ORAL CANCER & PRECANCEROUS LESIONS (221 EENT) – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Cancer Stats

answer
Estimated new cases & deaths from oral cancer in United States in 2013: • New cases: 41,380 (oral cavity & pharynx) • Deaths: 7,890 (oral cavity & pharynx)
question
Types of Oral Cancer
answer
• Squamous cell carcinoma • Lymphomas • Salivary gland tumors • Sarcomas • Melanoma •Other -Odontogenic -Metastasis
question
HOW TO RECOGNIZE ORAL CANCER
answer
Any of following lasting more than 2 weeks: • A sore that bleeds • Oral pain • A lump or thickening • A white or red patch • A sore throat or a feeling that something is caught in throat • Primary or metastatic lesions are possible in oral & maxillofacial region!
question
SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA
answer
Derived from squamous epithelium • Malignant neoplasm of stratified squamous epithelium that is capable of locally destructive growth & distant metastasis
question
ETIOLOGIC FACTORS
answer
-Tobacco & Alcohol -Viruses • HPV, • ? HSV, EBV, HHV8, HIV -Genetic derangements • oncogenes, mutation of tumor suppressor genes, etc -Loss of immunosurveillance
question
POSSIBLE CLINICAL PRESENTATIONS
answer
Leukoplakia Erythroplakia Combination Ulcer Mass Papillary growths Induration with fixation Loose teeth Paresthesia
question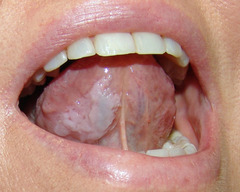
LEUKOPLAKIA

answer
• clinical term used to denote mucosal conditions that produce a whiter than normal coloration of mucous membranes • ONLY A CLINICAL TERM, NOT A HISTOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS!! • 1.5%-12% of population • 5% will evolve in to SSCA -16% in smokers Tobacco is a strong etiologic factor, but it may develop in absence of such products: • Friction or trauma ??? • EBV, Candida, LP • Biopsy is mandatory if no mechanical etiology is discovered TYPES: Hyperkeratosis Actinic cheilitis Tobacco Heat lesions Dysplasia Carcinoma Candidiasis Hairy Leukoplakia Lichen planus Lupus White sponge nevus Hairy tongue Geographic tongue
question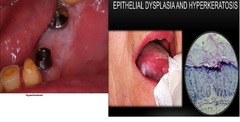
HYPERKERATOSIS (leukoplakia)

answer
Excessively thickened layer of stratum corneum composed of keratin Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia (PEH): • Excessively elongated rete pegs composed of normal keratinocytes that extend into immediately adjacent connective tissue, giving a false impression of a SCCA.
question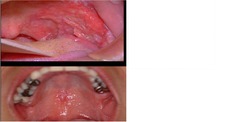
ERYTHROPLAKIA

answer
• Not a histologic diagnosis • A red patch of the oral mucosa frequently caused by epithelial dysplasia, CIS, or SCCA • It may coexist with Leukoplakia • 60-90% are dysplasia or carcinomas by histology • Older males, smokers
question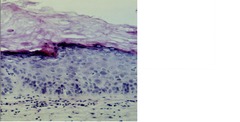
EPITHELIAL DYSPLASIA

answer
A premalignant change in epithelium characterized by a combination of individual cell and architectural alterations
question
CARCINOMA IN SITU
answer
The most severe stage of dysplasia, involving the entire thickness of the epithelium, with the epithelial basement membrane remaining intact.
question
INVASIVE SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA (SCC)
answer
• Neoplastic cells invade connective tisue • Well-moderate-poorly undifferentiated - Based on how similar to normal tissue they look like under microscope SITES: • Lower lip (sun-exposed area) 35% • Lateral/ventral tongue 25% • Floor of mouth 20% • Soft palate 15% • Gingiva/alveolar ridge 4% • Buccal mucosa 1%
question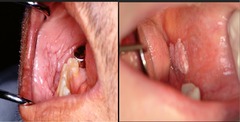
VARIANTS OF SCCA

answer
• Verrucous • Spindle • Nasopharyngeal • Adenoid squamous • Adenosquamous • Basaloid
question
Metastasis

answer
Via LYMPHATIC vessels: • Regional lymph nodes • Extra capsular invasion -Enlarged, firm, & fixed • Submandibular & sup/deep cervical chains DISTANT METASTASIS to: -lung, liver, brain, bones
question
Staging
answer
TNM: • Tumor -0, IS, 1(2-cm), 2(2-4-cm), 3(>4-cm), 4(adjacent structures) • Nodal involvement -0, 1(ipsilateral), 2(contralateral) • Metastasis -0(none), 1(positive mets) -X (no information) Stages I-IV
question
Oral/Oropharyngeal CA Treatment

answer
• Surgery • Radiation therapy • Chemotherapy • Targeted therapy • A combination of these
question
Chemo Drugs (Oral/Oropharyngeal)

answer
• Cisplatin • 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) • Carboplatin • Paclitaxel (Taxol®) • Docetaxel (Taxotere®) • Methotrexate • Ifosfamide (Ifos®) • Bleomycin • Cetuximab (Erbitux)
question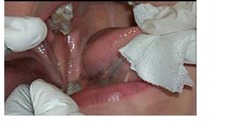
Early Detection

answer
Is Vital! • Periodic oral examinations by healthcare providers • Monthly self-examination (Light & mirror) • Regular dental checkups that include an exam of entire mouth are important in finding oral & oropharyngeal cancers (& pre-cancers) early • American Cancer Society also recommends doctors examine mouth & throat as part of routine cancer related checkup • Along with a clinical exam of mouth & throat, some dentists & doctors may use special dyes &/or lights to look for abnormal areas, especially if you are at higher risk for these cancers. If an abnormal area is spotted, some of these tests may also be used to help determine if they might be cancers (& therefore need biopsy) or to choose best area to sample for biopsy
question
How to Prevent Oral CA
answer
AVOID: • Tobacco • Alcohol • Ultraviolet light (lip cancer) • High risk HPV exposure • Marijuana PREVENTIVE FACTORS: • Healthy & balanced diet • 5 fruits & vegetables every day
question
Tobacco
answer
• TOBACCO is LEADING CAUSE of ORAL cancer! • ALL FORMS: cigarettes, pipes, cigars, & chewing (smokeless) tobacco, are linked to oral cancer. -risk of oral cancer increases with # of cigarettes smoked per day -Tobacco use is most likely to cause oral cancer in floor of mouth, but also causes cancer in oral cavity & oropharynx & lips • risk of oral cancer is GREATER in people who use BOTH tobacco & alcohol than it is in people who use only tobacco or only alcohol. • Tobacco users who have had oral cancer may develop SECOND cancers in oral cavity or nearby areas, including nose, throat, vocal cords, esophagus, & trachea • Results from clinical trials have shown that when a person STOPS SMOKING cigarettes, risk of oral cancer decreases by one-half (50%) within 5 years. -Within 10 years of quitting, risk of oral cancer is SAME as for a person who NEVER used tobacco.
question
Alcohol
answer
• EXCESSIVE ALCOHOL is a major risk factor for oral cancer. • risk of oral cancer increases with # of alcoholic drinks consumed per day • risk of oral cancer is GREATER in people who use BOTH ALCOHOL & TOBACCO than in people who use only alcohol or only tobacco • Results from clinical trials have NOT SHOWN a DECREASE IN RISK of oral cancer WHEN PERSON STOPS DRINKING ALCOHOL! • HPV (high risk types) are a risk factor for SCCa, in a dose-dependent way. (Probably represents a different disease due to separate pathophysiology but similar or same phenotype)
question
HPV
answer
• Being infected with a certain types of HPV (16, 18, 31, 45) increases risk of oral cancer! • Such "high-risk" viruses are considered oncogenic!
question
Sun Exposure
answer
• Being exposed to SUNLIGHT may increase risk of LIP CANCER, which occurs most often on LOWER LIP Avoiding sun &/or using lip balm with sunscreen or using colored lipstick may decrease risk of lip cancer
question
Marijuana
answer
• MARIJUANA may increase risk of ORAL cancer • Marijuana use by person with high-risk HPV infection may FURTHER INCREASE risk of oral cancer
question
Dietary Factors
answer
Eating a diet high in FRUITS & FIBER-rich VEGETABLES may lower risk of developing ORAL cancer
question
Chemoprevention
answer
• use of drugs, vitamins, or other agents to prevent or delay growth of cancer (Studies of chemoprevention are under way in patients at high risk for oral cancer, including those with precancerous oral lesions & those with a history of oral cancer)
question
AMERICAN CANCER SOCIETY'S MOST RECENT ESTIMATES FOR ORAL CAVITY ; OROPHARYNGEAL CANCERS IN US FOR 2012
answer
Most oftens: • tongue ; floor of mouth (25-30%) • tonsils (15-20%) • minor salivary glands (10-15%) • 2x as common in MEN than women. • Some cases related to infection with human papilloma virus (HPV) • average age of most people diagnosed with these cancers is 62, but they can occur in young people. • Diagnosed patients need to AVOID TOBACCO ; ALCOHOL, which increase risk for these SECOND cancers!



