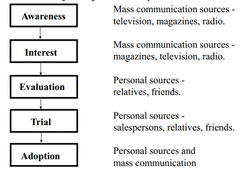

answer
Traditional model outlining marketing communication objectives
question
Marketing Communications Decisions • Objectives (e.g. awareness, purchase etc) • Target group - Which group(s) of customers? • Message - What are you trying to say/ how are you going to say it: rational or emotional themes?
answer
Marketing Communications Decisions
question
The areas that are creatively manipulated with to get your message across

answer
Integrated marketing communications mix
question
•Advertising: TV, press, radio, cinema, outdoor versus video blog, Youtube, viral •Personal selling: Personal versus online •Sales promotion: BOGOFF versus online vouchers, ItsOn sites •Direct marketing: Post/flyers versus online, email, mobile •Public relations: Press release versus twitter, memes, viral, WOM, •Difference is CONTROL: marketer versus customer ...
answer
incorporating the new
question
•Need to maximise budget, resources and reach by giving the target audience consistent, consistent and clear messages about the brand in an increasingly complex environment NB: Fundamentally you must start by understanding your brand, understanding your target audience(s) and comms objectives
answer
The need for integrated marketing communications
question
•Four common methods used to set the total budget for promotion: -Affordable method (increasingly new media usage) -Percentage-of-sales method -Competitive-parity method- supermarkets -Objective-and-task method- Objective to create awareness, make a case for target audience, but it in front of board -Other product-specific factors
answer
Setting the IMC budget and mix
question
• You should have a clearer understanding of the role of Promotion (P) - or Marketing Communications - within the marketing mix • Importantly the role of INTEGRATING marketing communications to maximise consistency, clarity and build the desired BRAND image through all media.
answer
summary promotion
question
"The process of gathering, interpreting and reporting information to help marketers solve specific problems or to take advantage of marketing opportunities" Often referred to as 'Consumer Insight'
answer
Market research definition
question
• Understand environmental trends (PESTLE) • Understand customer requirements/trends • Understand internal influences • Understand competitive position • Understand all elements of marketing mix - P's • Pre-testing, tracking, post launch/campaign evaluations - planning, implementation and evaluation
answer
Research required throughout the marketing mix
question
• Defining problem (or opportunity) and outline the research objectives. • Plan data collection methods and collect the data - primary or secondary data? - qualitative or quantitative? • Analyse the data and interpret the findings • Report research findings to marketing decisionmakers and implement changes....monitor and improve with further research...
answer
The Process of Marketing Research
question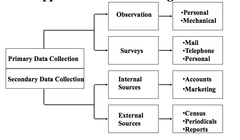

answer
Approaches to collecting data
question
Secondary research: Questions for marketer.... - Accuracy/dependency of the data? - Qualitative v quantitative? - When was it collected? - Purpose of the study? - Content of the data?
answer
Collection and analysis of data: Secondary research
question
• Qualitative research - research that deals with information too difficult or expensive to quantify, such as subjective opinions and value judgements, typically uncovered during interviews or discussion groups.
answer
Primary Data collection: Qualitative versus Quantitative Research
question
Research aimed at producing data that can be statistically analysed and results that can be expressed numerically with a big enough sample (or census?) to statistically account for populations' behaviours, choices, trends etc.
answer
Quantitative research
question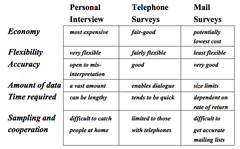

answer
Primary Data Collection: A Comparison of Survey Methods
question
• QUANTITATIVE - Advantages -inexpensive, fast turnaround, automated data collection, no interviewer bias, international co ordination - Disadvantages - respondents 'universe'. Sampling issues, self completion self selecting bias, technical difficulties • QUALITATIVE - Advantages - slightly faster than traditional focus groups, avoids dominant personalities, client control, illustrate concepts or web sites, recruitment advantages, international. - Disadvantages - lose non-verbal aspects, less useful for emotive issues, on-line moderation requires new skills, typing speeds vary, technical problems, sampling issues
answer
Recent changes: Internet research
question
• Big Data: customising versus privacy balance • Netnography • Co-creation
answer
New trends in market research...
question
• Don't under-estimate the importance of market research and customer insight in all aspects of the marketing mix: planning, implementation and evaluation! • Research fundamental part of the cycle or marketing process • Its not the fact that you do the research that it is important, it is how you interpret and use it.
answer
market research summary
question
• Small or saturated domestic markets • Demand • Economies of scale • International production • Customer relationships • Market diversification • International competitiveness
answer
Rationale for International Marketing
question
• Strategic and implementation -Need a broad strategy that takes into differences and difficulties of an internationalaudience -The costs for going international • Cultural differences • Market Segmentation -How your segmenting, who decisiion makers are, reflect into strategy • Monitoring and control -More difficult to control and monitor what's going on, understanding the differences in delivering and regulatory demands in different countries • Physical distribution and place decisions -Getting your stuff to where it needs to go -Centralized, urban, how people shop, understand the local area where you sell
answer
Differences between International and Domestic Marketing
question
HOW TO ENTER MARKET? (commitment, risk, control, profit) • EXPORT -Exporting goods • JOINT VENTURE -Join together with another company that has a foot in the international market • DIRECT INVESTMENT
answer
Market entry considerations
question
• Product - cultural, climatic, technical and economic issues affect product design. • Place - cost, distribution systems vary internationally • Promotion - affected by cultural issues (i.e. humour, religious and cultural norms). • Price - exchange-rate fluctuations. • People - foreign sales staff can give rise to motivational problems. • Processes - processes do not necessarily cross national boundaries. • Physical Evidence - can be affected by trading practices and cultural norms.
answer
Internationalisation and the 7-P Framework
question
• Demographic • Geographic • Political and legal factors • Economic factors • Sociocultural
answer
Factors to Consider in International Marketing
question
•Legislation •Ethical concerns •Political system •Co-operation versus conflict
answer
Political environment
question
•Economic development/climate •Consumer spending patterns •Income changes •Inflation •Trade
answer
Economic Environment
question
? Culture affect the way people behavie in a given society ? Values beliefs attitudes perceptiions ? KitKat different tastes and flavours
answer
Socio-cultural implications
question
• Increased economies of scale • Convergence of consumer tastes • Improved telecommunications and transport systems • Increased political acceptance of global trading • Continuing growth of large firms
answer
Impact of globalization
question
• Geographic segmentation (by country) • Trans-national segmentation (by consumer characteristics)
answer
Global Segmentation
question
• Keep product and promotion the same world-wide • Adapt promotion only • Adapt product only • Adapt both product and promotion • Invent new products
answer
International Market Entry Strategies
question
• Psychological Barriers • Operational Barriers • Organisational Barriers • Product/Market Barriers
answer
Barriers to International Marketing
question
• The gains can be much greater but it is much harder to manage a brand and market internationally • Key is understanding both your new market and new customers - can be very different • Local expertise and experience is helpful.
answer
international marketing summary



