Voice therapy Principles – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Voice Therapy- General Principles
answer
Boone- "Voice therapy is highly individualized, depending on the cause of the problem, its maintaining factors, the motivation of the patient, and the availability of appropriate management and treatment".(p.179, text) Determine which professionals need to be involved after evaluation: ENT, SLP, Psych. Determine if therapy by an SLP is necessary Determine if the patient is ready and is interested in therapy
question
More General Principles
answer
Determine which techniques are to be used by presenting causal and maintaining factors Determine which individuals need to be involved besides client. Parents, teachers? Age of client may effect therapy techniques chosen or whether treatment is recommended. Explore various techniques with adolescent/adult - find "best" voice and stabilize it.
question
Facilitating/Therapy Definitions Boone: coined the word "facilitating" techniques.
answer
Specific strategy helps the client move toward the target goal, a more optimal voice. "Techniques can be used in combination or sequentially with all etiologies
question
1. Auditory Feedback:

answer
May affect loudness and quality Real-time amplification on headphones (need amplifier, microphone, and headset) Combine approach with others so that pt. can chant, etc. with amplification 3 forms of feedback: Real-time amplification Metronome pacing Loop playback
question
Change of Loudness

answer
Treatment may affect pitch, loudness and quality of voice Loudness level of patient may be too loud or too soft Vocal abuse can result in inability to increase loudness levels Speaking environment may necessitate loud speaking Audiometric Evaluation - necessary before any therapy begins Rule out psychological factors Procedures 1. decrease loudness - practice quiet voice 2. increase loudness - discuss soft voice - explore best pitch
question
Chant Talk- therapy affects technique procedure
answer
- Technique may affect loudness and quality - Means of reducing effort for hyperfunction - Reciting many syllables on one continuous tone w/o stress or prosody changes - Create a singing monotone - Smooth and connected with no break between tones - Characterized by an elevation of pitch, prolongation of vowels, lack of syllable stress, softening of glottal attack Procedures: -Explain technique; demonstrate; only temporary -Urge client to imitate demonstration - Read aloud -Playback - Reduce chant quality
question
Digital Manipulation Technique may affect pitch and quality
answer
- Finger pressure on thyroid cartilage - Light pressure anteriorly can nudge cartilage back, shortening vf's and decreasing pitch - Monitoring vertical movements of larynx During swallow, fear-tension state, or singing high notes, overall larynx appears to rise - Unilateral digital pressure Finger pressure on lateral thyroid cartilage wall of affected side in unilateral vf paralysis can produce better vf approximation
question
Establishing new pitch
answer
Technique may affect pitch and quality Find out where pitch is and where it "should" be Speaking at bottom of pitch range requires too much force and effort Speaking at top of pitch range may be vocally fatiguing
question
Establishing new pitch Procedure

answer
Describe where patient is currently, and what target is Most patients can imitate their own pitch models, once they have been produced by appropriate facilitating technique Use of pitch analyzer, phonatory function analyzer, visi-pitch, B&K real-time frequency analyzer. Work first on single words, repeated in a pitch monotone (using target pitch), then introduce phrases and short sentences (still in pitch monotone) Introduce reading (monotone), and then move to real-life conversational situations
question
Focus Technique may affect pitch, loudness and quality
answer
Technique may affect pitch, loudness and quality Good focus of the voice is characterized by the voice coming "from the middle of the mouth, just above the surface of the tongue" (Boone, 1997) Problems in "horizontal" voice focus occur when tongue is too far forward or backward Most common focus problem is voice sounding as if it were deep in the throat "voice that feels focused high in the head" is more efficient and can survive extensive vocalization
question
Focus procedure
answer
Determine type of focus problem anterior focus Posterior focus Poor vertical focu
question
Glottal Fry Procedure
answer
True glottal fry is produced in relaxed manner with very little airflow and subglottic air pressure Valuable for patients with vocal nodules and other hyperfunctional problems
question
Glottal Fry therapy Procedure
answer
Attempt to produce same tone on inhalation and exhalation, then repeat words. Tape record glottal fry for target Repeat phrases ("easy does it", "squeeze the peach", "see the eagle") in a normal voice
question
Inhalation Phonation Technique may affect pitch, loudness and quality Procedure
answer
Patients with functional aphonia and functional dysphonia often benefit Introduces high-pitched inhalation voice
question
Inhalation Phonation Technique may affect pitch, loudness and quality Procedure
answer
Demonstrate by phonating a high-pitched sound while elevating the shoulders Now demonstrate inhalation (with raised shoulders) humming in a high pitch, then dropping the shoulders on exhalation and producing same voice Ask patient to imitate model Have patient prolong exhalation and drop from high pitch down to regular register (model) Practice phonating the "hum", then practice single words Fade shoulder elevation and depression Stay at single-word practice level until normal voicing is established
question
Pitch Inflections Technique may affect pitch (surprised? )

answer
In some individuals, lack of pitch variation is noticeable because resulting voice is monotonous and boring to listeners requires inhibition of natural inflection Usually observed in people who display very little affect Therapy for patients with monotone seeks not only to establish more optimum pitch levels, but also to increase pitch variability Combine work on increasing loudness with increasing pitch variability
question
Pitch Inflections Technique may affect pitch (surprised? ) Procedures
answer
Establish awareness of monotone through recorded tape Work on downward and upward inflectional shifts of same word Introduce inflectional shifts within specific words Pitch inflections (and targets) can be graphically displayed
question
Redirected Phonation Technique may affect pitch, loudness and quality
answer
common among patients with functional aphonia or functional dysphonia Start with vegetative phonation coughing, gargling, laughing, throat clearing or intentional voicing humming, singing, trilling If patient is able to voice one or more of these noncommunicative sounds
question
Redirected Phonation Technique may affect pitch, loudness and quality procedure

answer
Coughing, gargling, humming, laughing, playing the comb or kazoo, singing, throat clearing, trilling, um-hmm
question
Respiration Training Technique may affect loudness and quality
answer
Emphasis by singing teachers and vocal coaches on singers and actors SLP's don't use as much with patients with voice disorders Patient may only need some instruction on developing expiratory control
question
Respiration Training Technique may affect loudness and quality procedure
answer
Demonstrate how expiratory air can set up vibration (e.g., blowing air through lips) and explain vocal fold vibrations (briefly!) Briefly and simply present respiratory physiology; describe and demonstrate Demonstrate exaggerated breath (like in a sigh - a happy one!) Demonstrate quick inhalation and prolonged exhalation needed for speaking Various duration tasks, such as prolonging vowels, provide excellent practice in expiratory control Practice with reading
question
Tongue Protrusion /i/ Technique may affect pitch and quality
answer
May improve many hyperfunctional voice problems; especially helpful for patients with ventricular phonation or "tightness" in the voice When tongue is protruded and pulled out of pharynx, it opens the laryngeal aditus and offsets the squeezing of the pharynx
question
Tongue Protrusion /i/ Technique may affect pitch and quality procedure

answer
Demonstrate by opening mouth and protruding tongue while producing high-pitched, sustained /i/ Patient should go up and down in pitch while sustaining /i/, with mouth open and tongue protruded Ask patient to sustain the tone when you hear improved vocal quality Have patient chant /mimimimi/ at this level with tongue still protruded, then slowly "slip" tongue back into mouth Pitch is usually still high, so demonstrate lowered /i/ When new tone is established, gradually add words to sustained /i/
question
General "Must Knows" Habitual throat clearing:
answer
one study by Stemple and Lehmann showed 2/3 of all patients with vocal hyperfunction had habitual throat-clearing. May develop as result of mucous drainage from colds, flu, allergies, esophageal reflux, or laryngeal pathologies. What to do? Always expect success: self-fulfilling prophecy
question
Hydration: .
answer
phonation threshold pressure increases with dehydration and then patient increases effort to produce voice resulting in vocal fatigue Consume 48-64 ounces of water per day If whole body is not hydrated, secretions from secretory glands become more viscous. Mucous will cover vf
question
More "Must Knows" Patient (and sometimes family) must be motivated for vocal pattern to change ?
answer
Must be working with SLP and not against him/her Working with defense mechanisms may be difficult Patients may look to you as counselor What is your role
question
Laryngeal Cancer Laryngeal cancer: 1-2% of all cancers 20% of all head and neck cancers Occurs at one or a combination of 3 locations:
answer
Supraglottis Subglottis Glottis
question
Cancer treatment Radiation:
answer
Can cause swelling of mucosa followed by dryness and stiffness of vocal fold cover Long term- fibrosis of soft tissue
question
Surgery: when? laryngectomy or hemilarngectomy
answer
If tumor crosses midline, then total laryngectomy may be needed If tumor is on one side, hemilaryngectomy or other partial laryngectomy is possible May produce scarring and tissue deficits which can affect vocal cord vibration
question
Chemotherapy:
answer
Moderate to severe side effects, including: pain, diarrhea, constipation, mouth sores, nausea and vomiting, hair loss Effects can be short- or long-term
question
Facilitating Techniques
answer
Inhalation phonation using the vowels /i/ /u/ and /o/ Pitch shifts upward and downward Glottal fry Nasal glide stimulation Head turn plus lateral digital pressure to thyroid cartilage Loudness changes, usually lower Tongue protrusion /i/
question
Success of Treatment
answer
Dependent on integrity of vocal fold and preservation of mucosal wave Depends on scarring and stiffness of vocal folds Depends on degree of tissue loss
question
Vocal Hygiene More important than usual to be
answer
hydrated avoid alcohol avoid vocal misuse
question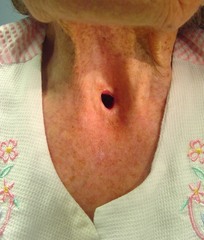
Laryngectomy

answer
Totally removes laryngeal cartilages, hyoid bone, all extrinsic and intrinsic laryngeal muscles, and upper rings of trachea Uppermost portion of trachea made flush with neck and external stoma is made, which is now patient's airway Alters respiration, swallowing, and speechPreoperative counseling (education) very important!
question
Postlaryngectomy Communication Options Esophageal speech
answer
air inhaled into pharyngoesophageal segment (PE) and then expelled, setting the tissue of the PE segment into vibration for a voice source
question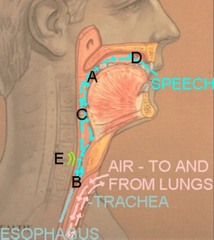
Electrolarynx

answer
introduces sound for speech through an instrument externally placed against the throat or oral structures
question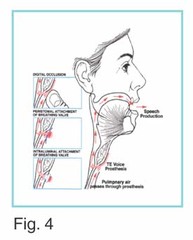
Tracheoesophageal speech

answer
an opening or puncture is made through the posterior wall of the trachea, extending through the anterior wall of the esophagus. A prosthesis inserted into the puncture shunts pulmonary air into the esophagus
question
Artificial Larynx Cooper-Rand intraoral electrolarynx:

answer
can be used right after surgery No pressure on neck where there is swelling...
question
Pneumatic types:
answer
one end placed over stoma and other end has mouthpiece Sound generator activated when user exhales through stoma
question
Ultravoice :

answer
embedded in upper dental plate
question
Esophageal Speech Injection:
answer
air moved from mouth to esophagus Begin by using plosive consonants (/p/, /t/, /k/) Start with production of /p/ by intraoral whisper Continue with plosives and then add vowels to consonants
question
Inhalation Method:
answer
esophagus inflates Air passes through pharyngoesophageal segment Patient practices inhalation/exhalation Add air into esophagus during inhalation Keep mouth closed, take large breath through stoma When lungs are half inflated, patient says "up" on exhalation Continue to other monosyllabic words
question
Tracheoesophageal Puncture Shunt (TEP)
answer
Most laryngectomees are candidates for tracheoesophageal puncture. Must have adequate pulmonary support and have cognitive and sensorimotor skills intact Also, a PE segment which vibrates to generate a speech source Insufflation testing Fistula dilated and prosthesis inserted
question
Evaluation of resonance disorders Listen carefully during spontaneous conversation Perceptual aspect is extremely important;
answer
however, even experienced listeners often have trouble determining type of nasality from conversational speech sample Loading sentences with nasal phonemes is helpful for making judgments regarding hyponasality ("many men in the moon") Only oral phonemes: "Betty takes Bob to the show", should have roughly the same quality with nose occluded or open
question
Continued assessment Oral Exam:
answer
Cannot see velar and pharyngeal function through oral cavity but can inspect tongue, velum, uvula, palates, dentition Make sure to inspect for clefts, fistulas, etc.
question
Nasovideoendoscopy The "Gold Standard"
answer
nasal fiberoptic endoscope places small flexible scope through nose into pharynx to see velopharyngeal closure from above Can also study dynamics of VP function Does not impede tongue, lip, or jaw movements, so can evaluate with speech
question
Treatment of Resonance Disorders Hypernasality with organic etiology Refer to specialist:
answer
plastic surgeon, orthodontist, prosthodontist Orthodontist can expand dental arches for more normal palatal growth and dentition (esp. with cleft)
question
Prosthodontist: acrylic bulbs Obturator: Palatal lift:
answer
fitted into VP port space to reduce nasality and emission ;;for velopharyngeal insufficiency ;;for velopharyngeal incompetency SLP can assist in choosing prosthesis or in evaluating speech after surgery or prosthesis. Surgical treatment: for structural inadequacies pharyngeal flap: mucosal tissue from pharynx used to bridge the excessive velopharyngeal opening, attaching tissue to the soft palate
question
Voice Therapy for hypernasality Must have adequate structural VP closure for voice therapy to be effective.
answer
Visual and auditory feedback Altering tongue position (place tongue too far back or forward) Change of loudness Establishing new pitch -lower Counseling Open mouth Focus Respiration training -to increase loudness
question
Voice Therapy for Hyponasality May be related to nasal obstruction (adenoids, infection, polyps)
answer
May be result of reduced airflow as result of surgery or prosthesis Techniques: Auditory feedback Counseling Feedback Nasal-glide stimulation Focus
question
Assimilative Nasality Nasality before and after nasal consonants and vowels. what is the therapy what are the conditions that cause it?
answer
May be functional or due to poor velar functioning Neurological conditions such as bulbar palsy, MS, and spastic dysarthria can keep velum from moving quickly Therapy includes auditory feedback, counseling
question
Cleft Palate & Resonance Disorders Three types of resonance problems: 1) Hypernasality: 2) Hyponasality: 3) Assimilative Nasality:
answer
1. too much nasal resonance during articulation of non-nasal consonants and vowels (all except /m/,/n/,/ng/) 2.May be due to VPI: must do nasopharyngoscopy to identify the inability of the velum to close off the nasal cavity for oral consonants and vowels. reduced nasal resonance of nasal sounds 3. vowels or voiced consonants sound nasal when they occur near nasal consonents
question
Prosthesis: silicone tube, one-way valve, tracheal flange
answer
-Prosthesis shunts air into esophagus and PE segment is set into motion. -Air is trapped in esophagus and patient occludes stoma to speak. -Also have one way valve which shuts off on expiration allowing air to travel through shunt into esophagus without occlusion
question
Nasal emission:
answer
place a mirror under nares and ask patient to say "Buy baby a bib." Mirror will fog on non-nasal sounds See-Scape: styrofoam disk "floats" with nasal airflow



