Unit II Test: Atomic Structure – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Five Principles of John Daltons Atomic Theory
answer
1. All matter is made of invisible, indestructible atoms 2. Atoms of a given element are identical in their physical and chemical properties 3. Atoms of different elements have different physical and chemical properties 4. Atoms of different elements combine into simple, whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds 5. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created or destroyed when they are combined, separated or rearranged in chemical reactions
question
The three problems for Daltons Theory
answer
1. Atoms are made of smaller particles 2. Atoms are split in nuclear reaction today 3. Atoms of the same element aren't identical because of isotopes and atoms
question
Significance of JJ Thompson
answer
1. Use of the cathode ray 2. Discovered isotopes with neon 3. Plum pudding model
question
Significance of Cathode Ray
answer
Identify protons and electrons
question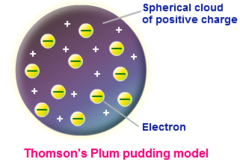
Plum pudding model

answer
By: JJ Thompson
question
Rutherford's gold foil experiment
answer
A positively charged beams shot through a thing sheets of gold foil. He found that some particles went through but some bounced back and some bounced back to the source
question
Rutherford's discoveries
answer
1. Atoms are made of empty space 2. Nucleus takes up 1/8000 of an atom
question
Contributions of Nils Bohr
answer
Used the quantum theory to modify Rutherford's model and show energy levels
question
Nils Bohrs Model
answer
Planetary Model: 2 electrons in first orbit, 8 on the outer
question
J. Chadwick contribution
answer
Discovers the neutron
question
Robert Millikan Contribution
answer
Uses Oil Drop Experiment to find mass of electron
question
Wavelength
answer
Distance from peak of one wave to the peak of the next wave
question
Frequency
answer
The number of waves that pass through a given area over a set time
question
Ground State
answer
All electrons at their lowest energy level
question
Excited State
answer
One (or more) electron absorbs energy and jumps to a higher orbital. Highly unstable.
question
Location of Nucleus
answer
Center of Atom; 99.9% of atom
question
The Nucleus _______ charged
answer
Positively
question
Electrons
answer
Negatively charged
question
Location of Electrons
answer
Electron Cloud; takes up entire volume; orbital
question
Orbital
answer
Part of Electron Cloud
question
The atomic number is equal to what?
answer
# of protons
question
Protons
answer
Identify the atom; if the number of this changes, the element changes
question
Average Atomic Mass equals what?
answer
Protons + Neutrons
question
Mass Number
answer
Rounded number of protons and neutrons
question
Isotopes
answer
Alternate forms of an element
question
Isotopes have the same number of _________ but different numbers of ________.
answer
Protons; Neutron
question
T/F: Many isotopes are radio active forms of an element
answer
True
question
There is no difference in the way the _________ users _______ or ________.
answer
Body; Isotopes; Atoms
question
T/F: Isotopes belong to the same family as atoms
answer
True
question
Ion
answer
When the number of electrons change
question
Cation
answer
More protons than electrons (positively charged; looses electrons)
question
Anion
answer
More electrons than protons (negatively charged; gains electrons)
question
Polyatomic Ion
answer
Ions made of different elements bound together
question
Valence Ions
answer
Atoms acquire this charge by gaining or loosing electrons from their outermost level
question
Quark
answer
All other particles located in the nucleus of an atom. These make protons and neutrons
question
Octet rule
answer
atoms want to have a stable outer energy level of valence 8 electrons
question
With 1, 2 or 3 valence electrons atoms ___________.
answer
Lose electrons and become cations
question
With 5, 6 or 7 valence electrons atoms ___________.
answer
gain electrons and become anions
question
How are electrons assigned to orbitals
answer
Diagonal rule and Hund's rule
question
Electron configurations identify _________.
answer
All the electrons for an atoms
question
Electron configurations relate to __________.
answer
The properties of that atoms and to its location on the periodic table
question
Hund's Rule
answer
Each orbital must contain one electron before paring occurs
question
Formation of a Participate
answer
When a solid forms from two liquids
question
Formation of heat/light
answer
Energy is given off or feeling cold to the touch as energy is absorbed; exchange of energy
question
Color change
answer
is not always an indicator such as food coloring
question
amu = ?
answer
Atomic mass unit



