NU275 Kaplan Review – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Anemia
answer
A condition in which the blood doesn't have enough healthy red blood cells.
question
Signs & Symptoms of Anemia
answer
dizziness, fatigue, lightheadedness, malaise, or weakness Tachycardia, palpitations brittle nails, headache, pallor, or shortness of breath
question
Treatment for Anemia
answer
Treatment depends on the underlying diagnosis. Iron supplements may be used for iron deficiency. Vitamin B supplements maybe used for low vitamin levels. Blood transfusions may be used for blood loss. Medications to induce blood formation may be used if the body's blood production is reduced.
question
Atherosclerosis
answer
The build-up of fats, cholesterol & other substances in and on the artery walls.
question
Signs & Symptoms of Atherosclerosis
answer
Atherosclerosis often has no symptoms until a plaque ruptures or the buildup is severe enough to block blood flow. People may experience: Pain the leg while exercising, erectile dysfunction, heart attack, mini-strokes (transient ischemic attacks), poor wound healing, or stroke
question
Treatment for Atherosclerosis
answer
A healthy diet and exercise can help. Treatments include medications, procedures to open blocked arteries and surgery. diet: LESS fat, sugar, red meat MORE fruit veggies, white meat, fish Medications: Statin, Blood thinners, and Cholesterol medication Medical procedure: Coronary stent Angioplasty Surgery Coronary artery bypass surgery Carotid endarterectomy
question
Peripheral vascular disease
answer
A circulatory condition in which narrowed blood vessels reduce blood flow to the limbs.
question
Symptoms of Peripheral Vascular Disease
answer
Symptoms may include leg pain, particularly when walking. People may experience: Pain areas in the buttocks, pain can occur in the leg and improved with rest or in the leg while exercising, cool skin, loss of hair on the legs, thinning of skin on the legs, or ulcers
question
Treatment for Peripheral Vascular Disease
answer
Self Care: Physical exercise, Quitting smoking, and Heart-Healthy diet Medications: Statin, Vasodilator, and Blood thinners Medical Procedure: Angioplasty
question
Liver Cancer (Hepatic Cancer)
answer
Cancer that begins in the cells of the liver.
question
Symptoms of Liver Cancer
answer
Symptoms are uncommon in the early stages of liver cancer. Later, symptoms may include weight loss, belly pain, bloating, fluid in abdomen, nausea, vomiting, & yellowed skin and eyes. Also cancer-related fatigue, loss of appetite, itching.
question
Treatment for Liver Cancer
answer
Medications: Chemotherapy Medical procedure Cryoablation, Percutaneous ethanol injection, Embolization, Transarterial chemoembolization, Sir-Spheres, and Radiofrequency ablation Surgery: Liver transplantation Hepatectomy
question
Cardiomyopathy
answer
An acquired or hereditary disease of the heart muscle.
question
Signs & Symptoms of Cardiomyopathy
answer
Symptoms include breathlessness, swollen legs and feet, and a bloated belly. Also: Pain in the chest, dizziness, fatigue, or loss of appetite, abnormal heart rhythm, tachycardia, or murmur, bloating or fluid in the abdomen. Also common: coughing, shortness of breath, swelling in extremities, or weight gain
question
Treatment for Cardiomyopathy
answer
Treatment consists of ace inhibitors and diuretics,drugs, implanted devices, surgery, and in severe cases, a transplant Medications: Blood thinners, Beta blocker, ACE inhibitor, Diuretic, Antihypertensive drug, Statin, and Antiarrhythmic agent Medical Procedure: Cardiac catheterization and Revascularization Surgery: Coronary artery bypass surgery and Heart transplant Devices: Pacemaker and Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator
question
Goiter
answer
Abnormal enlargement of thyroid
question
Signs and Symptoms of Goiter
answer
Lump or swelling in neck, and cough. Rarely, throat tightness or trouble breathing, coughing, tachycardia, heat intolerance, shortness of breath, underactive thyroid, or weight gain
question
Treatment for Goiter
answer
A small goiter that doesn't cause symptoms may not need treatment. Sometimes, medication or surgery. Medication: Antithyroid agent Hormone therapy Medical Procedure: Radioactive iodine therapy Surgery: Thyroid removal Partial thyroidectomy
question
Embolic stroke
answer
A blockage of blood supply to part of the brain caused by a clot or debris (embolus).
question
Symptoms of Embolic Stroke
answer
Symptoms include trouble walking, speaking, and understanding. Paralysis or numbness of the face, arm, or leg also may occur. People may experience: Muscular: weakness, problems with coordination, stiff muscles, weakness of one side of the body, or paralysis of one side of the body Cognitive: altered LOC, inability to recognize half of one's visual field (hemispatial neglect), inability to speak or understand, or mental confusion Visual: blurred vision, sudden visual loss, temporary loss of vision in one eye, or vision disorder Whole body: dizziness, fainting, or feeling faint Sensory: leg numbness, pins and needles, or reduced sensation of touch Speech: difficulty speaking, slurred speech, or impaired voice Facial: muscle weakness or numbness Also common: difficulty swallowing, limping, nausea, sleepiness, unsteadiness, weakness of limb, or difficulty raising the foot
question
Treatment for Embolic Stroke
answer
Treatment consists of blood thinners and clot busting medications Emergency treatment includes medications or a procedure to break up clots. Medications: Tissue plasminogen activator, Blood thinners, and Antihypertensive drug Surgery: Embolectomy Therapies: Stroke rehabilitation Medical Procedure: Left atrial appendage occlusion Supportive Care: IV fluids
question
Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH)
answer
Bleeding in the space between the brain and the tissue covering the brain.
question
Signs & Symptoms of Subarachnoid hemorrhage
answer
The main symptom is a sudden, severe headache. People may experience: double vision, sensitivity to light, or vision loss, nausea or vomiting, abnormal heart rhythm, altered LOC, coma, fainting, seizures, stiff neck, or weakness of one side of the body
question
Treatment for Subarachnoid hemorrhage
answer
Treatment depends on severity Hospital care is needed for supportive care and to stop bleeding and limit brain damage. Treatment may include surgery or catheter-based therapy. Medical Procedure: Endovascular coiling and Clipping Medications: Antihypertensive drug, Diuretic, and Anticonvulsant Surgery: Ventriculostomy and Craniotomy Supportive Care: Iv Fluids
question
Parkinson's disease
answer
A disorder of the central nervous system that affects movement, often including tremors.
question
Signs and Symptoms of Parkinson's disease
answer
Parkinson's often starts with a tremor in one hand. Other symptoms are slow movement, stiffness, and loss of balance. People may experience: Tremor: can occur at rest, in the hands, limbs, or can be postural Muscular: stiff muscles, difficulty standing, difficulty with bodily movements, involuntary movements, muscle rigidity, problems with coordination, rhythmic muscle contractions, slow bodily movement, or slow shuffling gait Sleep: early awakening, nightmares, restless sleep, or sleep disturbances Whole body: fatigue, dizziness, poor balance, or restlessness Cognitive: amnesia, confusion in the evening hours, dementia, or difficulty thinking and understanding Speech: impaired voice, soft speech, or voice box spasms Mood: anxiety or apathy Nasal: distorted sense of smell or loss of smell Urinary: dribbling of urine or leaking of urine Facial: jaw stiffness or reduced facial expression Also common: blank stare, constipation, daytime sleepiness, depression, difficulty swallowing, drooling, falling, fear of falling, limping, loss in contrast sensitivity, neck tightness, small handwriting, trembling, unintentional writhing, or weight loss
question
Treatment for Parkinson's disease
answer
Treatment consists of medications to increase dopamine Medications: Dopamine promoter, Antidepressant, Cognition-enhancing medication, and Anti-Tremor Selfcare: Physical Exercise
question
Spinal cord injury
answer
Damage to any part of the spinal cord or nerves at the end of the spinal canal.
question
Signs and Symptoms of Spinal cord injury
answer
A spinal cord injury often causes permanent loss of strength, sensation, and function below the site of the injury. People may experience: Muscular: muscle weakness, problems with coordination, stiff muscles, muscle spasms, or overactive reflexes Whole body: feeling faint or sweating Sensory: reduced sensation of touch or pins and needles Urinary: leaking of urine or urinary retention Also common: abnormal and painful sensation, leaking of stool, or shortness of breath
question
Treatment for Spinal cord injury
answer
Treatment depends on severity Rehabilitation and assistive devices allow many people with spinal cord injuries to lead productive, independent lives. Treatments include drugs to reduce symptoms and surgery to stabilize the spine. Supportive care Mouth-To-Mouth resuscitation Medications Steroid, Blood pressure support, and Muscle relaxant Surgery: Spinal Surgery Therapies Rehabilitation and Hydrotherapy Medical procedure Urinary catheterization and Traction
question
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
answer
A disease in which the immune system eats away at the protective covering of nerves.
question
Signs and Symptoms of Multiple Sclerosis
answer
Multiple sclerosis causes many different symptoms, including vision loss, pain, fatigue, and impaired coordination. Pain areas: in the back or eyes Pain circumstances: can occur in the back due to head nod or with eye movement Tremor: can occur during precise movements, in the hands, or limbs Muscular: cramping, inability to rapidly change motions, involuntary movements, muscle paralysis, muscle rigidity, muscle weakness, problems with coordination, stiff muscles, clumsiness, muscle spasms, or overactive reflexes Whole body: fatigue, dizziness, heat intolerance, poor balance, vertigo, or weakness Sensory: pins and needles, abnormality of taste, reduced sensation of touch, or uncomfortable tingling and burning Urinary: excessive urination at night, leaking of urine, persistent urge to urinate, or urinary retention Visual: blurred vision, double vision, or vision loss Sexual: erectile dysfunction or sexual dysfunction Mood: anxiety or mood swings Speech: slurred speech or impaired voice Also common: constipation, depression, difficulty swallowing, difficulty thinking and understanding, flare, headache, heavy legs, limping, numbness of face, rapid involuntary eye movement, sleep deprivation, tongue numbness, or difficulty raising the foot
question
Treatment for Multiple Sclerosis
answer
Treatment consists of immunosuppressants Physical therapy and medications that suppress the immune system can help with symptoms and slow disease progression. Medications Immunosuppressive drug and Steroid Therapies Counseling, Support group, Physical therapy, and Acupuncture Selfcare Physical exercise
question
Sleep apnea
answer
A potentially serious sleep disorder in which breathing repeatedly stops and starts.
question
Signs and Symptoms for Sleep apnea
answer
Symptoms include snoring loudly and feeling tired even after a full night's sleep. People may experience: Excessive daytime sleepiness, insomnia, nightmares, sleep deprivation, , episodes of no breathing, breathing through the mouth, or loud breathing, depression, dry mouth, dry throat, fatigue, headache, irritability, mood swings, or weight gain
question
Treatment for Sleep apnea
answer
Treatment consists of weight loss exercise, and the use of a breathing assistance device at night, such as a continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machine & air way management. If needed surgery, tonsillectomy, Adenoid removal, and Palatoplasty.
question
Asthma (bronchial asthma)
answer
A condition in which a person's airways become inflamed, narrow and swell, and produce extra mucus, which makes it difficult to breathe.
question
Signs and Symptoms of Asthma
answer
Difficulty breathing, chest pain, cough, and wheezing. The symptoms may sometimes flare-up. People may experience: Cough: can occur at night, during exercise, can be chronic, dry, with phlegm, mild, or severe Respiratory: difficulty breathing, wheezing, breathing through the mouth, fast breathing, frequent respiratory infections, rapid breathing, or shortness of breath at night Also common: chest tightness, flare, anxiety, early awakening, fast heart rate, or throat irritation
question
Treatment for Asthma
answer
Treatment consists of self care and bronchodilators Asthma can usually be managed with rescue inhalers to treat symptoms (albuterol) and controller inhalers that prevent symptoms (steroids). Severe cases may require longer-acting inhalers that keep the airways open (formoterol, salmeterol, tiotropium), as well as oral steroids. Medications: Bronchodilator, Steroid, and Anti-Inflammatory Self Care Quitting Smoking Supportive care Oxygen therapy
question
Tuberculosis
answer
Tuberculosis (TB) Infection caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Acid fast bacillus. Infectious disease Highly contagious Immunocompromised-HIV
question
Signs and symptoms & treatment of tuberculosis
answer
Clinical manifestations: Dyspnea, chest pain, hemoptysis Treatment: Long term antibiotics
question
Rheumatoid Arthritis:
answer
Inflammatory joint disease Autoimmune destruction to synovial membrane and joints Systemic disease that affects the heart, lungs, kidneys, skin, as well as the joints
question
CM Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
answer
Symmetric joint swelling, joint deformities Rheumatoid nodules in organs Caplan syndrome Autoantibodies RF Significantly more specific serum marker, anticitrullinated protein antibody (ACPA) Present for years to decades before synovial or radiographic changes become apparent Evaluation (four or more of the following) Morning joint stiffness lasting at least 1 hour Arthritis of three or more joint areas Arthritis of the hand joints Symmetric arthritis Rheumatoid nodules Abnormal amounts of serum RF Radiographic changes
question
Treatment for Rheumatoid Arthritis
answer
¥ Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) such as methotrexate (MTX, first line), azathioprine, sulfasalazine, hydroxychloroquine, leflunomide, and cyclosporine ¥ Biological DMARDs (bDMARDs): Medications affect specific processes in the development of RA: Tumor necrosis factor inhibitors ¥ Monoclonal antibodies ¥ Education ¥ Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), glucocorticoids, intraarticular steroid injections ¥ Physical and occupational therapy with therapeutic exercise and use of assistive devices ¥ Surgery: Synovectomy or joint replacement
question
HIV/AIDS (Also called: human immunodeficiency virus, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome)
answer
HIV causes AIDS and interferes with the body's ability to fight infections.
question
Signs and Symptoms of AIDS
answer
Within a few weeks of HIV infection, flu-like symptoms such as fever, sore throat, and fatigue can occur. Then the disease is usually asymptomatic until it progresses to AIDS. AIDS symptoms include weight loss, fever or night sweats, fatigue, and recurrent infections. People may experience: Pain areas: in the abdomen Pain can occur while swallowing Cough: can be dry Whole body: fatigue, fever, loss of appetite, malaise, night sweats, or sweating Gastrointestinal: nausea, persistent diarrhea, vomiting, or watery diarrhea Mouth: ulcers or white tongue Groin: sores or swelling Throat: difficulty swallowing or soreness Also common: opportunistic infection, headache, oral thrush, pneumonia, red blotches, severe unintentional weight loss, skin rash, or swollen lymph nodes
question
Treatment for AIDS
answer
Treatment consists of Medications: HIV antiviral and Enzyme replacement therapy No cure exists for AIDS, but strict adherence to anti-retroviral regimens (ARVs) can dramatically slow the disease's progress as well as prevent secondary infections and complications.
question
Chronic renal (kidney) failure (CKD)
answer
Longstanding disease of the kidneys leading to renal failure.
question
Signs and Symptoms of Chronic renal failure
answer
Symptoms develop slowly and aren't specific to the disease. Some people have no symptoms at all and are diagnosed by a lab test. Whole body: fatigue, high blood pressure, loss of appetite, malaise, or water-electrolyte imbalance Also common: kidney damage, abnormal heart rhythm, failure to thrive, fluid in the lungs, insufficient urine production, itching, kidney failure, severe unintentional weight loss, or swelling
question
Treatment for Chronic renal failure
answer
Treatment depends on severity Medications help manage symptoms. In later stages, filtering the blood with a machine (dialysis) or a transplant may be needed. Medical Procedure: Peritoneal dialysis, Hemofiltration, and Dialysis Self Care Low Protein Diet Medications Vitamin, Calcium reducer, Bone marrow stimulant, Diuretic, and Dietary supplement Surgery: Kidney Transplantation
question
Renal calculi (Kidney Stones, Also called: nephrolithiasis)
answer
A small, hard deposit that forms in the kidneys and is often painful when passed.
question
Signs and Symptoms of Renal calculi
answer
The most common symptom is severe pain, usually in the side of the abdomen, that's often associated with nausea. Pain areas: in the back or side part of the body Pain types: can be severe or sharp Pain circumstances: can occur during urination Gastrointestinal: nausea or vomiting Urinary: blood in urine or frequent urination Also common: acute abdomen or sweating
question
Treatment for Renal Calculi
answer
Treatment consists of fluids and urinary retention medications Treatment includes pain relievers and drinking lots of water to help pass the stone. Medical procedures may be needed to remove or break up larger stones. Supportive care Monitoring for changes or improvement, IV fluids, and Increase fluid intake Medications Urinary retention medication, Narcotic, Nonsteroidal anti-Inflammatory drug, and Diuretic Medical procedure Extracorporeal shockwave therapy, Ureteroscopic stone removal, and Laser lithotripsy
question
Acute Renal (Kidney) Failure (ARF)
answer
A condition in which the kidneys suddenly can't filter waste from the blood.
question
Signs and Symptoms of Acute Renal (Kidney) Failure (ARF)
answer
Decreased urinary output, swelling due to fluid retention, nausea, fatigue, and shortness of breath. Sometimes symptoms may be subtle or may not appear at all. Also: water-electrolyte imbalance, insufficient urine production or urinary retention, too much acid in blood and tissues
question
Treatment for Acute Renal (Kidney) Failure (ARF)
answer
Treatment varies to addressing the underlying cause, treatments include fluids, medication, and dialysis. Medications Diuretic Medical procedure Dialysis Devices Ureteral stent Supportive care Fluid replacement
question
Urinary tract infection (UTI, bladder infection)
answer
Inflammation of the urinary epithelium after invasion and colonization by some pathogen in the urinary tract Retrograde movement of bacteria into the urethra and bladder Classification: Location or complicating factors Complicated UTI versus uncomplicated UTI Cystitis: Bladder inflammation Pyelonephritis: Inflammation of upper urinary tract Most common pathogens Escherichia coli Staphylococcus saprophyticus
question
UTI Evaluation & Treatment
answer
Evaluation: Urine Culture, UA Treatment: Antimicrobial therapy
question
Osteoporosis
answer
Porous bone Poorly mineralized bone Primary versus secondary Bone density
question
Potential causes for Osteoporosis
answer
Decreased levels of estrogen and testosterone Decreased activity level Inadequate levels of vitamins D and calcium or magnesium Alterations in the osteoprotegerin (OPG), receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B (κB) ligand (RANKL), and receptor activator of nuclear factor κB (RANK): OPG/RANKL/RANK system Postmenopausal osteoporosis Increased osteoclast activity, changes in OPG, insulin-like growth factor (IGF), and family history Glucocorticoids Increase RANKL expression and inhibit OPG production by osteoblasts, leading to lower bone density
question
Clinical manifestations for osteoporosis
answer
Pain, bone deformity, fractures, kyphosis (hunchback), and diminished height
question
Prevention & treatment for osteoporosis
answer
Prevention: Regular moderate weight-bearing exercises Calcium intake sufficient to maintain normal calcium balance during adolescence Sufficient intake of magnesium Treatment: Estrogen Bisphosphonates, denosumab, teriparatide, parathyroid hormone (PTH) 1-84
question
Pleural Effusion
answer
Presence of fluid in the pleural space. Treatment: Chest tube
question
Diabetes Mellitus
answer
Is a dysfunction of the endocrine pancreas. Affects metabolism of fat, protein, and carbohydrates. Is characterized by hyperglycemia, resulting from defects in insulin secretion, insulin action, or both. Categories: Type 1 Type 2 Other specific types Gestational diabetes
question
Somogyi Effect
answer
Hypoglycemia with rebound hyperglycemia Counterregulatory hormones cause gluconeogenesis Most common in people with type 1 diabetes mellitus and children
question
Cirrhosis
answer
Inflammtory disorder of the liver The most common cause of ascites. Fibrotic scarring of the liver occurs in response to inflammation and tissue damage. Chronic liver diseases in children can progress to cirrhosis, although infrequently. Complications for cirrhosis in children are the same as those in adults. Children may also experience growth failure, nutritional deficits, and developmental delays.
question
Intestinal Obstruction
answer
Check book table36-2, pg 913. Common causes of intestinal obstruction: Herniation, Intussusception, volvulus, diverticulosis, tumor, paralytic ileus, adhesions.
question
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
answer
An inflammatory disease caused when the immune system attacks its own tissues.
question
Symptoms of SLE
answer
Fatigue, joint pain, rash, and fever.
question
Treatment for SLE
answer
Treatment consists of immunosuppressants While there's no cure for lupus, current treatments focus on improving quality of life through controlling symptoms and minimizing flare-ups. This begins with lifestyle modifications, including sun protection and diet. Further disease management includes medications, such as anti-inflammatories and steroids.
question
Glomerulonephritis
answer
inflammation of the tiny filters in your kidneys
question
Symptoms of Glomerulonephritis
answer
Pink or cola-colored urine from red blood cells in your urine (hematuria) Foamy urine due to excess protein (proteinuria) High blood pressure (hypertension) Fluid retention (edema) with swelling evident in your face, hands, feet and abdomen
question
Treatment for glomerulonephritis
answer
Treatment depends on acute or chronic form of the disease, The underlying cause, The type and severity of your signs and symptoms Some cases of acute glomerulonephritis, especially those that follow a strep infection, might improve on their own and require no treatment. If there's an underlying cause, such as high blood pressure, an infection or an autoimmune disease, treatment will be directed to the underlying cause. the goal of treatment is to protect your kidneys from further damage.
question
Nephrotic Syndrome
answer
A kidney disorder that causes the body to excrete too much protein in the urine.
question
Signs and symptoms of Nephrotic Syndrome
answer
Symptoms include swelling around the eyes and in the feet and ankles, foamy urine, and weight gain due to excess fluid retention.
question
Treatment for Nephrotic Syndrome
answer
Treatment consists of steroids and immunosuppressants Treatment addresses underlying conditions and might include blood pressure medications and water pills. Self-care low sodium diet Medications: Diuretic, ACE inhibitor, Antihypertensive drug, Statin, Steroid, and Immunosuppressive drug
question
Hodgkin Lymphoma
answer
Cancer of the part of the immune system called the lymphatic system.
question
Signs & Symptoms of Hodgkin Lymphoma
answer
Lymph nodes in the neck, armpits, or groin may swell. Fatigue, fever, and chills , loss of appetite, shortness of breath, or weight loss
question
Treatment for Hodgkin Lymphoma
answer
Chemotherapy, radiation, and in rare cases stem-cell transplant.
question
Mononucleosis (infectious Mononucleosis)
answer
Often called mono or kissing disease, an infection with the Epstein-Barr virus.
question
Signs & symptoms of Mononucleosis
answer
Fatigue, fever, rash, and swollen glands. The elderly may not have typical symptoms. Pain while swallowing, chills, or malaise, sore throat, swollen lymph nodes, swollen tonsils, body ache, headache, or nausea
question
Treatment for Mononucleosis
answer
Treatment involves rest, fluid replacement, and over-the-counter pain and fever-reducing medicines to ease symptoms.
question
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL)
answer
Cancer that starts in the lymphatic system.
question
Signs and Symptoms of NHL
answer
Symptoms include swollen lymph nodes, fever, belly pain, or chest pain., anemia, fatigue, loss of appetite, or night sweats, or weight loss
question
Treatment for NHL
answer
Treatments may include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, stem-cell transplant, or medications (bone marrow stimulant, steroids)
question
Multiple myeloma (Kahler's disease)
answer
Cancer of plasma cells
question
Symptoms of Multiple myeloma
answer
Symptoms may not be present or may be non-specific, such as loss of appetite, bone pain, and fever. People may experience: Pain areas: in the back or bones Whole body: anemia, fatigue, Also common: constipation, hypercalcemia, kidney damage, or weight loss
question
Treatment for Multiple myeloma
answer
Treatments include medications, chemotherapy, corticosteroids, radiation, or a stem-cell transplant. Medications: Chemotherapy, Blood transfusion, Steroid, and Bone health Surgery: Autotransplantation
question
Pancreatic Cancer
answer
Cancer that begins in the organ lying behind the lower part of the stomach (pancreas).
question
Symptoms of Pancreatic Cancer
answer
There are no symptoms in the early stages. Later stages are associated with symptoms. Pain areas: in the abdomen or middle back Gastrointestinal: fluid in the abdomen or nausea Whole body: fatigue or loss of appetite Also common: dark urine, weight loss, or yellow skin and eyes
question
Treatment for Pancreatic Cancer
answer
Treatment may include surgically removing the pancreas, radiation, and chemotherapy.
question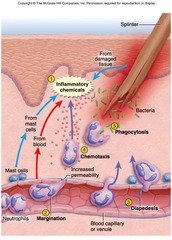
Chemotaxis

answer
During chemotaxis, cells move in response to chemical signals. The action of neutrophils is just one example of how the body uses chemotaxis to respond to an infection. Aside from the cells that are already in position in the tissues (such as the fixed tissue macrophages and mast cells), neutrophils are the first responders to inflammation.
question
Lung Cancer
answer
A cancer that begins in the lungs and most often in people who smoke.
question
Signs and Symptoms of Lung Cancer
answer
Symptoms include cough (often with blood), chest pain, wheezing, and weight loss. These symptoms often don't appear until the cancer is advanced. People may experience: Pain areas: in the chest or rib Cough: can be chronic, dry, with phlegm, or with blood Whole body: fatigue, loss of appetite, or weakness Respiratory: frequent respiratory infections, shortness of breath, or wheezing Also common: hoarseness, swollen lymph nodes, or weight loss
question
Treatment for Lung Cancer
answer
Treatments vary but may include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted drug therapy, and immunotherapy. Self Care: quitting smoking Medications: chemotherapy Surgery: Pulmonary lobectomy, Wedge resection, and Video-Assisted thoracoscopic surgery Medical Procedure: Thoracotomy and Radiation therapy
question
Edema
answer
Swelling caused by excess fluid trapped in your body's tissues. Most commonly noticed in the hands, arms, feet, ankles and legs. Edema can be the result of medication, pregnancy or an underlying disease — often heart failure, kidney disease or cirrhosis of the liver. Taking medication to remove excess fluid and reducing the amount of salt in your food often relieves edema. When edema is a sign of an underlying disease, the disease itself requires separate treatment.
question
Signs and Symptoms of Edema
answer
Swelling or puffiness of the tissue directly under your skin Stretched or shiny skin Skin that retains a dimple after being pressed for several seconds Increased abdominal size When to see a doctor May Experience: Shortness of breath Difficulty breathing Chest pain
question
Edema Tets & Diagnosis
answer
To understand what might be causing your edema, your doctor will perform a physical exam and ask you questions about your medical history. This information is often enough to determine the underlying cause of your edema. In some cases, X-rays, ultrasound exams, blood tests or urine analysis may be necessary.
question
Metaplasia
answer
A change of cells to a form that does not normally occur in the tissue in which it is found.
question
Neuropathic Pain (Nerve Pain)
answer
Type of chronic pain that occurs when nerves in the central nervous system become injured or damaged. Can erode quality of life.
question
Signs & Symptoms and Treatment for Neuropathic Pain
answer
Patients may describe their symptoms as sharp, dull, hot, cold, sensitive, itchy, deep, stinging, burning, or some other descriptor. Additionally, some patients may feel pain with a light touch or pressure. Medications: anti-seizure & anti-depressants
question
Hypoxia (Hypoxemia)
answer
Lack of oxygen reaching the tissues.
question
Signs & Symptoms of Hypoxia
answer
Acute: shortness of breath rapid breathing Tachycardia Other: Wheezing Sweating Coughing
question
Treatment for Hypoxia
answer
Give additional oxygen to the patient and into the body (blood) as quickly as possible Nasal Cannula Oxygen Masks Hyperbaric chamber
question
Pathologic Fracture: Hip Fracture
answer
A serious injury, with complications that can be life-threatening. The risk of hip fracture rises with age. Older people are at a higher risk of hip fracture because bones tend to weaken with age (osteoporosis). Multiple medications, poor vision and balance problems also make older people more likely to trip and fall (one of the most common causes of hip fracture.)
question
Signs & Symptoms of Hip Fracture
answer
Inability to move immediately after a fall Severe pain in your hip or groin Inability to put weight on your leg on the side of your injured hip Stiffness, bruising and swelling in and around your hip area Shorter leg on the side of your injured hip Turning outward of your leg on the side of your injured hip
question
Treatment for hip fracture
answer
Involves a combination of surgery, rehabilitation and medication Surgery: Internal repair using screws Partial hip replacement Total hip replacement.
question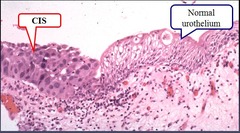
Carcinoma in situ (CIS)

answer
A group of abnormal cells that are found only in the place where they first formed in the body (see left panel). These abnormal cells may become cancer and spread to nearby normal tissue (see right panel).
question
Epidural Hematoma
answer
An epidural hematoma (EDH) is bleeding between the inside of the skull and the outer covering of the brain (called the dura). Often caused by a skull fracture during childhood or adolescence. This type of bleeding is more common in young people because the membrane covering the brain is not as closely attached to the skull as it is in older people and children younger than 2 years.
question
Signs and Symptoms of Epidural Hematoma
answer
LOC Confusion Dizziness Drowsiness or altered level of alertness Enlarged pupil in one eye Headache (severe) Head injury or trauma followed by loss of consciousness, a period of alertness, then rapid deterioration back to unconsciousness Nausea or vomiting Weakness in part of the body, usually on the opposite side from the side with the enlarged pupil
question
Treatment for Epidural Hematoma
answer
An EDH is an emergency condition. Treatment goals include: Taking measures to save the person's life Controlling symptoms Minimizing or preventing permanent damage to the brain
question
Cell Injury
answer
It is change in cell's morphology and function in response to stress. Occurs when the limits to an adaptive response (adaptation) have been exceeded or if the cells are not able to adapt
question
Causes Of Cell Injury
answer
1- Oxygen deprivation (hypoxia, ischemia) 2- Oxygen free radicals. 3- Physical agents (heat, cold, radiation, trauma). 4- Chemical agents e.g. drugs, toxins 5- Infectious organisms. 6- Immunologic reactions. 7- Genetic derangements. 8- Nutritional imbalances e.g. starvation, obesity
question
Immune Function in the Elderly
answer
As you grow older, your immune system does not work as well. The following immune system changes may occur: The immune system becomes slower to respond. This increases your risk of getting sick. Flu shots or other vaccines may not work as well or protect you for as long as expected. An autoimmune disorder may develop. This is a disease in which the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys healthy body tissues. Your body may heal more slowly. There are fewer immune cells in the body to bring about healing. The immune system's ability to detect and correct cell defects also declines. This can result in an increased risk of cancer.
question
To decrease the risks from immune system aging:
answer
Get the flu and pneumonia vaccines, and any other vaccines your health care provider recommends. Get plenty of exercise. Exercise helps boost your immune system. Eat healthy foods. Good nutrition keeps your immune system strong. DO NOT smoke. Smoking weakens your immune system. Limit your intake of alcohol. Ask your provider how much alcohol is safe for you. Look into safety measures to prevent falls and injuries. A weak immune system can slow healing.
question
Allergic Reaction
answer
Occur when your immune system reacts to a foreign substance — such as pollen, bee venom or pet dander — or to a food that doesn't cause a reaction in most people. Your immune system produces substances known as antibodies. When you have allergies, your immune system makes antibodies that identify a particular allergen as harmful, even though it isn't. When you come into contact with the allergen, your immune system's reaction can inflame your skin, sinuses, airways or digestive system.
question
Signs & Symptoms of Allergies
answer
Depends on person & type of allergy: Sneezing Itching of the nose, eyes or roof of the mouth Runny, stuffy nose Watery, red or swollen eyes (conjunctivitis) Tingling mouth Swelling of the lips, tongue, face or throat Hives Anaphylaxis A large area of swelling (edema) at the sting site Cough, chest tightness, wheezing or shortness of breath Itchy skin Rash Facial swelling Redden Flake or peel Loss of consciousness A drop in blood pressure Severe shortness of breath Skin rash Lightheadedness A rapid, weak pulse Nausea and vomiting
question
Treatment for Allergies
answer
Allergen avoidance. Medications. Immunotherapy. Sublingual drugs are used to treat some pollen allergies. Emergency epinephrine.



