Nuclear Chemistry Answers – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
alpha particle
answer
a helium nucleus that is emitted from a radioactive atom.
question
beta particle
answer
an electron that is emitted from a radioactive atom.
question
gamma particle
answer
energy that is emitted from a radioactive nucleus. It has zero mass and so do not affect the math in the word problems.
question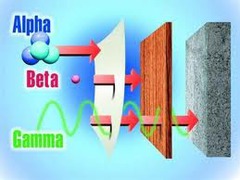
Arrange alpha, beta, and gamma particles in order of increasing ability to penetrate matter.

answer
alpha < beta< gamma. (Alpha can't go through paper. Beta can go through paper but not plywood. Gamma can go through moderately-thick layers of lead, but is stopped by thick layers of lead.)
question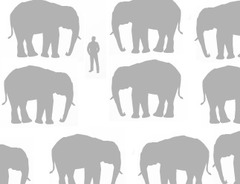
How much more mass does a proton contain compared to an electron?

answer
A proton is a little over 1800 times as massive as an electron. Here is an example I came up with that might be useful: This is roughly the difference in mass between an adult human and 53 full-grown Asian elephants.
question
nuclear radiation
answer
the emission of alpha particles, beta particles, or gamma rays from the nucleus of an atom
question
mass number
answer
the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom
question
atomic number
answer
the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. The number of protons is unique to each element and defines that element. Example: there is one and only one element in the whole universe with 6 protons, and that atom is carbon.
question
isotope
answer
atoms that have the same number of protons (and are therefore the same element) but different numbers of neutrons.
question
radioisotope
answer
an isotope that emits alpha particles, beta particles, and/or gamma rays.
question
stable isotope
answer
an "ordinary" element: an isotope that does not break down and does not emit particles or rays. Stable isotopes are the eventual breakdown products of radioisotopes.
question
atomic mass
answer
All elements have several isotopes that exist in nature. Atomic mass is the weighted average of all the isotopes of an element.(Be careful not to get this mixed up with mass number, which is the total number of protons and neutrons in a given atom.)
question
Based on your knowledge and on the symbol for tritium, how many protons does tritium have? How many neutrons?
answer
Tritium has 1 proton (the number on the bottom, aka the atomic number) and 2 neutrons (the number on the top, the mass number, is protons + neutrons, so the total number of neutrons is 3 - 1 = 2).
question
Based on your knowledge and on the symbol for carbon-14, how many protons does carbon-14 have? How many neutrons?
answer
Carbon-14 has 6 protons (the number on the bottom, aka the atomic number) as does every isotope of carbon. (6 protons is what makes it carbon) The number on the top, the mass number, is protons + neutrons, so 14 - 6 = 8 neutrons.
question
fission
answer
breaking a large nucleus into smaller nuclei. This is what releases the energy in nuclear reactors and atomic bombs.
question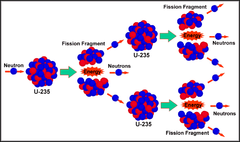
What subatomic particle sustains the nuclear chain reaction in nuclear reactors and atomic bombs?

answer
The neutron
question
fusion
answer
squashing smaller nuclei together to form larger nuclei. This releases even more energy than nuclear fission.
question
Which isotope of uranium is used to make nuclear reactors and atomic bombs?
answer
uranium-235
question
What is the most common nuclear reaction in the universe?
answer
The most common nuclear reaction in the universe is the fusion of hydrogen nuclei into helium-4. This is what causes stars to shine. It is also the reaction behind the energy release in hydrogen bombs. Fusion releases much more energy than fission, and there is no limit to the energy yield of a hydrogen bomb (e.g., it is entirely possible to make a hydrogen bomb big enough to knock the earth out of orbit.)
question
A beta particle is emitted from the nucleus. Where within the nucleus does it come from?
answer
A neutron breaks down into a proton and an electron. The proton stays put while the electron is kicked out of the nucleus as a beta particle.
question
What happens to the atomic number of an element when it undergoes beta decay? What does this do to the element? Why does this happen?
answer
*The atomic number goes up by one, which by definition means that it gains a proton and becomes a different element with a different atomic number. *A neutron in the nucleus decays into a proton and an electron, the latter of which is kicked out as a beta particle.
question
What happens to the mass number of an element when it undergoes beta decay? Why?
answer
Nothing. The mass number is the number of protons and neutrons. Since a neutron decays into a proton during beta decay, the decayed neutron is replaced by a proton. Therefore the mass number doesn't change because the total number of neutrons and protons stays the same. (If this isn't clear to you at first, see the examples in the following couple of cards.)
question
Write out the equation that represents sulfur-35 undergoing beta decay.
answer
Again, note the superscripts and subscripts on each side of the equation total up to the same numbers.
question
Suppose a radioisotope is unstable due to an abundance of neutrons compared to protons. How does the atom naturally decrease the number of neutrons?
answer
Beta decay.
question
Radioactive half-life
answer
The radioactive half-life for a given radioisotope is the time for half the radioactive nuclei in any sample to undergo radioactive decay.
question
The half-life of carbon-14 is 5730 years. Suppose a wooden cup is found in the Egyptian desert. The wood the cup is made of has 50% of the amount of carbon-14 that would be found in a living tree. How long ago was it that the tree this cup is made of was alive and exchanging carbon with the environment?
answer
5730 years
question
The half-life of carbon-14 is 5730 years. Suppose a paleontologist finds a frozen wooly mammoth that has 25% of the carbon-14 that would be found in a living animal. How long ago was it that the mammoth was alive, exchanging carbon-14 with the environment?
answer
17190 years
question
The half-life of tritium is 12 years. The level of radioactivity of a sample is often measured in disintegrations per minute (dpm). Suppose I accidentally spilled 800 dpm of tritium from a sample I'm working with onto the lab bench. How long before it goes down to a safer, near-background level of 50 dpm?
answer
800 dpm/2 = 400 dpm (1 half life) 400 dpm/2 = 200 dpm (2 half-lives) 200 dpm/2 = 100 dpm (3 half-lives) 100 dpm/2 = 50 dpm (4 half-lives) 4 half-lives x 12 years/half life = 48 years
question
What is the answer to Life, the Universe, and Everything?
answer
42



