Local Anesthesia Review – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Absolute MRD: 90 mg (10 carps) Onset: 6-10 mins Pulpal Anesthesia: 90-180 mins Contraindications: children, geriatric, people w/mental or physical disabilities. Indications: long apt, pulpal anesthesia for more than 90 mins, post op pain management. Caution: compromised cardiovascular system.

answer
0.5% Bupivacaine 1:200,000 epi
question
MRD (mg/lb): 3.0 MRD (mg/kg): 6.6 Absolute MRD: 400 mg (7.5 carps) Onset: 1.5-2 mins Pulpal Anesthesia: 20-40 mins Indications: children, geriatric, bisulfate allergy

answer
3% Mepivacaine plain
question
MRD (mg/lb): 3.0 MRD (mg/kg): 6.6 Absolute MRD: 400 mg (11 carps) Onset: 1.5-2 mins Pulpal Anesthesia: 60 mins Contraindications: cardiovascular disease (ASA III-IV), hyperthyroidism, tricyclic antidepressants.

answer
2% Mepivacaine 1:20,000 levo
question
MRD (mg/lb): 3.2 MRD (mg/kg): 7 Absolute MRD: 500 mg (6 carps) Onset: 2-3 mins Pulpal Anesthesia: 60 mins Contraindications: non-selective Beta blockers, cardiovascular disease (ASA III-IV), hyperthyroidism.

answer
2% Lidocaine 1:50,000 epi
question
MRD (mg/lb): 3.2 MRD (mg/kg): 7 Absolute MRD: 500 mg (11 carps) Onset: 2-3 mins Pulpal Anesthesia: 60 mins Contraindications: bisulfite allergy, non-selective beta blockers. Indications: drug of choice for pregnancy.

answer
2% Lidocaine 1:100,000 epi
question
MRD (mg/lb): 3.6 mg MRD (mg/kg): 8 mg Absolute MRD: 600 mg (8 carps) Onset: 2-4 mins Pulpal Anesthesia: Infiltrate: 10-15 mins; Block: 40-60 mins Contraindications: methemoglobinemia, APAP sulfonamides, nitrates, hypoxic cardiac/respiratory failure, anemia. Indications: bisulfate allergy, drug of choice for epi sensitive pts requiring more than 60 mins pulpal anesthesia (rapid bio-transformation- low toxicity). Caution: paresthesia (esp lingual nerve).

answer
4% Prilocaine plain
question
MRD (mg/lb): 3.6 mg MRD (mg/kg): 8 mg Absolute MRD: 600 mg (8 carps) Onset: 2-4 mins Pulpal Anesthesia: 60-90 mins Contraindications: methemoglobinemia, APAP sulfonamides, nitrates, hypoxic cardiac/respiratory failure, anemia. Indications: bisulfate allergy, drug of choice for epi sensitive pts requiring more than 60 mins pulpal anesthesia (rapid bio-transformation- low toxicity), cardiovascular disease, brittle diabetics. Caution: paresthesia (esp lingual nerve).

answer
4% Prilocaine 1:200,000 epi
question
MRD (mg/lb): 3.2 mg MRD (mg/kg): 7 mg Absolute MRD: based on pt weight (11 carps based on epi). Onset: Infiltrate: 1-2 mins; Block: 2-3 mins Pulpal Anesthesia: 75 mins Contraindications: bisulfite and Ester allergies Indications: nursing mothers, liver disease. Caution: paresthesia (esp lingual nerve), liver disease, cardiovascular disease, breastfeeding mothers, children under 4 yrs.

answer
4% Articaine 1:100,000 epi
question
MRD (mg/lb): 3.2 mg MRD (mg/kg): 7 mg Absolute MRD: based on pt weight (22 carps based on epi). Onset: Infiltrate: 1-2 mins; Block: 2-3 mins Pulpal Anesthesia: 45 mins Contraindications: bisulfite and Ester allergies Indications: nursing mothers, liver disease. Cautions: paresthesia (esp lingual nerve), liver disease, cardiovascular disease, breastfeeding mothers, children under 4 yrs.

answer
4% Articaine 1:200,000 epi
question
Trade name for Lidocaine- "the OCTOpus has a long arm SPAN so he can play the XYLOphone"

answer
Xylocaine
question
Trade name for Lidocaine

answer
Octocaine
question
Trade name for Lidocaine- "arm span"

answer
Lignospan
question
Trade name for Mepivacaine- "Mepivacaine is a photographer that takes scandalous POLaroid Pics"

answer
Polocaine
question
Trade name for Mepivacaine- "Mepivacaine is a photographer that takes scandalous polaroid pIcs"

answer
Isocaine
question
Trade name for Mepivacaine- "Mepivacaine is a photographer that takes scandalous polaroid piCs"

answer
Carbocaine
question
Trade name for Mepivacaine- "Mepivacaine is a photographer that takes SCANDalous polaroid picS"

answer
Scandonest
question
Trade name for Prilocaine plain- "I'm going to PRY the NEST out of the big (FORTE) tree"

answer
Citanest
question
Trade name for Prilocaine w/epi- "I'm going to PRY the NEST out of the big (FORTE) tree"

answer
Citanest Forte
question
Trade name for Articaine- "ARTI has a ScEPTer"

answer
Septocaine
question
Bupivacaine- " MARC and Viv like to BUP each other on the nose."
answer
Marcaine
question
Bupivacaine- "Marc and VIV like to BUP each other on the nose."
answer
Vivacaine
question
Trade name for Articaine- "ARTI likes to dress up like ZORO"
answer
Zorocaine
question
Slowly injecting the LA solution
answer
What is the most important step in preventing a local anesthetic overdose?
question
9 mg
answer
How many milligrams of a local anesthetic is in a full 0.5% solution carpule?
question
36 mg
answer
How many milligrams of a local anesthetic is in a full 2% solution carpule?
question
54 mg
answer
How many milligrams of a local anesthetic is in a full 3% solution carpule?
question
72 mg
answer
How many milligrams of local anesthetic is in a full 4% solution carpule?
question
Mepivacaine and Prilocaine (weakest).
answer
Which local anesthetics are weak vasodilators?
question
Procaine. Later named Novocaine when it came out in the US.
answer
What was the first local anesthetic?
question
Pregnancy (1:100,000 epi), methemoglobinemia, and ester allergies.

answer
What is Lidocaine the drug of choice for?
question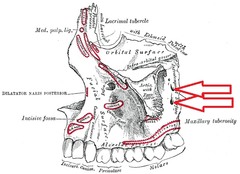
The height of the mucobuccal fold, over the distobuccal root/cusp of the maxillary 2nd molar.

answer
What are the landmarks for administering a PSA nerve block?
question
pKa. The higher the pKa, the longer, or slower the onset. The lower the pKa, the faster the onset.
answer
What affects the onset of the local anesthetic?
question
The lipid solubility (how many LA molecules can go through the nerve membrane)
answer
What affects the potency of the local anesthetic?
question
BisulFITE allergy, recent coronary bypass, heart attack or stroke within 6 mos, uncontrolled high BP/diabetes/hyperthyroidism, daily angina.
answer
Absolute contraindications for vasoconstrictors
question
Controlled hyperthyroidism/diabetes/high BP, tricyclics antidepressants (do NOT use levonordefrin), non selective beta blockers, glaucoma, cocaine abuse (do NOT use LA if used cocaine in last 24hrs)
answer
Relative contraindications for vasoconstrictors. (Use cardiac dose)
question
Children, geriatric or mental/physical disorder patients
answer
Contraindications for Bupivacaine
question
Cardiovascular disease (ASA 3-4), hyperthyroidism and tricyclic antidepressants due to Levo.
answer
Contraindications for 2% Mepivacaine 1:20,000 Levo
question
Nonselective beta blockers, bisulfATE allergy, hyperthyroidism (1:50,000 epi), cardiovascular disease (1:50,000 epi)
answer
Contraindications for Lidocaine
question
Methemoglobinemia, APAP sulfonamides, Nitrates, hypoxic cardiac/respiratory failure, hemoglobinopathies. Caution: paresthesia, esp for lingual nerve (IA injection)
answer
Contraindications for Prilocaine
question
Ester allergies, bisulfITE allergy. Caution: paresthesia, esp lingual nerve (IA injection)
answer
Contraindications for Articaine
question
True. Amides rare, esters more common.
answer
True or false? Allergies to amides are rare.
question
Esters. (pseudo-cholinESTERase) administer with caution.
answer
What is a relative contraindication for atypical pseudo-cholinesterase?
question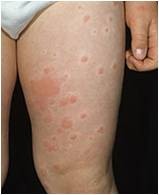
It is NOT dose dependent (can have reaction no matter how much local anesthetic given). Develop rash/hives (aka wheals), localized swelling, wheezing, dyspnea (difficulty breathing)

answer
Allergic reactions to local anesthesias
question
Administer antihistamine, sit upright. If anaphylactic Pt will have respiratory distress and will need to administer epinephrine and oxygen.

answer
Treatment for allergic reaction to local anesthesia
question
Talkative, apprehension, excitable, slurred speech, nystagmus, sweating, vomiting, increased BP/heart rate/respiration, metallic taste, bilateral numbness of tongue.
answer
Symptoms of minimal-moderate LA overdose
question
Tonic clinic seizure followed by CNS depression, decreased BP/heart rate/respiration.
answer
Moderate-high LA overdose symptoms
question
Pallor, dizziness, weakness, nausea, THROBBING headache, anxiety, tremor, heart palpitations, increased heart rate/BP (sharp rise in systolic BP)

answer
Symptoms of vasoconstrictor overdose
question
Stop injection, keep in supine position, loosen clothing, reassure patient, monitor vitals, administer oxygen, 911 if patient goes into seizure, CPR if needed, if seizure lasts more than 5 mins administer IV diazepam.
answer
Treatment of LA overdose
question
Terminate procedure, sit patient erect, reassure patient, monitor vitals, administer oxygen, CPR, call 911 if symptoms last more than 5 mins.
answer
Treatment of vasoconstrictor overdose
question
Limited opening of the jaw

answer
What is Trismus?
question
Muscle trauma on injection (happens most to medial pterygoid), low grade infection in injection area, multiple needle penetrations in area, hemorrhage (happens with hematoma)
answer
What causes Trismus?
question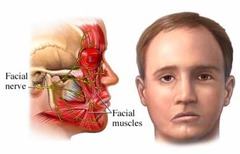
Injecting into the parotid gland and hitting the facial nerve (cranial nerve VII)

answer
What causes facial paralysis?
question
Rapid injection of solution, low pH of LA (contains vasoconstrictor), contaminated solution.
answer
What causes a burning sensation upon injection?
question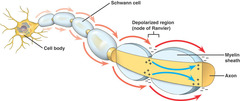
Rapid transmission of nerve impulses along a myelinated nerve fiber that jumps along the nodes of ranvier.

answer
What is saltatory conduction?
question
Anterior and medial to IA
answer
Where is the lingual nerve in relation to the IA nerve?
question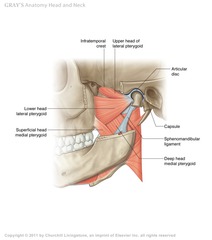
Medial to the lateral pterygoid muscle,

answer
Where is the IA nerve
question
Milligrams: 0.9-1.8, Carpules: 1/2 to 1
answer
Recommended amount of LA given for a posterior superior alveolar (PSA) injection
question
Milligrams: 0.9-1.2, Carpule: 1/2-3/4
answer
Recommended amount of LA given for a middle superior alveolar (MSA) injection
question
Milligrams: 0.9-1.2, Carpule: 1/2-3/4
answer
Recommended amount of LA given for an anterior superior alveolar (ASA) injection
question
Milligrams: 0.45-0.6, Carpule: 1/4-1/3
answer
Recommended amount of LA given for a greater palatine (GP) injection
question
Milligrams: 0.45, Carpule: 1/4
answer
Recommended amount of LA given for a nasopalatine (NP) injection
question
Milligrams: 0.6, Carpule: 1/3
answer
Recommended amount of LA given for a supraperiosteal/infiltration injection
question
Milligrams: 1.5, Carpule: 5/6
answer
Recommended amount of LA given for an inferior alveolar (IA) injection
question
Milligrams: 0.3, Carpule: 1/6
answer
Recommended amount of LA given for a long buccal (LB) injection
question
Milligrams: 0.6, Carpule: 1/3
answer
Recommended amount of LA given for a mental (M) injection
question
Milligrams: 0.6-0.9, Carpule: 1/3-1/2
answer
Recommended amount of LA given for an incisive (IN) injection
question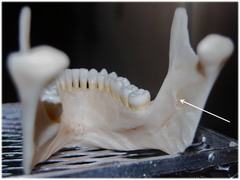
Superior to mandibular foramen (most common cause of LA failure is being too inferior to the nerve, so must be superior.)

answer
Where is the target site for the needle in an inferior alveolar nerve block?
question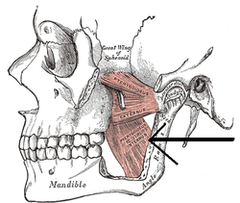
The medial pterygoid.

answer
What muscle is penetrated during the inferior alveolar nerve block?
question
Immediately after a stimulus has initiated an action potential, a nerve is unable to respond to another stimulus regardless of its strength.
answer
Absolute refractory period
question
1-2 mins
answer
What is the minimum length of time it should take to administer one cartridge of a local anesthetic solution?
question
1-Remain calm, do not panic 2- Have patient remain open 3- If needle is visible, remove with hemostats/cotton pliers. 3a- If not, DO NOT probe for fragment or make an incision to find it. b- Calmly inform patient and attempt to allay fear and apprehension. c- Refer patient to an oral surgeon. d- Note incident in patient's records, keep remaining needle fragment and inform your insurance carrier (prepare for litigation).

answer
What should you do if a needle breaks while giving an injection?
question
Depolarization phase (this is the phase before an impulse is fired)
answer
What stage of a nerve impulse conduction does a local anesthetic take effect?
question
Sodium bisulFITE (commonly causes allergic reactions- esp in asthma patients)
answer
Preservative added to vasoconstrictors
question
0.09 mg (1.8 x 0.05 mg/ml)
answer
Milligrams of epinephrine in a full 1:20,000 solution cartridge
question
0.036 mg (1.8 x 0.02 mg/ml)
answer
Milligrams of epinephrine in a full 1:50,000 solution cartridge
question
0.018 mg (1.8 x 0.01 mg/ml)
answer
Milligrams of epinephrine in a full 1:100,000 solution cartridge
question
0.009 mg (1.8 x 0.005 mg/ml)
answer
Milligrams of epinephrine in a full 1:200,00 solution cartridge
question
Decreases the possibility of a toxic adverse reaction by decreasing systemic uptake. Lowers PH.
answer
The effect vasoconstrictors have on local anesthetics
question
Lateral to the pterygomandibular raphe, medial to the internal oblique ridge, at the height of the coronoid notch.
answer
Site of injection for an IA nerve block
question
Atypical plasma cholinesterase
answer
Contraindication for esters
question
The cartridge was frozen. (small bubbles normal from manufacture, large bubbles mean LA contaminated and if stopper is extruded it means LA was frozen).
answer
A large bubble (>2mm) and an extruded stopper on a local anesthetic cartridge most likely means
question
3 cartridges. (4 will elicit the response. Give 3 as to not actually elicit response).
answer
Epinephrine produces an elevation in blood sugar levels. How many cartridges can be safely given before this response is elicited?
question
Maxillary canines to the centrals on injected side, and facial tissue in that area. (May innervate the maxillary premolars and the mesiobuccal root of the 1st molar if MSA not present).
answer
The ASA nerve innervates
question
Maxillary premolars, and sometimes the mesiobuccal root of the 1st molar. Also buccal tissue in that area.
answer
The MSA nerve (when present- 50-72% missing) innervates
question
Maxillary molars and the buccal tissue in that area. (Mesiobuccal root of 1st molar may not be innervated due to innervation of MSA nerve).
answer
The PSA nerve innervates
question
All mandibular teeth in quadrant, buccal mucosa from the premolars to the midline, floor of mouth and 1/2 of tongue on quadrant side.
answer
The IA nerve innervates
question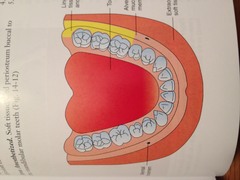
Buccal mucosa of mandibular molars.

answer
The long buccal nerve innervates
question
The buccal tissue of the mandibular premolars to the midline on side of injection.
answer
The mental nerve innervates
question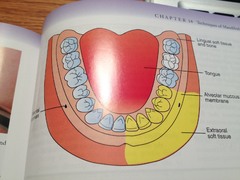
Mandibular premolars to the midline on side of injection and skin of the lower lip and chin from the mandibular premolars to the midline.

answer
The incisive nerve innervates
question
High pH, high protein binding , lower concentration of anesthetic agent.
answer
Articaine may be more effective than other anesthetics due to what characteristics?
question
0.04mg (1/5 healthy dose)
answer
Cardiac dose for epinephrine
question
0.2 mg
answer
MRD of epinephrine for healthy patient
question
1.0 mg (11 carps)
answer
MRD of Levonordefrin for healthy patient
question
0.2 mg (2 carps)
answer
Cardiac dose for Levonordefrin
question
Upper respiratory infection
answer
Absolute contraindications for nitrous oxide
question
A myocardial depression
answer
The direct action of local anesthetics on the myocardium is:
question
60 mins
answer
Pulpal anesthesia for 2% Mepivacaine 1:200,000 Levo
question
Infiltration: 5-10 mins Block: 20-40 mins
answer
Pulpal anesthesia for 3% Mepivacaine plain
question
60 mins
answer
Pulpal anesthesia for 2% Lidocaine 1:50,000 epi
question
60 mins
answer
Pulpal anesthesia for 2% Lidocaine 1:100,000 epi
question
Infiltration: 10-15 mins Block: 40-60 mins
answer
Pulpal anesthesia for 4% Prilocaine plain
question
60-90 mins
answer
Pulpal anesthesia for 4% Prilocaine 1:200,000 epi
question
75 mins
answer
Pulpal anesthesia for 4% Articaine 1:100,000 epi
question
45 mins
answer
Pulpal anesthesia for 4% Articaine 1:200,000 epi
question
90-180 mins
answer
Pulpal anesthesia for 0.5% Bupivacaine 1:200,000 epi
question
A-delta and C
answer
Nerve fibers involved in dentistry
question
A higher concentration means more base molecules, and more base molecules are needed to diffuse through mucous membranes (ex. 20% Benzocaine vs 4% anesthetic solution)
answer
Why are topical anesthetics manufactured in higher concentrations than local anesthetics?
question
1.8 ml
answer
Milliliters in 1 full cartridge of a LA
question
0.9 ml
answer
Milliliters in 1/2 a cartridge of a LA
question
0.45 ml
answer
Milliliters in 1/4 cartridge of a LA
question
0.6 ml
answer
Milliliters in 1/3 cartridge of a LA
question
1.2 ml
answer
Milliliters in 2/3 cartridge of a LA
question
1.4 ml (1.35 ml to be exact)
answer
Milliliters in 3/4 cartridge of a LA
question
0.2 ml
answer
Milliliters in 1 "stopper full" (1/9) of a cartridge of a LA
question
Palatal tissue from canine of one side, to the canine of the other, and the anterior 1/3 of the hard palate.
answer
The Nasopalatine nerve innervates
question
1:50,000 epi 4% LA solution- reduce dose to half.
answer
What anesthetic and vasoconstrictor concentrations should be avoided with palatal injections?
question
Bilateral maxillary centrals, laterals and canines- to a lesser degree, facial and palatal tissues in area but NOT lip (Good for cosmetics).
answer
Palatal ASA (P-ASA) nerve block anesthetizes:
question
Maxillary premolars to incisors, and buccal and palatal tissues in area. Facial and lip tissue NOT anesthetizes- good for cosmetics.
answer
Anterior MSA (A-MSA) nerve block anesthetizes:
question
Medial to canine eminence, at height of mucobuccal fold. Insert needle 6mm. Deposit 1/2-3/4 carp over 30-40 secs.
answer
Injection technique for ASA
question
Between roots of premolars at height of mucobuccal fold. Insert needle 6mm towards apex of 2nd premolar. Deposit 1/2-3/4 carp over 30-40 secs.
answer
Injection technique for MSA (absent in 50-72% of population)
question
Distobuccal root of 2nd molar at height of mucobuccal fold. Insert needle 16mm in 45•, 45•, 45• direction (Barrel of syringe in corner of mouth, aligned with ala of the nose and pointing towards opposite corner of head- think of head as a cube). Deposit 1/2-1 carp over 30-60 mins.
answer
Injection technique for PSA
question
(Child's weight/150) x MRD
answer
Clark's rule
question
(MRD x child's age)/12+child's age
answer
Young's rule
question
The lipophilic portion allows the solution to diffuse through the nerve membrane. The hydrophilic portion allows the solution to diffuse through the interstitial tissue.
answer
Hydrophilic and lipophilic portions of local anesthetics
question
Absence of pain sensation only
answer
Analgesia
question
Loss of pain, touch, temperature and pressure.
answer
Anesthesia
question
1800-2100 psi
answer
What is the pressure in a full tank of oxygen?
question
650-900 psi
answer
What is the pressure in a full tank of nitrous oxide?
question
900-1100 psi
answer
What is the pressure in half a tank of oxygen?
question
650-900 psi (nitrous gauge does not accurately show level of nitrous in tank, but does in oxygen)
answer
What is the pressure in half a tank of nitrous oxide?



