Chapter 28 : medications (II) – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Drug Nomenclature
answer
• Chemical name: identifies drug's atomic and molecular structure • Generic name: assigned by the manufacturer that first develops the drug • Official name: name by which the drug is identified in official publications United States Pharmacopeia (USP) and National Formulary (NF) • Trade name: brand name copyrighted by the company that sells the drug
question
Drug preparations
answer
• Oral - Capsule, pill, tablet, extended release, elixir, suspension, syrup • Topical - Liniment, lotion, ointment, suppository, transdermal patch • Injectable
question
extended release
answer
DONT crush
question
topical meds
answer
- change the location WHY : same place = not proper absorption (could cause redness, swelling)
question
Which type of drug preparation is a medication in a clear liquid containing water, alcohol, sweeteners, and flavor? A. Elixir B. Suspension C. Solution D. Syrup
answer
Answer: A. Elixir rationale: An elixir is a medication in a clear liquid containing water, alcohol, sweeteners, and flavor. A suspension contains finely divided, undissolved particles in a liquid medium. A solution is a drug dissolved in another substance. A syrup is medication combined in a water and sugar solution.
question
Drug Classifications
answer
• Effect on body system (oral VS IV) • Chemical composition () • Clinical indication (USE) or therapeutic action (WHAT DOES IT DO)
question
Pharmacokinetics (Effect of Body on Drug)
answer
• Absorption • Distribution • Metabolism • Excretion
question
Factors Affecting Absorption ofMedications
answer
• Route of administration (speed of ABSORPTION) • Lipid solubility (pt WEIGHT) • pH • Blood flow • Local conditions at the site of administration • Drug dosage
question
Pharmacodynamics (CELLULAR LEVEL)
answer
• Pharmacodynamics is the process by which drugs alter cell physiology and affect the body. • Drugs turn on, turn off, promote, or block responses that are part of the body's processes. • Drug-receptor interaction occurs when the drug interacts with one or more cellular structures to alter cell function. • Drugs may also combine with other molecules in the body to achieve their effect. • Other drugs act on the cell membrane or alter the cellular environment to achieve their effect.
question
Adverse Drug Effects
answer
• Allergic effects: ANAPHYLACTIC reaction --- check for RED band • Drug tolerance -- if pt cant tolerate the drug --> different drug • Toxic effect • Idiosyncratic effect • Drug interactions: antagonistic and synergistic effects
question
Factors Affecting Drug Action
answer
• Developmental considerations (neonate VS old) • Weight • Gender • Genetic and cultural factors • Psychological factors • Pathology • Environment • Timing of administration -- WHY IMPORTANT ------ food in stomach ------ drowsiness ------ diuretic at night ------ 1/2 life ------ Insulin & food ------ frequency : early pain meds request : try diff methods (distractions)
question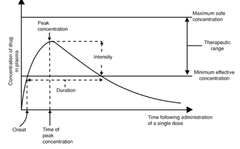
Drug Dose and Serum Drug Levels

answer
• *Therapeutic range*: concentration of drug in the blood serum that produces the desired effect without causing toxicity • *Trough level*: the point when the drug is at its lowest concentration, indicating the rate of elimination • *Half-life*: amount of time it takes for 50% of blood concentration of a drug to be eliminated from the body
question
Types of Medication Orders
answer
• *Standing order* (routine order): - carried out until cancelled by another order - specific procedures - certain meds at certain time - routine orders for unexpected situations • *PRN order*: as needed - only when pt request •* Single or one-time order* - supplements ----pt has low K --> give K+ •*Stat order*: carried out immediately --- call pharmacy
question
Tell whether the following statement is true or false. Only pain medications may be give to patients without a medication order from a licensed practitioner. A. True B. False
answer
Answer: B. False Rationale: No medications may be give to patients without a medication order from a licensed practitioner.
question
Parts of the Medication Order
answer
• Patient's name • Date and time order is written • Name of drug to be administered • Dosage of drug • Route by which drug is to be administered • Frequency of administration of the drug • Signature of person writing the order
question
Medication Supply Systems
answer
• Stock supply (PYXIS) • Individual unit dose supply • Medication cart • Computerized automated dispensing system • Bar code-enabled medication cart (BCMA)
question
In which of the following medication supply systems are large quantities of medications kept on the nursing unit making them immediately available to the nurse? A. Individual supply B. Stock supply C. Unit dose system D. Bar-coded medication cart
answer
Answer: B. Stock supply Rationale: With the stock supply system, large quantities of medications are kept on the nursing unit. The medications are readily available to the nurse, but this eliminates the double-check system by the pharmacy.
question
Controlled Substances Required Information
answer
• Name of patient receiving narcotic • Amount of NARCOTIC used -- witness -------- people may steal it -- dispose extra med in a specific way • Hour narcotic was given • Name of physician prescribing narcotic • Name of the nurse administering narcotic
question
Metric System Conversions
answer
• To convert larger unit to smaller unit, move decimal point to right • To convert smaller unit to larger unit, move decimal point to left - 1 kilogram = 1,000 grams - 1 gram = 1,000 milligrams - 1 milligram = 1,000 micrograms
question
1.5 grams equals how many milligrams? A. 001.5 B. 15 C. 150 D. 1,500
answer
Answer: D. 1,500 Rationale: To convert a larger unit into a smaller unit, move the decimal point to the right (the new number is larger than the original). To convert a smaller unit into a larger unit, move the decimal point to the left (the new number is smaller than the original).
question
Three Checks of Medication Administration
answer
• READ THE LABEL: - When the nurse reaches for the container or unit dose package - After retrieval from the drawer and compared with the CMAR, or compared with the CMAR immediately before pouring from a multidose container - Before giving the unit dose medication to the patient or when replacing the multi-dose container in the drawer or shelf
question
Rights of Medication Administration MAIN : Patients Do Drugs Round The Day
answer
• Right medication • Right patient • Right dosage • Right route • Right time • Right reason OTHER CONSIDERATION: • Right assessment data • Right documentation • Right response • Right to education • Right to refuse
question
Identifying the Patient
answer
• Checking the identification bracelet • Validating the patient's name (FIRST IDENTIFIER) • Validating the patient's identification number, medical record number, and/or birth date (second identifier) • Comparing with the CMAR or MAR ----- VERIFICATION • Asking the patient to state his or her name if possible
question
Oral Medications
answer
• Solid form: tablets, capsules, pills • Liquid form: elixirs, spirits, suspensions, syrups
question
Administration of Oral Medications
answer
• *Oral route*: having patient swallow drug • *Enteral route*: administering drug through an enteral tube ----- TUBE FEEDING ----- Flush the line BEFORE and AFTER ------------ with regular tap water ----- crush the pill , mix w/water, draw up med --> tube • *Sublingual administration*: placing drug under tongue • *Buccal administration*: placing drug between tongue and cheek
question
Administration of Parenteral Medications
answer
• *Subcutaneous injection*: subcutaneous tissue • *Intramuscular injection*: muscle tissue • *Intradermal injection*: corium (under epidermis) • *Intravenous injection*: vein • *Intra-arterial injection*: artery • *Intracardial injection*: heart tissue • *Intraperitoneal injection*: peritoneal cavity • *Intraspinal injection*: spinal canal • *Intraosseous injection*: bone
question
Criteria for Choosing Equipment for Injections
answer
• Route of administration • Viscosity of the solution • Quantity to be administered • Body size • Type of medication
question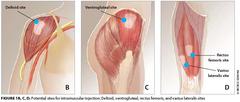
Sites for Intramuscular Injections

answer
• Ventrogluteal site • Vastus lateralis site • Deltoid muscle site • Dorsogluteal site is no longer recommended.
question
Tell whether the following statement is true or false. The recommended intramuscular site for an adult is the vastus lateralis. A. True B. False
answer
Answer: B. False Rationale: The recommended intramuscular site for an adult is the ventrogluteal or deltoid.
question
Preparing Medications for Injection
answer
• Ampules • Vials • Prefilled cartridges or syringes • Mixing medication in one syringe • Mixing insulins in one syringe • Reconstituting powdered medications
question
Intradermal Injections.
answer
• Administered into the dermis, just below the epidermis. • Has the longest absorption time of all parenteral routes. • Used for sensitivity tests and local anesthesia. • Body's reaction to the substances is easily visible. • Sites commonly used are the inner surface of the forearm and the upper back, under the scapula. • A 1/4? to 1/2?, 25- or 27-gauge needle is used and the angle of administration is 5 to 15 degrees. • The dosage given intradermally is small, usually less than 0.5 mL
question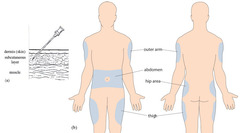
Subcutaneous injections

answer
• Administered into the adipose tissue layer just below the epidermis and dermis. • Various sites used: - Outer aspect of the upper arm - Abdomen (from below the costal margin to the iliac crests) - The anterior aspects of the thigh - The upper back - The upper ventral or dorsogluteal area
question
Intravenous Administration of Medication

answer
• Delivers the drug directly into the bloodstream • Medication has an immediate effect and cannot be recalled or actions slowed • Route most often used in emergency situations
question
Topical Administration of Medications
answer
• Skin applications • Eye instillations and irrigations • Ear instillations and irrigations • Nasal instillations • Vaginal applications • Rectal instillations
question
Medication Errors
answer
• Check patient's condition immediately; observe for adverse effects. • Notify nurse manager and primary care provider. • Write description of error and remedial steps taken on medical record. • Complete form used for reporting errors, as dictated by the facility policy.
question
Type of Medication Errors
answer
• Inappropriate prescribing of the drug • Extra, omitted, or wrong doses • Administration of drug to wrong patient • Administration of drug by wrong route or rate • Failure to give medication within prescribed time • Incorrect preparation of drug • Improper technique when administering drug • Giving drug that has deteriorated
question
Medical Record Documentation
answer
• Name of the medication • Dosage • Route and time of administration • Name of person administering medication • Site used for an injection • Intentional or inadvertently omitted drugs • Refused drugs • Medication errors
question
Patient Teaching
answer
• Review techniques of medication administration. • Remind the patient to take the medication as prescribed for as long as prescribed. • Instruct the patient not to alter dosages without consulting a physician. • Caution the patient not to share medications.



