Shoulder (pt 2 winged scapula-fractures) – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
winged scapula is usually due to (glenohumeral pathology/weak serratus anterior muscle)
answer
weak serratus anterior muscle
question
pt. present with c/o peri-scapular pain, states they feel like their shoulder is popping. on wall push up you see the left shoulder scapula is sticking out markedly, patient also has slight atrophy. Pt. most likely has: a. idiopathic serratus anterior weakness b. glnohumeral joint pathology c. long thoracic nerve pathology d. ac jt dislocation
answer
c (pt has winged scapula, atrophy indicates likely muscle innervation problem and most common is long thoracic nerve, get an EMG to confirm, if you suspected GH pathology would want MRI)
question
when should you refer a winged scapula? a. always b. if patient doesn't respond to conservative measures c. if patient has long thoracic nerve injury d. if patient requires surgery
answer
a (always)
question
pt present to office following a fall off their dirt bike, has a history of right shoulder instability, now has obvious dislocation of the right shoulder, what is most important part of the physical exam? a. compare deformity bilaterally b. look for fracture c. check neruovascular status d. get an MRI
answer
c (check neruovascular status)
question
Electrocution/seizure is more likely to cause an (anterior/posterior) GH dislocation
answer
posterior
question
Treatment for an anterior dislocation following a traumatic injury? a. physical therapy b. GH jt injection c. reduction/sling d. surgery
answer
c (reduction/sling, only if you're comfortable doing so)
question
Pt. presents to the office with history of separated shoulder, following a fall off his bike in spin class where he caught himself with his outstretch arm. On physical exam he has pain over AC joint and you note a "piano-key deformity". patient is likely struggling with: a. sternoclavicular dislocation b. AC jt arthritis c. subacromial bursitis d. AC jt dislocation
answer
d (common history of fall onto shoulder/outstretched arm, and you can literally see the separation)
question
If a patient has an AC ligament rupture with partial tear of coracoclavicular what grade AC jt separation is this? a. Grade I b. Grade II c. Grade III d. Grave IV e. Grade V
answer
b (Grade II)
question
If patient has a complete tear of AC/CC ligaments and clavicle disrupts deltoid/trapezius, what grade AC jt separation is this? a. Grade I b. Grade II c. Grade III d. Grave IV e. Grade V
answer
d (grade IV)
question
if pt. has complete tear of AC/CC ligaments and clavicle is displaced 100% from acromion? a. Grade I b. Grade II c. Grade III d. Grave IV e. Grade V
answer
e (Grade V)
question
If a patient has a mild sprain of the AC ligament following a fall on outstretched hand, and has pain at the AC joint, what is appropriate treatment? a. NSAIDs and rest b. Corticosteroid injection c. Sling x 4-6 weeks d. refer to ortho for coracoacromial ligament repair
answer
c (grade I or II sling for 4-6 weeks)
question
Pt. presents to office and reports a fall onto the shoulder, now having pain "in the front middle area" of their chest. on physical exam you notice bruising over the sternoclavicular area. What is the appropriate imaging study? a. CT scan b. XR c. MRI d. U/S
answer
b (pt has sternoclavicular dislocation, study of choice is xray, only do CT scan for chronic or posterior dislocation)
question
Pt. presents to office and reports a fall onto the shoulder, now having pain "in the front middle area" of their chest. on physical exam you notice bruising over the sternoclavicular area. on xray you see minor anterior dislocation. what is appropriate treatment? a. sling b. steroid injection c. medical emergency, refer! d. rest
answer
a (sling if anterior dislocation, posterior is medical emergency, always refer)
question
pt presents to office complaining of deep ache in her right shoulder, states it is worse in the morning but then goes away. has about 150 FF, 20 ER and pain with active ROM. What would be the diagnostic study of choice? a. CT scan b. XR c. MRI d. U/S
answer
b (xray, pt has GH jt OA, only need MRI or CT in sever cases or if patient is undergoing arthroplasty)
question
T/F glenohumeral OA can be treated by primary care in acute setting
answer
true (try to treat with NSAIDs, PT, injection, and if they fail conservative treatment, refer to ortho)
question
pt presents with shoulder pain but when they move their arm it doesn't hurt. you should be most concerned for: a. abdominal pain b. cardiac cause c. shoulder/hand syndrome d. herpes zoster
answer
b (any time shoulder pain but no association with shoulder movement, be worried about non-shoulder causes, most dangerous is always cardiac, but something like pneumonia is also possible)
question
which of the following is a medical cause for shoulder pain? a. herpes zoster b. brachial neuritis c. carpal tunnel syndrome d. shoulder/hand syndrome e. metastatic breast cancer f. ruptured spleen g. all of the above
answer
g ( a lot of medical causes)
question
patient presents with right shoulder pain, and complains of numbness/tingling in the right hand, states sometimes feels like their hand falls asleep. pt has a negative spurlings test, a positive Adson's test and positive Roo's sign. You rule out cervical radiculopathy and EMG comes back with no other identifiable causes. Pt. is most likely struggling with: a. rotator cuff tear b. brachial plexus c. thoracic outlet syndrome d. clavicle fracture
answer
c (thoracic outlet syndrome, extremely difficult to dx or prove, vague symptoms, easily confused, has to be diagnosis of exclusion)
question
what is NOT one of the three types of thoracic outlet syndrome? a. cervical rib/scalene muscle induced b. glenohumeral c. costaclavicular d. hyperabduction
answer
b (first one is d/t the ribs/muscles pressing the neurovascular bundle, costaclavicular occurs under clavicle, and hyerabduction occurs in subcoracoid region)
question
If a patient has a positive diagnosis of thoracic outlet syndrome, should refer to: a. ortho b. cardiothoracic c. neurosurgery d. any/all of the above
answer
d (send to someone else)
question
highschool football player presents to ED with complaint of sudden onset electric shock, burning, heaviness in right upper extremity following a hit in practice that afternoon. based solely on history, patient is likely struggling with: a. rotator cuff tear b. brachial plexus injury c. thoracic outlet syndrome d. cervical radiculopathy
answer
b (brachial plexus, common in football, "stingers", classic presentation of electrical shock, burning, heaviness, or weakness in upper extremity)
question
in a traction mechanism of a brachial plexus injury when the patients head is forced into lateral flexion toward the right side, this will affect the (right/left) side arm
answer
left (traction the brachial plexus of the side that is pulled )
question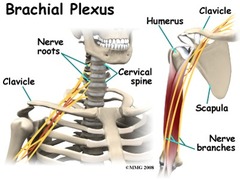
in the (traction/compression) mechanism of brachial plexus injury the plexus, which passes 2-3 cm superficial to the clavicle in front of transverse process of C6, "erb's point", gets pinched

answer
compression (the side that head is moving towards gets pinched)
question
T/F brachial plexus injuries are usually temporary and will resolve on their own but may take several weeks
answer
true (but if it persists should get an EMG/MRI, and REFER if in any doubt)
question
most clavicle fractures occur: a. in lateral 1/3 of clavicle b. in middle 1/3 of clavicle c. in medial 1/3 of clavicle d. no pattern
answer
b (middle, makes sense that this would be weakest)
question
pt. presents to ED after a fall on their right shoulder, states it hurts to reach arm up overhead. on physical exam you notice an anterior deformity between shoulder and manubrium, palpation of the area illicits pain. pt is most likely struggling with: a. clavicle dislocation b. brachial plexus injury c. thoracic outlet syndrome d. clavicle fracture
answer
d (clavicle fracture, usually notable deformity over clavicle, want to look for break in skin and evaluate neurovascular function)
question
pt. presents to ED after a fall on their right shoulder, states it hurts to reach arm up overhead. on physical exam you notice an anterior deformity between shoulder and manubrium, palpation of the area illicits pain. Appropriate studies would be: a. clavicle series XR b. CT scan c. MRI d. U/S
answer
a (clavicle series, only get CT if doesnt heal and pt needs surgery)
question
pt. presents to ED after a fall on their right shoulder, states it hurts to reach arm up overhead. on physical exam you notice an anterior deformity between shoulder and manubrium, palpation of the area illicits pain. x ray shows a closed, non displaced, mid-clavicular fracture. What is appropriate treatment? a. surgical ORIF b. conservative, discontinue use of that shoulder and take NSAIDs c. conservative, sling or figure 8 strap d. no treatment needed
answer
c (give a patient a sling unless, displaced or not healing)
question
Pt. is a 55 year old female who presents to ED after falling down the steps in their split level, she has severe right arm pain and is too afraid to try to lift it. On exam you see pt has edema, ecchymosis bruising over the upper arm. patient has full movement and sensation of fingers. on xray you see a distal, non-displaced, humeral fracture. what is the best treatment? a. surgery, ORIF b. reverse total shoulder arthroplasty c. long arm cast d. sling, cant use cast if above elbow
answer
c (long arm cast appropriate for distal humerus fracture)
question
Pt. is a 55 year old female who presents to ED after falling down the steps in their split level, she has severe right arm pain and is too afraid to try to lift it. On exam you see pt has edema, ecchymosis bruising over the upper arm. What is the most important testing you need to do next? a. xray, A/P lateral, oblique b. test wrist/digit extension c. test elbow extension d. CT
answer
b (must rule out radial nerve injury, need to test wrist/digit extension)
question
Pt. is a 55 year old female who presents to ED after falling down the steps in their split level, she has severe right arm pain and is too afraid to try to lift it. On exam you see pt has edema, ecchymosis bruising over the upper arm. patient has full movement and sensation of fingers. on xray you see a mid-humerus 3 part non-union fracture. what is the best treatment? a. sling b. long arm cast c. surgical repair using plate d. reverse total shoulder arthroplasty
answer
c (surgical repair for malunion, non-union or unstable fractures, use intramedullary nailing vs plate)
question
Pt. is a 80 year old Caucasian female who presents to the office after falling on her driveway due to the ice, she has a lot of pain in her right shoulder and is too afraid to lift her arm. you see edema and ecchymosis over the shoulder area on x-ray you see three part greater tuberosity fracture. What is the best treatment option. a. conservative management in a sling b. fix using a plate c. reverse total shoulder arthroplasty d. total shoulder arthroplasty
answer
c (pt has a proximal humerus fracture, fix if it is a 3 or 4 part fracture, options are hemiarthroplasty vs reverse, but IMHO reverse would make more sense for an 80 year old b/c she likely doesn't have a great RC anyway, and you can't but a plate on the ball of the joint)
question
T/F if a patient has a non-displaced fracture of the humeral head can heal conservatively with a sling
answer
true (wait to do physical therapy until arm is healed though)
question
Pt. presents to ED following an MVA, has pain and tenderness over the scapula and you believe they have fractured their scapula, where is the most likely part of the scapula to be fractured? a. coracoid b. glenoid c. body d. neck e. acromion f. spine
answer
c (body)
question
Pt. presents to ED following an MVA, on xray you see a fracture of the body of the scapula, what other pathologies should you be concerned about in this patient? a. axillary artery injury b. pneumothorax c. rib fractures d. pulmonary contusion e. brachial plexus injuries f. all of the above
answer
f (as he explained it, if that much energy is passing through the body, something in front is likely injured too)
question
Pt. presents to ED following an MVA and has pain and tenderness over the posterior shoulder, has edema and ecchymosis over the scapula, inability to move the arm. has full movement and sensation of fingers. You need to rule out: a. scapula fracture b. cardioplumonary involvement c. brachial plexus injury d. neurological deficit
answer
b (with scapula fracture always rule out cardiopulmonary involvement, always assess neurovascular status)
question
most common form of treatment for scapula fracture is (ORIF/sling)
answer
sling (if displacement may require ORIF)



