Extra and Intra Oral Exam – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Why is the death rate of oral cancer high?
answer
It is discovered very late in development
question
What percentage of those who have visited the dentist regularly have had an oral cancer exam
answer
less than 25%
question
What is the survival rate of oral cancer if found during early stages?
answer
80-90%
question
Describe the risk of developing a second tumor with oral cancer
answer
20x more likely, risk lasts 5-10 years
question
When measuring the oral cancer with a probe, what measurement might ensure a cure rate as high as 60%
answer
15 mm (1.5 cm)
question
In what gender is oral cancer twice as common?
answer
Men
question
What is the average age of most people diagnosed with oral cancer
answer
62
question
Oral cancer is most common in men over 40 who are also ___________?
answer
Heavy smokers and drinkers
question
What is the age group that has the fastest growing population to have oral cancer
answer
Age group BELOW 50
question
Which countries have a higher rate of oral cancer
answer
Hungry and France
question
Which countries have the least common rate of oral cancer
answer
Mexico and Japan
question
What are the most common sites of oral cancer?
answer
Tongue Floor of mouth Lips Minor salivary glands
question
The anterior of the mouth, tobacco and alcohol associated cancers have _____________________?
answer
Declined with smoking
question
Posterior of the oral cavity sites associated with the HPV16 viral cause are ____________________?
answer
Increasing
question
Can someone that was cured from oral cancer eventually develop cancer in the lungs, mouth, throat, etc.
answer
YES, lungs usually
question
What are risk factors of oral cancer?
answer
-TOBACCO -alcohol -sun exposure -irritation
question
What percentage of of people with oral cavity and oropharyngeal cancer use tobacco
answer
90%
question
90% of oral cancers are usually what type>
answer
Squamous cell carcinoma
question
Pipe smoking is a particularly significant risk for cancers in which area?
answer
Lips or any area touching pipe steam
question
Oral tobacco products (snuff or chewing tobacco) are linked with cancers of which areas?
answer
cheek, gums, and inner surface of the lips
question
Which type of alcohol increases your risk of oral cancer?
answer
ALL TYPES
question
When combining tobacco and heavy use of alcohol, how much more likely is the risk of developing oral cancer?
answer
15 times
question
About how many head and neck cancers particularly in patients over the age of 50 are detected in patients who do not smoke or drink alcohol
answer
1 out of 4
question
The combination of alcohol and tobacco exert a "feeding off each other" relationship called>
answer
Synergistic
question
What percentage of lip cancers develop from prolonged exposure to the sun
answer
30%
question
What type of virus is found in some oral cancers (one fourth of oral cancers)?
answer
HPV 16
question
What groups are rapidly replacing those who were diagnosed with oral cancer from tobacco use
answer
Women in their 20's Men in 30's
question
What are some other risk factors for oral cancers
answer
immunosuppresive drugs for transplants or immune diseases
question
Does poor nutrition also increase the risk?
answer
YES
question
What are the warning signals of oral cancer
answer
- Hoarseness, persistent coughing -non healing sore throat -dysphagia -Parastheisa -Pain -White patches not healing -firm nodes
question
Nodes arising from acute inflammatory conditions tend to be tender, soft, enlarged and freely moveable
answer
Reactive node
question
Cancer lymph nodes often fixed to surrounding structures, nontender, hard, involves multiple nodes
answer
Malignant node
question
Lymph node enlargement due to cancer spreading there from a different area of the body
answer
Metastatic node
question
Lymph node enlargement due to previous infectious condition (i.e. mono)
answer
Residual node
question
Multiple palpable lymph nodes in one localized area
answer
Lymphadenopathy
question
Taking factors of size, location, color, consistency, morphology and history arriving at two or three most probable diagnoses
answer
Differential diagnosis
question
Involves a histopathologic examination of a biopsy specimen. The histopathologic examination accompanied by a lesion description
answer
Definitive diagnosis
question
What five things must you include when describing a lesion
answer
size color morphology location history
question
The deeper a fluid lesion, the more _________ it will appear
answer
pinker
question
Superficial fluid lesions appear more
answer
Translucent
question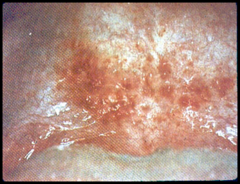
minute red spot on skin/mucous membrane resulting from escape of small amount of blood

answer
Petechia
question
small flat hemorrhagic patch, larger than a petechia on the skin/mucous membrane
answer
Ecchymosis
question
larger than eccymosis localized collection of blood, usually clotted, in an organ, space or tissue
answer
Hematoma
question
Most common red lesion, protective tissue reprise to injury or tissue destruction (usually around a lesion)
answer
inflammation
question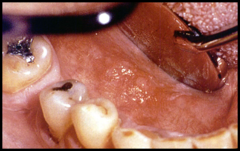
persistent velvety red patch that does not clinically represent any any other condition (not used in lesion description) (you need a biopsy to use this term)

answer
Eryhtroplasia
question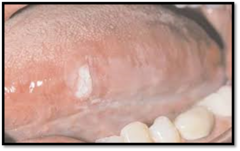
thickening of outer surface of epithelium, similar to callus on the skin, most common white lesion (not used for lesion description) (need biopsy to use this word) Carcinoma

answer
Hyperkeranitization
question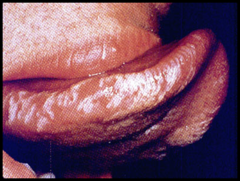
a clinical white patch/plaque that does not rub off and does not clinically represent any other condition (not used for lesion description) (need biopsy to use this word)

answer
Leukoplakia
question
most common morphologic characteristic associated with red and white lesions (usually round, white, distinctive red border, ask a lot of questions, esp. if they smoke) high risk for carcinoma

answer
Ulcers
question
Yellow lesions are usually
answer
lymph tissue, pus
question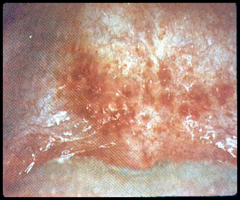
numerous and in proximity to one another, margins may emerge and leave a single lesion if they enlarge only slightly after initial appearance

answer
Coalescing
question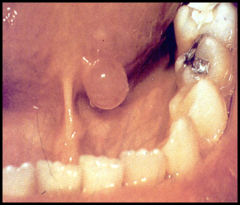
lesion contains fluid, has translucent appearance and a soft consistency

answer
Blisterform
question
Three types of blisterform
answer
Vesicle, bulla, pustule
question
blisterform lesion < 5mm in its greatest diameter and contains serum or mucin
<img src="https://chmanchacentro.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/07/blisterform-lesion-5mm-in-its-greatest-diameter-and-contains-serum-or-mucin.png" title="blisterform lesion < 5mm in its greatest diameter and contains serum or mucin" alt="blisterform lesion
answer
Vesicle
question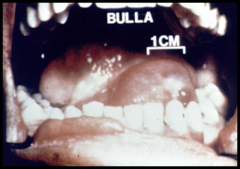 5mm in its greatest diameter which may contain serum or mucin, extravasated blood occasionally" alt="blisterform lesion > 5mm in its greatest diameter which may contain serum or mucin, extravasated blood occasionally">
5mm in its greatest diameter which may contain serum or mucin, extravasated blood occasionally" alt="blisterform lesion > 5mm in its greatest diameter which may contain serum or mucin, extravasated blood occasionally">
blisterform lesion > 5mm in its greatest diameter which may contain serum or mucin, extravasated blood occasionally
 5mm in its greatest diameter which may contain serum or mucin, extravasated blood occasionally" alt="blisterform lesion > 5mm in its greatest diameter which may contain serum or mucin, extravasated blood occasionally">
5mm in its greatest diameter which may contain serum or mucin, extravasated blood occasionally" alt="blisterform lesion > 5mm in its greatest diameter which may contain serum or mucin, extravasated blood occasionally">answer
Bulla
question or or
or or
blisterform lesion containing pus, not clear fluid, which imparts a yellow coloration; may be > or < 5mm
 or or
or or answer
Pustule
question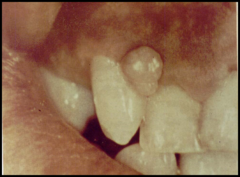
lesion is solid, contains no fluid and has firm consistency

answer
Nonblisterform
question
Four types of nonblisterform
answer
Papule Nodule Tumor Plaque
question
nonblisterform lesion which is < 5mm in its greatest diameter
<img src="https://chmanchacentro.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/07/nonblisterform-lesion-which-is-5mm-in-its-greatest-diameter.png" title="nonblisterform lesion which is < 5mm in its greatest diameter" alt="nonblisterform lesion which is
answer
Papule
question 5mm and 5mm and
5mm and 5mm and
nonblisterform lesion > 5mm and < 2 cm in its greatest diameter
 5mm and 5mm and
5mm and 5mm and answer
Nodule
question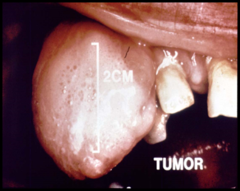 2 cm in its greatest diameter" alt="nonblisterform lesion > 2 cm in its greatest diameter">
2 cm in its greatest diameter" alt="nonblisterform lesion > 2 cm in its greatest diameter">
nonblisterform lesion > 2 cm in its greatest diameter
 2 cm in its greatest diameter" alt="nonblisterform lesion > 2 cm in its greatest diameter">
2 cm in its greatest diameter" alt="nonblisterform lesion > 2 cm in its greatest diameter">answer
Tumor
question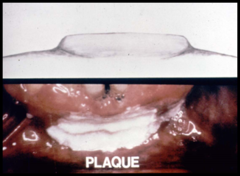 5mm in diameter "Pasted on" appearance" alt="slightly raised, nonblisterform lesion with a broad, flat top like a plateau -usually > 5mm in diameter "Pasted on" appearance">
5mm in diameter "Pasted on" appearance" alt="slightly raised, nonblisterform lesion with a broad, flat top like a plateau -usually > 5mm in diameter "Pasted on" appearance">
slightly raised, nonblisterform lesion with a broad, flat top like a plateau -usually > 5mm in diameter "Pasted on" appearance
 5mm in diameter "Pasted on" appearance" alt="slightly raised, nonblisterform lesion with a broad, flat top like a plateau -usually > 5mm in diameter "Pasted on" appearance">
5mm in diameter "Pasted on" appearance" alt="slightly raised, nonblisterform lesion with a broad, flat top like a plateau -usually > 5mm in diameter "Pasted on" appearance">answer
Plaque
question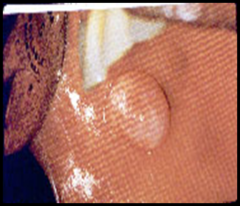
papule, nodule or tumor whose base or attachment to normal mucosa is the greatest diameter of the lesion

answer
Sessile
question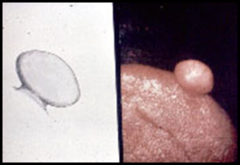
papule, nodule or tumor that has an attachment to the normal oral mucosa which is smaller than the greatest diameter of the lesion itself; attached by a stalk

answer
Pedunculated
question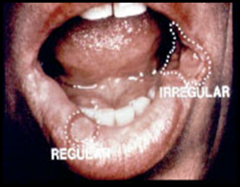
ulcer with continuous linear outline that resembles a circle or oval

answer
regular outline
question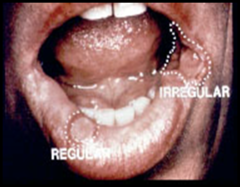
ulcer with numerous deviations from a circular or oval pattern

answer
Irregular outline
question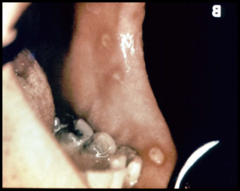
Ulcer above plane or mucosa

answer
Raised margin
question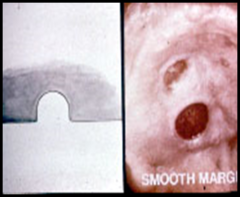
Ulcers on the same plane

answer
smooth margin
question
distance from base of the depression to the plane of the margin of the depression
answer
Depth
question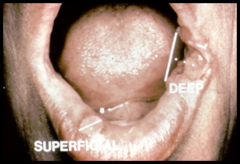
Ulcer depth is less than 3 mm

answer
Superficial
question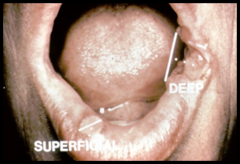
Ulcer depth is greater than 3mm

answer
Deep
question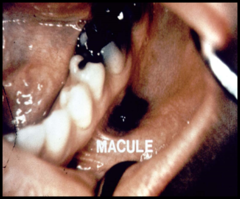
flat lesion of abnormal color

answer
Macule
question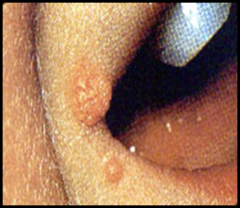
covered by wart like growths (wart like)

answer
Verrucous
question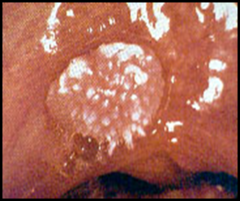
covered by nipple-like projections (cauliflower like)

answer
Papillary
question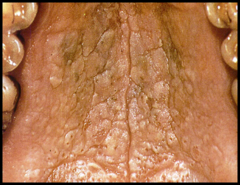
cracked surface

answer
Fissured
question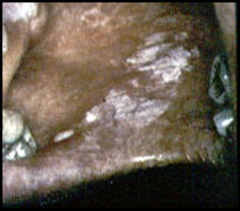
wrinkled appearance

answer
Corrugated
question
dry or scab-like

answer
Crusted



