Urinary System – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Normal Nephron
answer
Filtration Reabsorption Secretion Endocrine
question
Overview of Major Kidney Diseases
answer
Glomerular Pathology Immunologic disorders (e.g., glomerulonephritis) Metabolic disorders (e.g., diabetic nephropathy) Circulatory disturbances (e.g., prerenal renal failure) Bacterial infections (e.g., pyelonephritis) Tumors
question
glomerulonephritis
answer
Ab/Ag complexes forming elsewhere in body infection or sepsis
question
glomerulosclerosis
answer
vascular abnormality destroying vessels that provide blood flow
question
Clinical Syndromes
answer
Acute Renal Failure Nephritic Syndrome Nephrotic Syndrome
question
Acute Renal Failure
answer
Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis over a period of several weeks Hematuria, oliguria (progressing to) anuria
question
Nephritic Syndrome
answer
Generalized edema, hypertension, hematuria, proteinuria, and hypoalbuminemia SLE
question
Nephrotic Syndrome
answer
Generalized edema, proteinuria, hypoalbuminemia, hyperlipidemia, lipuria Diabetes
question
End Stage Renal Disease
answer
Chronic glomerulonephritis Uremia Kidneys Shrunken, finely granular
question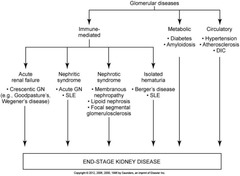
Glomerulopathies

answer
KIDNEY IS MOST SUCCESSFULLY TRANSPLANTED ORGAN 3 SUB CATEGORIES: IMMUNE MEDIATED METABOLIC CIRCULATORY
question
IMMUNE MEDIATED
answer
ACUTE RENAL FAILURE - GOOD PASTURES NEPHRITIC SYNDROME NEPHROTIC SYNDROME - ISOLATED HEMATURIA - BERGER'S DISEASE
question
METABOLIC
answer
DIABETES AMYLOIDOSIS
question
CIRCULATORY
answer
HYPERTENSION ATHERIOSCLEROSIS DIC
question
Urinary Tract Infections
answer
UTI's Pyelonephritis Cystitis
question
UTIs
answer
Uropathogens (gram negative bacteria - MOST COMMON CAUSE OF UTI) Escherichia coli - MOST COMMON BACTERIA, Klebsiella, and Pseudomonas aerogunisa BLOOD BORN INFECTION
question
Pyelonephritis
answer
BLOOD BORN INFECTION Bacterial infection of kidneys
question
Cystitis
answer
ENTRY INTO THE BODY THRU URETHRA Bacterial infection of the urinary bladder
question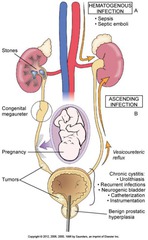
Routes of Renal Infection

answer
HEMATOGENOUS - FROM BLOOD SUPPLY (DOESN'T USU DESCEND) ASCENDING INFECTION - FROM OUTSIDE ; ASCENDS
question
Urolithiasis
answer
FORMATION OF URINARY STONES - OBSTRUCT OR ERODE TISSUE Classified by chemical structure; MOST COMMON IS CALCIUM Tx voided; lithotripsy; sx Sign ; symptom (S;S): hematurea - BLOOD IN URINE, recurrent UTI, colic (intermittent pain if stone is in ureter)
question
Neoplasms of Urinary Tract
answer
More often malignant than benign WILM'S TUMOR: only neoplasm found in children; all others occur in older adults Originate fromEPITHELIAL CELLS of kidney or UROTHELIUM (transitional cell lining of pelvis, ureter, urinary bladder, posterior urethra)
question
Urinary Tract Tumors - 3 TUMOR TYPES
answer
Kidneys Ureters Urinary Bladder
question
KIDNEYS
answer
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) - KIDNEY TUMOR (UNCOMMON) Wilm's tumor (children) Renal pelvis - Transitional cell carcinoma (TCC) - FAIRLY COMMON MALIGNANT NEOPLASM
question
URETERS
answer
Transitional cell carcinoma (TCC)
question
URINARY BLADDER
answer
Transitional cell carcinoma (TCC)
question
URETHRA
answer
Squamous cell carcinoma
question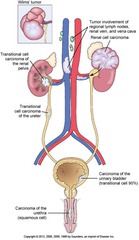
Urinary Tract Tumors (Cont'd)

answer
SPREAD THRU VASCULAR
question
Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC)
answer
Common: 27,000 new cases; 11,000 cancer-related deaths per year in U.S. No strong risk factors identified Found in 5% of chronic end-stage kidney disease patients Occurs in older adults (>50 years) Prognosis guarded: 50% survive 5 years
question
Renal Cell Carcinoma: Clinical Features
answer
HEMATURIA: most common finding (50%) Typical triad (hematuria,FLANK PAIN, palpable abdominal mass) found only in 10% Nonspecific symptoms common, often found accidentally ("internist's tumor")
question
Wilms' Tumor
answer
WILM'S TUMOR of infancy, childhood Composed of BLASTIC (IMMATURE CELLS) resembling renal blastema Related, in some cases, to deletion or mutation of tumor suppressor gene WT1 May be familial or bilateral in 10% cases Good prognosis: surgery + chemotherapy
question
Carcinoma of Urinary Bladder
answer
MOST COMMON CANCER OF URINARY TRACT: 52,000 new cases per year in the U.S.; 10,000 cancer-related deaths Most tumors are transitional carcinomas (TCC), but may be squamous or adenocarcinomas Variable prognosis: depends on grade/stage of tumor
question
Urinary Bladder Carcinoma
answer
Most are TCC (90%) +/- invasion Can be multifocal Etiology - unknown, but risk factors are SMOKING, exposure to INDUSTRIAL CHEMICALS S&S - hematurea, DYSURIA - PAINFUL URINATION, LOWER ABDOMINAL PAIN; often symptoms appear early and therefore dx'd early, tx is early and px is better Tx - Sx, chemotherapy & BCG (AN ORGANISM THAT PROMOTES CHRONIC INFLAMMATION RESPONSE) immunotherapy
question
Tumors of the Female Reproductive System
answer
15% of all malignant tumors; 10% of all cancer deaths in women 70,000 new cases per year; 23,000 deaths BENIGN TUMORS MORE COMMON, 5 benign for every 1 malignant tumor
question
Gynecologic Tumors: Statistics
answer
CARCINOMA OF THE VULVA (SCC) MOST COMMON PROGNOSIS IS VARIED, DEPENDS ON IF SPREAD
question
Carcinoma of the Cervix
answer
Related to HPV INFECTION (98% ASSOC W/THIS VIRUS) TYPES 16, 18: 70% of all cervical cancers INCORPORATE INTO NORMAL CELLS & AFFECTS CELL @ TRANSITION ZONE Types 31, 33, 34 and 35 lesser extent Preceded by carcinoma in situ (DYSPLASIA - ABNORMAL CELL CHANGES ON SURFACE OF CERVIX, PRONE TO DEVELOP MUTATION progressing to CIN - CERVICAL INTRAEPITHELIAL NEOPLASM & invasive carcinoma) Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) Early detection by Pap smear Variable prognosis: depends on stage of tumor
question
Tumors of Uterus
answer
Myometrial tumors Leiomyoma (benign, common) - FIBROIDS Leiomyosarcoma (malignant, rare) Endometrial tumors Adenocarcinoma ALMOST ALWAYS MALIGNANT, common) *ALL CONNECTIVE TISSUE _________________________________ Note: All endometrial tumors are malignant; no adenomas
question
Endometrial Adenocarcinoma
answer
Related to hyperestrinism - ESTROGEN May be preceded by endometrial hyperplasia Occurs in perimenopausal, postmenopausal (older) women Variable prognosis: depends on stage & to lesser extent on grade FAIRLY COMMON
question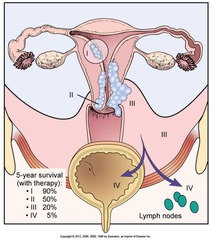
Staging of Endometrial Carcinoma

answer
Staging of Endometrial Carcinoma
question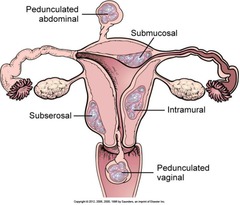
Leiomyoma of the Uterus

answer
Leiomyoma of the Uterus
question
Endometriosis
answer
Foci of endometrium found outside uterus Most often located on ovary, pelvic peritoneum Very common, clinically causing: Cyclic pain Infertility
question
ENDOMETRIOSIS
answer
ABNORMAL CONDITION RELATING TO ENDOMETRIUM NORMAL TISSUE GROWING IN ABNORMAL PLACES
question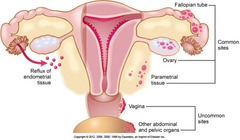
Endometriosis (Cont'd)

answer
Endometriosis (Cont'd)
question
Ovarian Neoplasm - SILENT KILLER
answer
Tumors of surface epithelium (70%)
question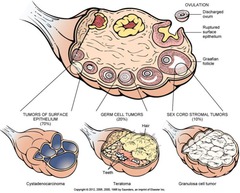
Histogenesis of Ovarian Tumors

answer
Histogenesis of Ovarian Tumors
question
Ovarian Surface Epithelial Tumors
answer
Benign Borderline Malignant Malignant
question
BENIGN
answer
Serous cystadenoma - BENIGN CYSTS, WATERY SECRE Mucinous cystadenoma - PRODUCES MUSIN
question
BORDERLINE MALIGNANT
answer
Serous tumor of borderline malignancy Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma
question
MALIGNANT
answer
Serous cystadenocarcinoma Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma Endometrioid adenocarcinoma - SAME TYPE THAT ARISES IN UTERINE BODY
question
Benign Breast Tumors: Fibroadenoma
answer
Well-encapsulated mass, 2-5 cm in diameter Found in young women 15-35 years old Composed of fibrous stroma, glandular epithelium Easily removed surgically; does not recur; does not become malignant
question
Carcinoma of Breast: Basic Facts
answer
MOST COMMON MALIGNANT TUMOR IN WOMEN; 1 in 9 will have it during her life span In U.S., 210,000 new cases diagnosed yearly; 40,000 die
question
Risk Factors
answer
Sex: FEMALE > male Genetic factors: family history, BRCA1 - GENETIC MUTATIONS THAT ARE TESTED FOR TO SEE IF BREAST CANCER IS PRESENT, BRCA2 Race: white > Africans > East Asians Age: rare before puberty Hormones: exogenous estrogen Premalignant breast changes intraductal papilomatosis:, ATYPICAL INTRADUCTAL HYPERPLASIA Other cancers: ovary, uterus, breast
question
Histologic Classification: Invasive Breast Carcinoma
answer
INVASIVE DUCTAL CARCINOMA (70%) - LOBAR CARCINOMA (10%) - USU OVER 70 YRS OLD Medullary carcinoma Mucinous carcinoma Tubular carcinoma
question
INVASIVE DUCTAL CARCINOMA (70%)
answer
PRECURSOR TO DUCTAL CARCINOMA IN SITU
question
CARCINOMA IN SITU
answer
MALIGNANT NEOPLASM OF BREAST THAT HASN'T INVADED THE BASEMENT MEMBRANE
question
LOBAR CARCINOMA (10%)
answer
USUALLY OVER 70 YRS OLD
question
LOBAR AND DUCTAL
answer
2 BREAST CELLS
question
DIAGNOSIS
answer
MAMMOGRAPHY, - MEASURES IRREGULARITY, DENSITY, MICRO DUCTAL CALCIFICATIONS, MASS BREAST X-RAY
question
Clinical Presentation
answer
Breast mass discovered by palpation Tumor discovered by mammography Pain (mastodynia) or painful breast mass Nipple retraction, eczematoid reaction, or discharge Distant metastases
question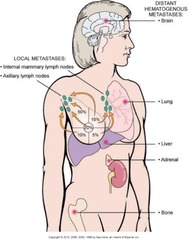
Metastases: Breast Carcinoma

answer
SPREADS TO: BONE, LUNG, BRAIN, LIVER REGIONAL NODES



