O2 Therapy ATI – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
1. Tachycardia, 2. tachypnea 3. Restlessness, anxiety, confusion 4. Pale skin, mucus membranes 5. Elevated blood pressure 6. use of accesory muscles nasal flaring, tracheal tugging, adventitous lung sounds
answer
Indications of hypoxemia Early
question
Stopr cyanotic skin bradypnea hypotension cardiac dysarthmia
answer
Later indicatons of hypoxemia
question
used around fire or in an environment where there's a potential for sparks. It is recommended that oxygen delivery systems be kept 10 feet from any open flame
answer
O2 should not be
question
The electrical equipment must be functioning properly and well grounded. Both have the potential to cause sparks if they malfunction and could result in fire. Teach children receiving oxygen therapy not to play with electric or friction toys since they can also cause sparks.
answer
Caution patients when using electrical equipment in such as razors or radios when oxygen is in use.
question
oxygen is supplied in different ways. In inpatient settings, oxygen is usually stored in large holding tanks outside of the building and piped in to patient rooms via outlets on the wall that are located behind the patient's bed. In home care, oxygen is usually supplied in small portable tanks.
answer
Depending on the setting,
question
Keep them upright and secured with a chain or in an appropriate holder to keep them from falling and the valve rupturing. Store empty oxygen tanks upright as well and secure them appropriately.
answer
Always handle oxygen tanks with caution.
question
make sure all equipment is checked. The oxygen should be turned on and the flow meter and regulator checked to make sure they are functioning properly. The gauge indicating the level of oxygen in the tank should also be checked to make sure there is an adequate amount remaining.
answer
Before initiating oxygen therapy,
question
who are recovering from surgery and may be in pain or still sedated. It also includes patients who have a respiratory illness that causes excessive secretions to accumulate in the lungs or conditions that reduce the circulation of blood through the lungs. Many patients with cardiac conditions are also at risk of developing hypoxia and benefit from oxygen therapy.
answer
Oxygen therapy is indicated for patients who are at risk for developing hypoxia. This includes patients
question
what signs and symptoms he or she will exhibit. The patient's age, general health, current disease process, and history of chronic illness also play a role in how the patient responds to hypoxia.
answer
The degree of hypoxia the patient is experiencing usually determines
question
the patient is often restless and confused and might report feeling anxious. The patient's vital signs might also vary from baseline, with heart rate, respiratory rate, and blood pressure elevated.
answer
n the early stages of hypoxia,
question
the patient is likely to develop hypotension, bradycardia, and metabolic acidosis. The patient may also develop cyanosis, a bluish discoloration of the skin and mucous membranes.
answer
In the late stages of hypoxia,
question
1. clubbing of their fingers and toes, 2. peripheral edema, 3. right-sided heart failure, and an oxygen saturation below 87%.
answer
chronic hypoxia, the manifestations differ and develop over time. These patients often have
question
the patient's condition can deteriorate, resulting in a decrease in activity level, an increase in confusion, a decrease in level of consciousness, and possibly coma.
answer
If hypoxia is left untreated,
question
1. Restlessness 2. Confusion 3. Anxiety 4. Elevated Blood pressue 5. Increased Heart Rate 6. Increased resp. Rate 7. Dyspnea
answer
Early Signs of hypoxia
question
1. Decreased level of conciousness 2. Decreased activity level 3. Hypotension 4. Bradycardia 5. Metabolic acidosis 6. Cyanosis
answer
Late signs of hypozia
question
1. Clubbing of the fingers and toes 2. Peripheral Edema 3. Right sided heart failure 4. Resp. Acidosis 5. O2 saturation less than 87 percent
answer
Chronic
question
(a complication that causes confusion, tremors, convulsions, and coma) can result. This complication can ultimately lead to respiratory arrest if left untreated. Positioning is also very important;
answer
Assess patients receiving oxygen therapy, especially those diagnosed with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), frequently for any changes in their condition. When patients with COPD receive oxygen at too high a flow rate, carbon dioxide narcosis
question
semi- or high-Fowler's position helps facilitate lung expansion. Turning and repositioning, coughing and deep breathing will also promote ventilation.
answer
having the patient in a
question
delivering oxygen should help prevent or resolve the manifestations of hypoxia. With effective oxygen therapy for patients who have hypoxia, vital signs and oxygen saturation should move closer to normal or to the patient's baseline readings.
answer
Since the goal of oxygen therapy is to prevent or relieve hypoxia,
question
check to make sure the equipment is functioning properly, the correct oxygen delivery device is in use, and the flow rate is set correctly. If the equipment and flow rate are appropriate, you might have to adjust the oxygen's flow rate. Because oxygen is considered a medication, you must obtain an order from the provider before adjusting the flow rate. -Perform a respiratory assessment along with a complete set of vital signs, including oxygen saturation indicated via pulse oximetry. After assessing your patient, also document the patient's skin color, level of consciousness, and other signs and any manifestations of hypoxia. -, perform a skin assessment where the oxygen-delivery device comes into contact with the patient's skin. Inspect the nose, the ears, and under the chin for redness, irritation, and skin breakdown. To help prevent irritation and skin breakdown, consider padding pressure areas when initiating oxygen therapy. Keeping the patient's skin clean and dry can also help reduce the risk of skin irritation and breakdown.
answer
If a patient is not improving with oxygen therapy,
question
-These include a flow meter, extension tubing, an oxygen-delivery device, and if the flow rate is more than 4 L/min, sterile water for humidification. -The flow meter attaches to the oxygen outlet and regulates the amount of oxygen delivered to the patient. Because most hospitals have outlets for both oxygen and air on the equipment panel at the bedside, it is important to confirm that the flow meter is attached to the oxygen outlet, designated by a green "oxygen" label, and not the air outlet, designated by a yellow "air" label, before initiating oxygen therapy.
answer
O2 therapies and Supplies
question
The two metal prongs fit into the wall outlet. The green collar behind the prongs twists to release the flow meter from the wall outlet, allowing it to be removed. The cylinder portion of the flow meter has numbers and lines indicating how many liters of oxygen are being delivered per minute (L/min).
answer
Basic parts of flow rate:
question
devices are used to administer oxygen. The device used often depends on why the patient is receiving oxygen, the flow rate (L/min) prescribed, and the length of time the patient will receive oxygen therapy.
answer
Many different types of oxygen-delivery
question
accomplished by attaching a bottle of sterile water to the oxygen-delivery equipment. As the oxygen bubbles through the water, it picks up moisture and helps keep the patient's mucous membranes from becoming dry. Be sure to replace the sterile water at least every 24 hours or according to the facility's policy. With high flow rates (FiO? of 4 L/min or more), humidification is required.
answer
Depending on the flow rate prescribed, humidification might be required. This is usually
question
1. the patient's age 2. level of consciousness 3. presence of an artificial airway 4. and environment (hospital or home) when choosing an oxygen-delivery device.
answer
A variety of oxygen-delivery devices are available for administering oxygen therapy. Which device to use often depends on the degree of hypoxia the patient is experiencing and any underlying respiratory diseases, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It is also important to consider
question
Most patients tolerate this device well, and it is simpler to use than a mask. The fraction of inspired oxygen (FiO?) varies depending on the flow of oxygen in L/min and the rate and depth of the patient's breathing.
answer
Nasal Canula
question
Flow: 1 to 2 L
answer
FiO?: 24% to 28% —
question
Flow: 3 to 4 L
answer
FiO?: 32% to 36% —
question
Flow: 5 to 6 L
answer
FiO?: 40% to 44% —
question
1. device most often used to administer oxygen therapy. It consists of a length of tubing, usually 7 to 14 feet long, with two small prongs to insert into one of the patient's nares. 2. It also has a plastic piece at the neck that slides up under the patient's chin to tighten the tubing and keep it in place. It is available in a range of sizes and can be used for various age groups.
answer
A nasal cannula is the
question
24% to 44% with flow rates from 1 to 6 L/min through the cannula. The exact concentration inspired depends on the flow rate and on the patient's rate and pattern of breathing and the depth of respirations. A
answer
A nasal cannula delivers oxygen concentrations of
question
nasal cannula is usually used for patients who are noncritical with minor breathing problems and for patients who cannot or will not wear an oxygen mask. Because this device administers low-flow oxygen, humidification is usually not required until the liter flow rate exceeds 4 L/min.
answer
What kInd of patient need nasal canula
question
This device requires a fairly high oxygen flow to prevent rebreathing of carbon dioxide. About 75% of the inspired volume is room air that the patient breathes through the holes in the side of the mask. An accurate FiO? is difficult to estimate. FiO?: 40% to 60% — Flow: 5 to 8 L
answer
Simple face mask
question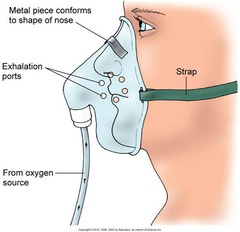
for patients who require a moderate flow rate for a short period of time. It is composed of a plastic mask that fits snugly over the patient's mouth and nose. The mask has holes (vents) on each side that are used for exhalation and for air entrainment if the flow rate is too low. An adjustable elastic strap that fits over the patient's head holds the mask in place. A piece of tubing connects the mask to the oxygen source. Extension tubing is usually added to allow the patient more freedom of movement.

answer
A simple mask is usually used
question
40% to 60% with flow rates from 5 to 8 L/min. Because carbon dioxide can build up in the mask at low flow rates, do not use a flow rate lower than 6 L/min with this type of mask. When using this mask, consider humidification to keep the patients' mucous membranes from becoming dry.
answer
A simple mask has the ability to deliver oxygen concentrations of
question
- This device is used to deliver high flow rates and high concentrations of oxygen. Like the simple mask, the nonrebreather mask fits snugly over the patient's mouth and nose. An adjustable elastic strap that fits over the patient's head holds the mask in place.
answer
NonBreather Mask
question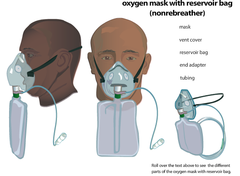
-The reservoir bag allows a higher FiO? to be administered. -At flow rates slower than 6 L/min, the risk of rebreathing carbon dioxide increases. A valve closes during expiration so that exhaled air does not enter the reservoir bag and is not rebreathed. The valves on the side ports of the mask allow exhalation but close on inspiration to prevent inhalation of room air. FiO?: 80% to 95% — Flow: Liter maintaining reservoir bag 2/3 full

answer
Nonrebreather face mask
question
way valve that allows the patient to breathe in the oxygen supplied by the source as well as oxygen from the reservoir. This provides the patient with an oxygen concentration of nearly 100%. A piece of tubing, usually connected to extension tubing, connects the mask to the oxygen source.
answer
A nonrebreather mask has vents on each side that are covered by flaps to keep the patient from breathing in room air and ensure that a high concentration of oxygen is delivered. The mask also has a reservoir bag that is inflated with pure oxygen. Between the mask and the bag is a one-
question
do not allow the reservoir bag to deflate or the oxygen source to deplete. If the bag deflates or the oxygen source diminishes, the patient is likely to breathe in large amounts of exhaled carbon dioxide.
answer
A nonrebreather mask can deliver oxygen concentrations of 80% to 95% with flow rates from 10 to 15 L/min. When using a nonrebreather mask,
question
1. so most of the expired air escapes. 2. There is no inspiratory valve, so some of the exhaled air returns to the bag and mixes with the inspired air.
answer
Partial rebreather masks may also be used to deliver an FiO? of 60% to 75% with a flow rate of 6 to 11 L/min. The partial rebreather mask has ports
question
This device uses different size adaptors to deliver a fixed or predicted FiO?. The FiO? delivered depends on the flow rate and/or entrainment port size. It is used for patients who have COPD when an accurate FiO? is essential and carbon dioxide buildup must be kept to a minimum. Humidifiers usually are not used with this device. FiO?: 24% to 50% — Flow: 4 to 10 L
answer
Venturi Mask
question
-have COPD when an accurate FiO? is essential and carbon dioxide buildup must be kept to a minimum. -24% to 50% — Flow: 4 to 10 L
answer
Venturi mask is used for patient with
question
-of a specific concentration of oxygen. It consists of a mask with holes on each side that allow exhaled air to escape. At the base of the mask and connected to the tubing are color-coded adaptors. Each adaptor is marked to tell which specific oxygen concentration the patient will receive and at what liter flow rate to set the oxygen.
answer
A Venturi mask is most often used for critically ill patients who require administration
question
24% to 50% with flow rates from 4 to 10 L/min. This is the most accurate form of oxygen delivery. Because this device delivers a precise oxygen concentration and carbon dioxide buildup is minimal, it is commonly used for patients who have COPD. Humidification is usually unnecessary with this device. The Venturi mask interferes with talking and eating; therefore, a prescription for oxygen via nasal cannula may be necessary for the client to use during meals.
answer
A Venturi mask can deliver accurate oxygen concentrations from
question
This soft aerosol mask fits loosely around the patient's face and neck. It is an alternative to an aerosol mask for patients who feel claustrophobic, but it is sometimes difficult to keep in place. It is convenient for providing humidification and oxygenation; however, oxygen concentration cannot be controlled. FiO?: 24% to 100% — Flow: At least 10 L
answer
Face Tent
question
especially for patients who report feeling claustrophobic with an aerosol mask. I .
answer
A face tent is often used as an alternative to an aerosol mask,
question
it is composed of a soft mask that fits under the patient's chin and loosely covers the mouth and nose. An adjustable elastic strap holds it in place. Face tents are often used after nasal and oral surgery.
answer
What is face tent like?
question
24% to 100% with flow rates of at least 10 L/min. This device is convenient for delivering both humidification and oxygen; however, it is difficult to control the concentration of oxygen administered since the actual concentration of oxygen depends on the rate and depth of the patient's respirations
answer
A face tent delivers oxygen concentrations of
question
concentrations of oxygen to a patient prior to a procedure, such as suctioning or intubating, and during respiratory or cardiac arrest. It can also be used to assist patients who are breathing but not adequately.
answer
A manual resuscitation bag is used to provide high
question
mask, a self-inflating bag that is compressed to ventilate the patient, and an oxygen port where the oxygen tubing is connected. It might also have an adapter that fits onto an oxygen port where the oxygen tubing is connected. It might also have an adapter that fits onto an endotracheal tube when it is going to be used for an intubated patient.
answer
The manual resuscitation bag consists of a
question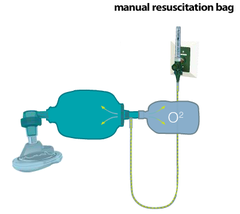
The mask fits over the patient's nose and mouth and has a soft air-filled cushion around the mask that forms an airtight seal when placed on the patient's face. The apex, or narrow portion of the mask, is placed over the nose and the base, or broader portion of the mask, over the mouth. The self-inflating bag is made of a firm, rubber-like material that is manually compressed to give the patient "a breath." The bag has an oxygen port where oxygen tubing can be connected. The oxygen flow meter is usually set at 10 to 15 L/min when performing manual resuscitation. There is also a valve on the bag that ensures one-way pressure into the mask and then allows the bag to reinflate from ambient air or from an oxygen source.

answer
Resuscitation bag
question
The oxygen flow meter is usually set at 10 to 15 L/min when performing manual resuscitation. There is also a valve on the bag that ensures one-way pressure into the mask and then allows the bag to reinflate from ambient air or from an oxygen source.
answer
O2 flow rate for manual resuscitation bag
question
A tracheostomy mask, sometimes referred to as a tracheostomy collar, is a small mask that fits over the patient's tracheostomy site. An adjustable elastic strap that fits around the patient's neck holds it in place. The mask has an exhalation port that remains patent at all times and a port that connects to the oxygen source with large-bore tubing. The flow rate is usually set at 10 L/min, with a nebulizer set at the appropriate oxygen concentration.
answer
Tracheostomy mask
question
The flow rate is usually set at 10 L/min, with a nebulizer set at the appropriate oxygen concentration.
answer
Flow rate for Tracheostomy Mask
question
1. Patients who have artificial airways require continuous humidification since the airway bypasses the normal filtering and humidification process of the nose and mouth. The two devices most commonly used are a t-tube and a tracheostomy mask.
answer
Who needs tracheostomy Mask ?
question
A t-tube is a t-shaped device with a piece that connects the oxygen source to the artificial airway (endotracheal tube or tracheostomy). The recommended flow rate when using a t-tube is 10 L/min, with a nebulizer set at the appropriate oxygen concentration.
answer
What is a T tube
question
The recommended flow rate when using a t-tube is 10 L/min, with a nebulizer set at the appropriate oxygen concentration.
answer
The Recommended flow rate for T tube
question
n alternative to mechanical ventilation, is used to maintain positive airway pressure and to improve alveolar ventilation without the need for an artificial airway. It is commonly used for patients who have congestive heart failure, sleep disorders, and pulmonary diseases to improve oxygenation, reduce and reverse atelectasis, reduce pulmonary edema, and improve cardiac function. The two types of noninvasive ventilation are CPAP and BiPAP.
answer
noninvasive Ventilation
question
who have congestive heart failure, sleep disorders, and pulmonary diseases to improve oxygenation, reduce and reverse atelectasis, reduce pulmonary edema, and improve cardiac function. The two types of noninvasive ventilation are CPAP and BiPAP.
answer
It is commonly used for patients
question
provides a set positive airway pressure throughout the patient's breathing cycle. It is commonly used for patients who experience sleep apnea because the continuous positive pressure keeps the airway open and prevents the upper airway from collapsing. The usual CPAP pressure is between 5 and 20 cm of water.
answer
Continuous positive pressure ventilation (CPAP)
question
sleep apnea because the continuous positive pressure keeps the airway open and prevents the upper airway from collapsing. The usual CPAP pressure is between 5 and 20 cm of water.
answer
CPAP is commonly used for patient who have
question
assistance during inspiration and keeps the airway from closing during expiration. The benefits of BiPAP include an increase in the amount of air in the lungs at the end of expiration, reduced airway closure, and improved oxygenation. Both CPAP and BiPAP will be discussed in more detail in another Skills
answer
Bilevel positive airway pressure (BiPAP) provides
question
an increase in the amount of air in the lungs at the end of expiration, reduced airway closure, and improved oxygenation.
answer
The benefits of BiPAP include
question
This canopy encloses the child and is used to provide oxygen, humidification, and/or a cool environment to control temperature. FiO?: Approximately 50% — Flow: 10 to 15 L
answer
Oxygen tent and hood
question
pediatric patients who have airway inflammation, croup, or other respiratory infections. The oxygen tent consists of a canopy that surrounds the child. It provides oxygen, humidification, and a cool environment to help control body temperature. An oxygen tent can provide oxygen concentrations of up to 30% with flow rates from 10 to 15 L/min.
answer
Oxygen tents and hoods are usually used for
question
disposable vinyl box that fits over the child's head. It provides warm humidified oxygen at a specific temperature. When using a hood, it is important to ensure that there is enough space between the curve of the hood and the child's neck to allow carbon dioxide to escape. An oxygen hood delivers a 28% to 85% oxygen concentration varying with the prescribed flow rate and size of the hood.
answer
The oxygen hood consists of a
question
28% to 85% oxygen concentration varying with the prescribed flow rate and size of the hood.
answer
An oxygen hood delivers a
question
Determines the amount of oxygen delivered the patient. Measured in liters per minute. Rate Varies according to patient's condition & route of O2 administration
answer
O2 Flow rate
question
Oxygen Analyzers ABG Analysis Pulse oximetry
answer
To regulate oxygen percentage concentration: We can take the help of
question
Nasal Cannula Nasal catheter Trans tracheal catheter Simple mask Partial re-breather mask Non re-breather mask Venturi mask Oxygen tent
answer
Devices
question
Common & inexpensive device Easy to apply: Position properly in nares Does not interfere with eating or talking Relatively comfortable Permits some freedom movement Well tolerated by clients
answer
Nasal Canulla
question
Delivers relatively low concentration of O2 (24& to 44%) at a flow rate of 2L to 6L per minute (Potter & Perry, 2013, p. 851). Above 6L/min client tends to swallow air and FiO2 is not increased. Humidify anything more than 4L (Potter & Perry, 2013, p. 851).
answer
Canula FLow Rate
question
Oxygen mask is fitted carefully to avoid leakage of O2. Mask should not be tight.
answer
Face Mask
question
Simple face mask Partial re-breather mask Non re-breather mask Venturi mask
answer
Common face masks
question
Has vents on each side in order for room air to leak in and there by diluting the source O2. Allows exhaled CO2 to escape. Used when increased O2 delivery is needed for short period (e.g. less than 12 hours) (Potter & Perry, 2013, p. 851).
answer
Simple Face mask
question
Delivers one of the highest O2 concentration possible by a mask (60% to 80%) at a flow rate of 6L to 10L/Minute (Potter & Perry, 2013, p. 852).
answer
Non Rebreather Mask
question
One way valves on the mask and between the mask and the reservoir prevent the room air and the client's exhaled air entering the bag so only oxygen in the bag is inspired (Potter ; Perry, 2013, p. 852). This also should not deflate.
answer
Non rebreather
question
Delivers O2 concentrations varying from 24% to 40% or 60% at a flow rate of 4L to 12L/minute(Potter ; Perry, 2013, p. 852). Incentive spirometer allows the patient to take a deep breath and provides the ability to visualize the volume.
answer
Venturi Mask
question
Measures diffusion and perfusion by reading oxygen saturation in the blood.
answer
Pulse Oximetry
question
The color of blood varies depending on how much oxygen it contains. A pulse oximeter shines two beams of light through a finger (or earlobe), one beam is red light, one is infrared light. These two beams of light can let the pulse oximeter detect what color the arterial blood is and it can then work out the oxygen saturation. (Potter ; Perry, 2013, p. 458)
answer
Pulse Oximetry
question
Therapy to mobilize pulmonary secretions (Potter ; Perry, 2013, p. 842). Include: postural drainage, chest percussion, and vibration (Potter ; Perry, 2013, p. 842). CPT, in most cases, causes productive coughing. In the patient with a decreased ability to cough, suctioning is required (Potter ; Perry, 2013, p. 842).
answer
CPT
question
Supplies Administering oxygen therapy (oxygen source, delivery device, flow meter, extension tubing, sterile water, humidifier, small gauze pads)
answer
Verify Order Patient record and need for procedure Identify, Gather, and Prepare Equipment and
question
• Remove device from package and connect extension tubing • Assure flow meter is securely attached to oxygen source • Connect tubing to flow meter and adjust flow rate • Insert prongs of nasal cannula into nares • Gently bring tubing up and around ears • Bring tubing down under chin and secure with plastic slide • Pad tubing where needed • Provide skin care to nares every 4 hours or per policy
answer
Nasal cannula
question
• Remove device from package and connect extension tubing • Assure flow meter is securely attached to oxygen source • Connect tubing to flow meter and adjust flow rate • Place mask on face from nose downward • Place elastic band around head • Adjust mask to fit snugly and form a secure seal • Provide skin care as needed where mask touches face
answer
Simple mask
question
• Remove device from package and connect extension tubing • Assure flow meter is securely attached to oxygen source • Connect tubing to flow meter and adjust flow rate high enough to inflate the reservoir bag partially • Place mask on face from nose downward • Place elastic and around head and adjust mask to fit snugly and form a secure seal • Provide skin care as needed where mask touches face
answer
Nonrebreather mask
question
• Remove device from package and connect extension tubing • Add sterile water to humidifier • Assure flow meter is securely attached to oxygen source • Connect humidifier to flow meter and adjust flow rate • Place face tent under chin, then over mouth and nose • Place elastic band over head and adjust for a loose fit • Provide skin care as needed where mask touches face
answer
Face tent
question
• Remove device from package and connect extension tubing • Attach color-coded adapter for prescribed oxygen flow rate • Connect tubing to adapter • Assure flow meter is securely attached to oxygen source • Connect oxygen tubing to flow meter and adjust to a high flow rate • Place mask on face from nose downward • Place elastic and around head and adjust mask to fit snugly and form a secure seal • Provide skin care as needed where mask touches faces
answer
Venturi mask
question
Date and time - initiated Method of delivery - cannula, simple mask Flow rate - in L/min Patient's response - any adverse reactions Condition of patient's skin - ears, nose Respiratory assessment - before and after oxygen therapy Patient and family teaching - done
answer
Document



