Pharm 7 – Inhalation Agent Pharmacokinetics – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
What is a partial pressure of a gas? How do we alter partial pressure? How would 6% desflurane translate into a partial pressure measurement?
answer
The pressure exerted by a gas that is altered by the variables of the ideal gas law (PV=nRT) In anesthesia the # of molecules (n) is the only variable intentionally altered (by adjusting the dial on the vaporizers) 6% des = 6% of 760mmHg = 45.6mmHg
question
What is PA?
answer
The alveolar partial pressure.
question
What is Pa?
answer
The arterial partial pressure.
question
What is Pb?
answer
The brain partial pressure.
question
Why is the PA used as an index of the depth of anesthesia?
answer
The PA mirrors the Pb, as a result, the PA is an indirect measure of the Pb.
question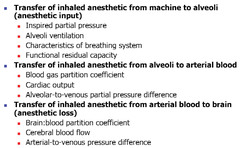
What factors will effect partial pressure gradients necessary for anesthesia?

answer
Anything that influences the PA
question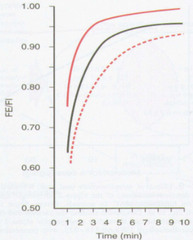
How does the inspired concentration of inhaled anesthetic effect the rate of increase of the alveolar concentration?

answer
? PI = more rapid ?PA (PI=FI) (also ?s the maximum PA possible)
question
What is the second gas effect?
answer
-Using a second gas (nitrous) to speed the induction when using a slow agent is used (slow agents have high B:G SC like iso or halothane)
question
How does alveolar ventilation effect the rate of increase in PA?
answer
?alveolar ventilation = ? rate of PA increase (Increased ventilation, like PI, promotes input of inhaled anesthetic to offset uptake into blood. The net effect is a more rapid rate of increase in the PA, and thus an increase in induction of anesthesia.)
question
Explain the differences between spontaneous vs mechanical ventilation.
answer
-Spontaneous: protective mechanism to prevent excessively deep anesthesia -Mechanical: no protection & caution required to prevent too deep & toxicity (With spontaneous breathing inhaled anesthetics produce a dose-dependent depressant effect on alveolar ventilation. This negative-feedback protective mechanism prevents excessive depth of anesthesia when ventilation is decreased. When concentration of partial pressure in the brain decreases to a certain threshold, ventilation increases and the delivery of the anesthetic to the lungs increases.) (The protective mechanism associated with spontaneous breathing is lost, for this reason it may be appropriate to decrease the PI of volatile anesthetics when ventilation is changed from spontaneous to controlled to maintain the PA similar to that present during spontaneous ventilation.)
question
How does the characteristics of the breathing system effect PA?
answer
The breathing system can buffer the rise in PA on induction as well as the fall in PA on emergence. (not such an issue anymore) -volume of the system -solubility of the "rubber" components (Volume of the system acts as a buffer to slow the attainment of PA. Solubility of inhaled anesthetics in the rubber or plastic components of the system initially slow the rate at which PA rises, and at the conclusion of the anesthetic may slow the rate at which PA decreases. Gas inflow from the anesthetic machine help to negate the buffering effect.)
question
Reuse of the same anesthetic rebreathing system on another patient could expose the patient to what?
answer
-trace concentration & risk for MH (Trace concentrations of that anesthetic, even if another anesthetic drug or technique is selected. Exposure to trace amounts of triggers can increase the risk of development of MH.)
question
What is FRC?
answer
Functional reserve capacity.
question
How does FRC effect PA and thus rate of induction of anesthesia?
answer
The greater the alveolar ventilation to FRC ratio, the more rapid is the rate of increase in PA.
question
What factors of pulmonary ventilation will effect the rate of PA? (x2)
answer
rate depth (tidal volume - dead space) in other words, alveolar ventilation
question
How does pulmonary blood flow effect PA? What agents are most affected by this
answer
?pulm blood flow = ? rate of PA rise agents that are more soluble (iso, halothane) are affected greater by pulmonary blood flow (An increase in pulmonary blood flow exposes more blood to the anesthetic and thus reduces the rate of rise in arterial tension particularly for anesthetics with moderate to high solubility.)
question
What denotes the solubility of the inhaled anesthetics in the blood and tissues?
answer
The partition coefficient
question
What is the partition coefficient?
answer
A distribution ratio describing how the inhaled anesthetic distributes itself between two phases at equilibrium (partial pressures equal in both phases).
question
How does blood solubility effect the rate of PA and rate of induction?
answer
Less soluble (sevo, des, nitrous) have more rapid PA rise. (Induction of anesthesia is slower with more soluble anesthetic gases. When blood solubility is low, relatively few molecules of anesthetic are required to raise its partial pressure and the arterial tension rises quickly, this results in more rapid equilibrium with the brain and faster induction of anesthesia.)
question
*!* What agents are considered to be soluble, intermediate soluble, and poorly soluble anesthetics?
answer
soluble: Methoxyflurane intermediate-soluble: Halothane, enflurane, isoflurane poorly-soluble: Nitrous oxide, desflurane, sevoflurane
question
What is the Oil:Gas PC? What does this represent?
answer
solubility in olive oil This coefficient parallels anesthetic requirements. MAC can be calculated as 150 divided by oil:gas PC.
question
How does Cardiac Output effect the rate of PA increase?
answer
?CO = faster PA increase (opposite of IV agents) vs good CO will equilibrate slower (A high CO results in more rapid uptake, such that the rate of increase in PA is slowed. A low CO speeds the rate if increase in PA since there is less uptake into the blood to impose output.)
question
What is the alveolar to venous partial pressure differences?
answer
The A-vD reflects tissue uptake of the inhaled anesthetic.
question
-What tissues are classified as highly perfused? -What tissues are poorly perfused? -How do the individual agents concentrate into each of these tissues? -What effect does this have on the onset and duration of action of each of the individual inhalation agents?
answer
-highly perfused: Brain, heart, kidneys -poorly perfused: Skeletal muscle and fat -see picture -agents that have high uptake to tissues have delayed onset & prolonged duration of action (iso>des,sevo,nitrous)
question
How are the inhalation agents eliminated?
answer
The pulmonary epithelium is the channel of elimination.
question
What drug characteristic will have the greatest effect on elimination?
answer
solubility (more soluble = more uptake) -duration of exposure is also important (The lower the solubility in blood and brain, the faster the rates of elimination. Long duration of exposure can affect time of recovery because it causes accumulation in tissues with low blood perfusion. The higher the blood solubility, the higher the extent of accumulation over the same exposure of time.)
question
What is MAC?
answer
Defined as that concentration at 1 atm pressure which causes immobility in 50% of patients when exposed to a noxious stimulus such as surgical incision.
question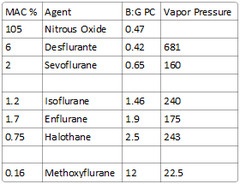
What is the MAC of nitrous oxide?

answer
105
question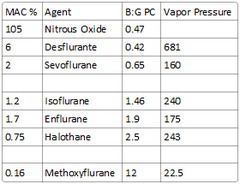
What is the MAC% of halothane?

answer
0.75
question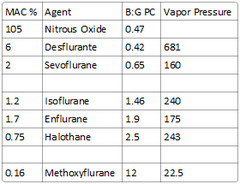
What is the MAC% of methoxyflurane?

answer
0.16
question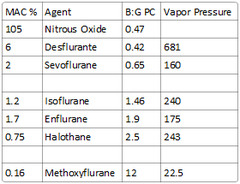
What is the MAC% of enflurane?

answer
1.7
question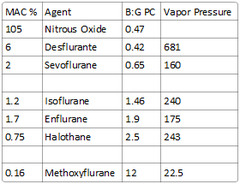
What is the MAC% of desflurane?

answer
6
question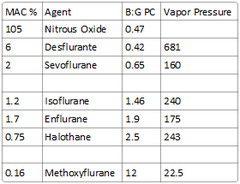
What is the MAC% of sevoflurane?

answer
2
question
What factors will increase MAC?
answer
Hyperthermia, chronic alcohol use, drug induced increases in CNS catecholamine levels (MAOI, cocaine, ephedrine, levodopa), hypernatremia, hyperthyroid.
question
What factors will decrease MAC? (just read the card)
answer
Hypothermia, increasing age, pre-op meds, drug induced decreases in CNS catecholamine levels, alpha 2 agonist, acute alcohol ingestion, postpartum, pregnancy, lithium, neuraxial opioids, lidocaine, hypoxia (PaO2 <38), BP (<40), cardiopulmonary bypass, hyponatremia, anemia, metabolic acidosis.
question
What drugs decrease MAC? (just read the card)
answer
Opioids, opioid agonist-antagonist, diazepam, methyldopa, respirine, chronic dextroamphetamine, alpha-2 agonist, lithium, ketamine, pancuronium, physostigmine (10 x clinical dose), lidocaine, chlorpromazine, verapamil, hydroxyzine, ?-9 tetrahydrocanabinol.
question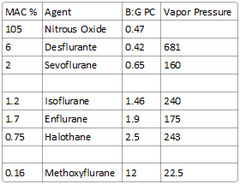
What is the vapor pressure of halothane?

answer
243
question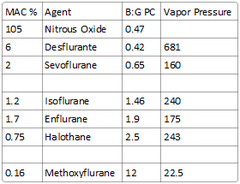
What is the vapor pressure of methoxyflurane?

answer
22.5
question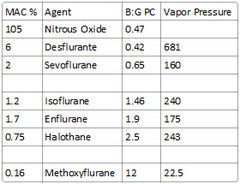
What is the vapor pressure of enflurane?

answer
175
question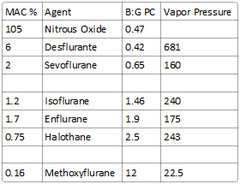
What is the vapor pressure of desflurane?

answer
681 (requires heated vaporizer)
question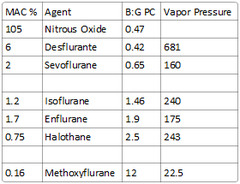
What is the vapor pressure of sevoflurane?

answer
160
question
Input vs Uptake
answer
-Input is the delivery to the alveoli (speeds things up) -Uptake is loss of the drug from the alveoli to into arterial blood (which is lost into the tissues) (slows induction & ?s effect of inhalational agents)
question
Describe metabolism & elimination of inhalation agents. What are some exceptions (x2)?
answer
-eliminated by the lungs unmetabolized -exception is halothane which is ~15% metabolized in the liver -sevoflurane has minimal metabolism (6-7%) in the liver
question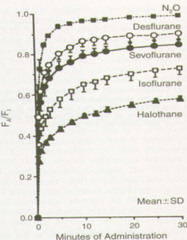
What is the FA to FI ratio? What would a FA:FI of 1 mean? How does the blood:gas partition coefficient relate?

answer
-Compares the inspired to expired gas concentrations. -A value of 1 indicates tissues are no longer uptaking any agent (not possible). -A low blood:gas partition coefficient indicates more rapid equilibrium [less uptake to tissues]
question
How does the alveolar ventilation to FRC ratio relate to speed of induction? -compare adults & neonates
answer
(alveolar ventilation is MV minus dead space) -the higher the AV:FRC ratio the more rapid the induction -ratio in neonates is 5:1 vs 1.5:1 in adults (neonates will induce much more rapidly)
question
What is FD
answer
fraction delivered (the dial setting on the vaporizer)
question
Volume of the breathing circuit
answer
6 L
question
What is FA? How is it measured?
answer
also called PA, it is the alveolar concentration or alveolar partial pressure, mirrors Pbr -measured on expiration
question
What 3 agents equilibrate rapidly? What values (x3) represent this ability to rapidly equilibrate?
answer
-Nitrous (B:G PC of 0.47) -Sevoflurane (B:G PC of 0.65) -Desflurane (B:G PC of 0.42)
question
An agent with a low B:G PC would induce ____ & come off ____
answer
rapidly, fast
question
Calculate the expected alveolar partial pressure of 6% of desflurane at 1 atm and at equilibrium
answer
45.6 mmHg (6% of 760mmHg is 45.6)
question
Calculate the expected alveolar partial pressure of 1.2% isoflurane at 1 atm and at equilibrium
answer
9.12 mmHg (1.2% of 760 is 9.12 mmHg)
question
What are the blood-gas partition coefficients of the agents we use? (x4) What are they for the agents we don't use? (x3)
answer
Desflurane - 0.42 Nitrous Oxide - 0.47 Sevoflurane - 0.65 Isoflurane - 1.4 Enflurane - 1.9 Halothane - 2.4 Methoxyflurane - 12
question
What 3 things will ? uptake to the tissues? How does this affect FA? What equation describes these variables?
answer
-?cardiac output -?B:G SC -?concentration gradient (alveolar to venous partial pressure difference) ?s FA ; inhibits a rapid rise (slows induction ; prevents equilibrium) Uptake = CO X concentration gradient X b:g solubility Uptake = Q x (Pa-Pv) x ?
question
What inhalation agents benefit more from using methods to offset uptake (overpressuring, ?alveolar ventilation, ?FGF, etc.)?
answer
Agents with a high B:G SC (iso, halothane, enflurane,) benefit more than those with a lower B:G SC (nitrous, des, sevo)
question
What methods can be used to offset uptake (speed induction)? (x4)
answer
-overpressurize (concentrating effect) -?FGF -? alveolar ventilation -second gas effect
question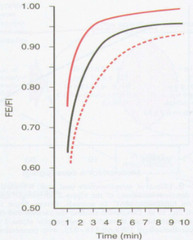
How does turning up the dial on your agent affect the alveolar partial pressure (x2)

answer
-speed of increase of FE (PA=FA=FE) to equilibrate with FI (FI=PI) increases. -maximum FE (PA) that can be achieved increases.
question
Which agent that we use would have the greatest benefit to overpressurization, 2nd gas, ?MV, etc.? Why?
answer
Isoflurane -has moderate solubility (B:G PC of 1.4) (halothane, enflurane, ; methoxyflurane are also more soluble ; would benefit but we don't use these)
question
If you increased the inspired concentration (FI=PI) (turned up your dial) by double, what would you expect the alveolar concentration (FE=PA=FA) to do?
answer
Increase by more than double (not a linear effect) -?ing the inspired concentration results in a disproportionately high alveolar concentration
question
What 2 effects result from mechanical ventilation that might require a decrease in concentration of agent compared to someone who is spontaneously breathing?
answer
-? alveolar ventilation (?input) -? cardiac output (?uptake)
question
How is depth of anesthesia somewhat autoregulated with spontaneous breathing?
answer
-inhaled anesthetics produce dose-dependent depression of alveolar ventilation = ? input -as concentration falls in the brain, ventilation increases = ? input
question
After induction & the agent has mostly equilibrated you convert the pt from spontanous breathing to controlled ventilation. What might you need to do? Why?
answer
? PI (PI=FI) [turn down the agent] to maintain PA (PA=FE=FA) similar to that present during spontaneous ventilation Pts lose their hypoventilatory protective mechanism with mechanical ventilation that prevents excessive depth of anesthesia
question
Would hyperventilation speed induction using desflurane? Why?
answer
Not really it has a low enough B:G PC that other slower agents with higher B:G PC like iso would benefit from this more
question
Equation to calculate MAC
answer
MAC = 150 / Oil:gas partition coefficient
question
What are the oil:gas partition coefficients of all of the agents?
answer
just divide 150 by the MAC% (not perfect but can give you a ballpark #) (MAC% = 150 / Oil:gas PC)
question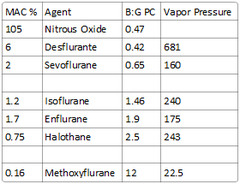
What is the blood:gas partition coefficient of Nitrous Oxide?

answer
0.47
question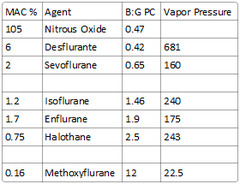
What is the blood:gas partition coefficient of Desflurane?

answer
0.42
question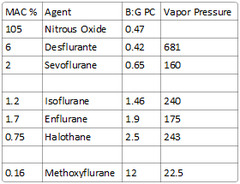
What is the blood:gas partition coefficient of Sevoflurane?

answer
0.65
question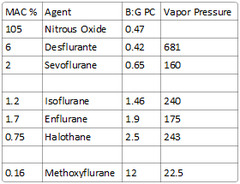
What is the blood:gas partition coefficient of Isoflurane?

answer
1.46
question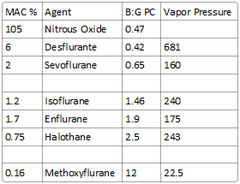
What is the blood:gas partition coefficient of Enflurane, halothane, & methoxyflurane?

answer
Enflurane: 1.9 Halothane: 2.5 Methoxyflurane: 12
question
What does the alveolar to venous difference (A-vD) indicate
answer
uptake of the anesthetic (a high A-vD difference means significant amounts are being uptaken by the tissues)
question
Highly perfused tissues (brain, heart, kidneys) in the adult account for ____ % of the body mass but receive ____% of the cardiac output.
answer
10% body mass 75% of cardiac output
question
How does lipid solubility relate to accumulation in tissues?
answer
The higher the lipid solubility (& lower the MAC) the more accumulation will occur in the tissues (prolonged use leads to more accumulation)
question
Why fast offset (des, sevo) may be an issue at the end of the case (think pt comfort)
answer
If surgery is associated with pain they will feel it right away (you need to give analgesic soon enough that it will have taken effect at time of emergence)
question
What effect does low doses (0.1 MAC) of volatile anesthetics have on pain?
answer
exaggerate pain
question
What agent do we use still has 6% liver metabolism?
answer
sevoflurane
question
What is the anesthetic MAC range? (since everyone responds differently & 1 MAC would prevent surgical stimulation in 50% of subjects)
answer
0.5-2 MAC
question
What effect does hypermetabolic issues (hyperthermia, hyperthyroid, etc.) have on MAC requirements?
answer
? MAC requirements
question
What effect does hypometabolic issues (hypothermia, etc.) have on MAC requirements?
answer
? MAC requirements
question
What effect does drugs that increase CNS catecholamine levels (ephedrine, MAOIs, levadopa, cocaine) have on MAC requirements?
answer
? MAC requirements
question
What effect does sodium have on MAC requirements?
answer
hypernatremia - ? MAC requirements hyponatremia - ? MAC requirements
question
What effect does pregnancy have on MAC requirements? When does this resolve?
answer
? MAC (30%?) resolves 24-72 hrs postpartum
question
What effect does lithium have on MAC requirements?
answer
? MAC requirements
question
What effect does hypoxia & metabolic acidosis have on MAC requirements?
answer
? MAC requirements
question
What effect does anemia have on MAC requirements?
answer
? MAC requirements
question
What effect does cardiopulmonary bypass have on MAC requirements?
answer
? MAC requirements
question
What effect does lidocaine & neuraxial opioids have on MAC requirements?
answer
? MAC requirements
question
*!* What is the maximum (ceiling) each of the opioids can decrease MAC? (x5)
answer
-Sufentanil can ? MAC by 70-90% -Remifentanil can ? MAC by 50-90% -Alfentanil can ? MAC by 70% -Morphine an ? MAC by 65% -Fentanyl can ? MAC by 50%
question
What effect do drugs that decrease catecholamine levels (methyldopa, alpha-2 agonists, older antihypertensives) have on MAC requirements?
answer
? MAC requirements
question
What effect does ketamine have on MAC?
answer
? MAC requirements
question
What effect does verapamil have on MAC?
answer
? MAC requirements
question
What effect do opioids, opioid agonist-antagonist, diazepam, chlorpromazine have on MAC?
answer
? MAC requirements
question
Define MAC-bar
answer
MAC that blocks adrenergic and cardiovascular response in 50% of patients. Typically this is 1.5 MAC (1.7-2 in notes)
question
Define MAC-Awake
answer
MAC that still allows eye opening on command. Typically 0.5 MAC (0.3-0.5 in notes)
question
What MAC tends to prevent movement to noxious stimuli in 99% of patients
answer
1.3 MAC



