Organic Chemistry 1 Chapter 1-3 – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Methane
answer
1 C; CH4; CH4
question
Ethane
answer
2 C; C2H6; CH3CH3
question
Propane
answer
3 C; C3H8; CH3CH2CH3
question
Butane
answer
4 C; C4H10; CH3CH2CH2CH3
question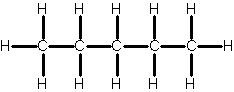
Pentane

answer
5 C; C5H12; CH3(CH2)3CH3
question
Hexane
answer
6 C; C6H14; CH3(CH2)4CH3
question
Heptane
answer
7 C; C7H16; CH3(CH2)5CH3
question
Octane
answer
8 C; C8H18; CH3(CH2)7CH3
question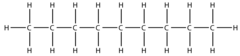
Nonane

answer
9 C; C9H20; CH3(CH2)8CH3
question
Decane
answer
10 C; C10H22; CH3(CH2)8CH3
question
Ionic bond
answer
To obtain a noble gas configuration, atoms may transfer electrons from one atom to another. Electron density completely transferred from one atom to another.
question
Covalent bond
answer
Electron density is shared between two atoms, where each atom has a full valence shell.
question
Nonpolar Covalent Bonds
answer
Electrons are shared equally by two bonded atoms.
question
Polar Covalent Bonds
answer
Electrons are shared unequally by two bonded atoms.
question
Electronegativity
answer
Is the relative ability of an atom in a particular molecule to attract shared electrons to itself. It is used to determine whether a given bond with be non polar covalent, polar covalent, or an ionic bond.
question
Electronegativity range
answer
values range from 0.7-4.0; larger values means the element attracts electrons more strongly (negative end), while the smaller values attract electrons weakly (positive end).
question
Electronegativity scale on the Periodic Table
answer
It increases as you go from left to right and as you go from bottom to top.
question
How are bonds classified?
answer
Classified based upon the difference in electronegativity between the bonding atoms.
question
Pure Covalent Bonds (non polar) Classification
answer
Difference is 0-0.4; Shared equally. C-H 2.5-2.1=0.4
question
Polar Covalent Bonds Classification
answer
Difference is >0.4-2.0; H-F 2.1-4.0=1.9
question
Ionic Bonds Classification
answer
Difference is >2.0; electron has been completely transferred at this point. NaCl 0.9-3.0=2.1
question
G.N Lewis
answer
American chemist who built the UC Berkeley Chem. Dept. Lewis symbols and structures and Lewis acid-base theory.
question
Octet Rule
answer
When atoms bond together to form molecules, the atoms transfer or share electrons in such a way as to attain a filled shell of electrons.
question
Drawing Lewis Structures 1
answer
Determine the number of electrons in the structure by: summing the valence electrons for each atom in the formula, then add 1 for each negative charge or subtract 1 for each positive charge.
question
Drawing Lewis Structures 2
answer
Draw skeletal structure- central atom generally least electronegative element. Hydrogens are always outer atoms. Connect the atoms with lines (bonds).
question
Drawing Lewis Structures 3
answer
Count the number of electrons used and subtract from the total available.
question
Drawing Lewis Structures 4
answer
With the remaining electrons start with the outer atoms and add pairs of electrons to complete the octets for atoms bonded to the central atom.
question
Drawing Lewis Structures 5
answer
If any electrons remain after step 4, place them on the central atom.
question
Drawing Lewis Structures 6
answer
If any atoms lack an octet at this point, move non-bonding pairs of electrons to make double or triple bonds until atoms have an octet.
question
Lone Pairs
answer
AKA Nonbonding electrons, are valence shell electrons that are not shared between atoms.
question
Condensed Structures
answer
All atoms are drawn in, but the bond lines are omitted (double and triple bonds are usually drawn). Atoms drawn next to the atoms to which they are bonded. Parentheses are used around similar groups bonded to the same atom. Lone pairs are omitted. CH3(CH2)2CH3
question
Heteroatom
answer
Any element other than carbon or hydrogen.
question
Skeletal Structures
answer
AKA Line structures: don't label carbon atoms, they are at the intersection of 2 or more lines and at the end of lines. Don't draw hydrogens attached to carbon (it is a given that they are there). Draw in all heteroatoms and hydrogens directly bound to them.
question
Formal Charge
answer
A hypothetical charge on an atom. They are not real or measured.
question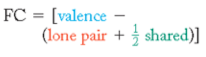
How to calculate formal charge
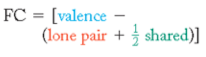
answer
+( # of valence electrons of atom) - ( # of unshared electrons of atom) - ( 1/2 # of shared electrons.
question
Expanded Octets
answer
Some elements form more than 4 bonds. Such as Sulfur and Phosphorous form up to 6 bonds, meaning they share 12 electrons.
question
Paramagnetic
answer
Substances that are attracted to magnetic fields. They have one or more unpaired electrons. The more unpaired electrons, the stronger the attraction. Elemental Oxygen (O2) is paramagnetic, but the Lewis structure doesn't show unpaired electrons.
question
Diamagnetic
answer
Substance that are weakly repelled by magnetic fields. They have no unpaired electrons.
question
Molecular Orbital Theory
answer
The combination of atomic orbitals on different atoms forms molecular orbitals. Electrons in these orbitals belong to the molecule. Provides us with electron distributions, bond energies, and magnetic properties.
question
Valence Bond Theory
answer
Bonds result from the sharing of electrons in overlapping orbitals of different atoms. Orbitals may be atomic or hybridized atomic. Electrons are localized in the bonds between the two atoms.
question
Antibonding
answer
higher energy
question
Bonding
answer
lower energy
question
Pi Bonding
answer
The sideways overlap of two parallel p orbitals leads to pi bonding MO and an pi* anti bonding MO. It is not as strong as most sigma bonds.
question
Boundary Surface Representation for s Orbitals
answer
circular (ball-like)
question
Boundary Surface Representations for p Orbitals
answer
1 infinity sign. 2px, 2py, and 2pz
question
Boundary Surface Representation for d Orbitals
answer
4 infinity signs together. dyz, dxz, dxy, dx2-y2, and dz2
question
The overlap of s, p, d and f atomic orbitals often result in
answer
unpredictable predictions.
question
Hybrid Orbitals
answer
s, px, py, and pz atomic orbitals can be combined to give four spy hybrid orbitals.
question
VSEPR
answer
Each group of valence electrons around a central atom is located as far away from others as possible to minimize repulsions. The repulsions maximize the space that each object attached to the central atom occupies, result is 5 arrangements of electron-groups.
question
The electron groups of VSEPR define the__ but the molecular shape is defined by the ___.
answer
object arrangement; relative portions of the atoms bonded to the central atom.
question
Drawing in 3D
answer
Simple lines represent bonds that are in the plane of the paper. Wedge shaped lines represent bonds that project forward to atoms. Dashed lines indicate bonds that go back to atoms.
question
Rotation of Single Bonds
answer
Ethane is composed of two methyl groups bonded by the overlap of the spy hybrid orbitals. There is free rotation along single bonds. The hydrogens arrange themselves around the central atoms when rotation occurs.
question
Bonding in Ethylene
answer
Ethylene has three sigma bonds formed by its sp2 hybrid orbitals in a trigonal planar. The unhybridized p orbital of one carbon is perpendicular to its sp2 hybrid orbitals, and it is parallel to the unhybridized p orbital of the second carbon. Overlap of these 2 p orbitals will produce a pi bond (double bond) that is located above and below the sigma bond.
question
Can rotation occur in double bonds?
answer
No they are permanent.
question
Bond Dipole Moments
answer
Due to difference in electronegativity. They depend on the amount of charge and distance separation. Measured in debyes (D).
question
Molecular Dipole Moments
answer
The vector sum of the bond dipole moments. Depends on bond polarity and bond angles. Lone pairs of electrons contribute.
question
Intramolecular Forces
answer
bonding forces; exist within each molecule. They influence the chemical properties of the substance.
question
Intermolecular Forces
answer
non-bonding forces; exist between molecules. They influence the physical properties of the substance. Intermolecular are much weaker than intramolecular. When a substance melts or boils the intermolecular forces are broken.
question
Dipole-dipole interactions
answer
The attractive forces between the permanent dipoles of two polar molecules.
question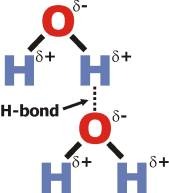
Hydrogen Bonds

answer
They are very strong dipole-dipole forces. Interaction between a H covalently bonded to strongly electronegative atoms (Z=O, N or F) and nonbonding electron pairs on other strongly electronegative atoms (O, N or F). As electrons are pulled away from H by an electronegative atom, what is left is an unshielded proton that will strongly attract neighboring electrons. Represented by a dotted or dashed line.
question
H-bond Acceptor between two water molecules
answer
An H is forming a hydrogen bond to the lone pair on the oxygen of the other molecule. This means that the molecule with the oxygen attached is the H-bond acceptor.
question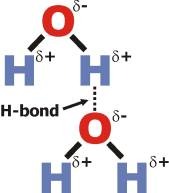
H-bond Donor between two water molecules

answer
An H is forming a hydrogen bond to the lone pair on the oxygen of the other molecule. This means that it is the molecule with the hydrogen attached is the H-bond donor.
question
Water is a molecule that is capable of being either the ___ or the ____ of a hydrogen bond.
answer
an acceptor or a donor.
question
Some molecules have the ability to hydrogen bond, but they are only capable of playing the role of an acceptor.
answer
For example, 2 molecules of Acetone cannot hydrogen bond because the oxygen does not have a hydrogen covalently bonded to it. However, Acetone could hydrogen bond with water where water is the H-donor and Acetone is the H-acceptor.
question
London dispersion forces
answer
One instantaneous dipole can induce another instantaneous dipole in an adjacent molecule (or atom). London dispersion forces are the forces between instantaneous dipoles. AKA induced dipoles or Van der Waals forces. All molecules have them and th
question
London dispersion forces characteristics
answer
All molecules have them and they are temporary. The size of the force depends on: The number of electrons and the shapes of the molecules.
question
Surface area determines strength of Intermolecular Forces.
answer
The larger the surface area, the larger the attractive force between two molecules, and the stronger the intermolecular forces.
question
Strength of Ion-Dipole
answer
Basis of Attraction: Ion-charge-dipole charge Energy: 40-600 kJ/mol
question
Strength of H bond
answer
Basis of Attraction: Polar bond to H-dipole charge (high EN of N,F, O) Energy: 10-40 kJ/mol
question
Strength of Dipole-Dipole
answer
Basis of Attraction: Dipole Charges Energy: 5-25 kJ/mol
question
Strength of Ion-induced dipole
answer
Basis of Attraction: Ion-charge-polarizable electron cloud. Energy: 3-15 kJ/mol
question
Strength of Dipole-induced dipole
answer
Basis of Attraction: Dipole-charge-polarizable electron cloud. Energy: 2-10 kJ/mol
question
Strength of Dispersion (London)
answer
Basis of Attraction: Polarizable electron cloud. Energy: 0.05-40 kJ/mol
question
3 States of Matter-> How many types of Solutions?
answer
7
question
Gas as Solute:
answer
Solvents: Gas: (O2 in N2) Air Liquid: (CO2 in H2O) Carbonated Beverages Solid: (CH4 in Ice) Methane Hydrate
question
Liquid as Solute
answer
Solvents: Gas: Not possible Liquid: (HC2H3O2 in H2O) Vinegar Solid: (Hg in Ag) Dental Fillings
question
Solid as Solute
answer
Solvents: Gas: Not possible Liquid: (NaCl in H2O) Ocean Water Solid: (Zn in Cu) Brass
question
The process of dissolution represents a competition:
answer
-Energy of the solvent-solute interactions. -Energy of the intermolecular forces of the solute itself. -Energy of the intermolecular forces of the solvent itself.
question
If the solvent-solute interactions win:
answer
The material may dissolve (said to be soluble or miscible.)
question
If the solute-solute interactions win:
answer
The material may not dissolve (insoluble or immiscible.)
question
The solute-solvent interactions are greater than:
answer
the sum of the solute-solute and solvent-solvent interactions. Favorable for solution formation.
question
The solute-solvent interactions are less than:
answer
the sum of the solute-solute and solvent-solvent interactions. Not favorable for solution formation.
question
Resonance Structures
answer
When there is more than one Lewis structure for a molecule that differ only in the position of the electrons. Lone pairs and multiple bonds in different positions. One resonance contributor is converted by another by the use of curved arrows which show the movement of electrons.
question
Resonance Hybrid
answer
The actual molecule is an average of all the resonance forms. It doesn't resonate between forms, although we draw it that way.
question
Rules for Resonance:
answer
-Individual structures exist only on paper. -Individual structures must be valid Lewis Structures. -Only electrons are allowed to move between resonance structures. -position of nuclei must remain the same. -only electrons in pi bonds and lone pairs can be moved.
question
Resonance forms can be compared using the following criteria, beginning with the most important:
answer
1. Has as many octets as possible. 2. Has as many bonds as possible. 3. Has the negative formal charge on the most electronegative atom. 4. Has as little formal charge separation as possible.
question
Assessing unequal resonance forms with the use of formal charges:
answer
1. The fewer and smaller the formal charges of a Lewis structure, the better the structure. 2. Negative formal charges should reside on more electronegative atoms.
question
The better resonance form for Sulfuric Acid
answer
One resonance structure for Sulfuric Acid contains more bonds (extending the octet rule on Sulfur with 12 electrons attached) but has less formal charges. We would think that this would be the better structure due to the formal charges and that Sulfur is capable of having an extended octet. This is not the case, the better resonance form would be to have less bonds (octet rule is being abided by sulfur with only 8 electrons attached) and having a larger formal charge. Octet rule is more important than a smaller formal charge.



