Nursing Care of Adults Pancreas & Biliary Problems – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
*Pancreatitis*
answer
- an inflammatory condition Acute pancreatitis in the U. S. 70 - 80 cases per 100,000 80% admitted with mild disease 20% with severe disease, mortality reaching up to 30%, 40 - 70% if necrosis suspected Estimated cost $3 to $6 billion Chronic pancreatitis in the U. S. 3 - 10 per 100,000
question
Acute pancreatitis - etiology
answer
Biliary tract disease Alchoholism Trauma (post surgical & abdominal) Viral infections (mumps & coxsackievirus B) Penetrating duodenal ulcer Cysts, abscesses Cystic fibrosis Kaposi's sarcoma Certain drugs
question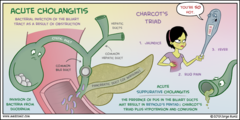
Predisposing factors

answer
Most common are gallstones (45% of the cases) and alcohol abuse (35%) The term suggests an infection, most patients don't have one Infection may occur as a complication
question
Acute pancreatitis - pathophysiology
answer
Acute inflammatory process of the pancreas Intra-pancreatic activation of enzymes Common pathogenic mechanism is autodigestion of the pancreas that occurs before the enzymes leave the pancreas instead of going into the small intestine
question
Autodigestion
answer
Leads to erosion through the pancreas and into the abdominal cavity Produces -profound inflammation - Fluid shifts - Hypovolemia - Hemorrhage - May cause abdominal compartment syndrome
question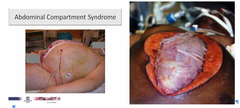
abdominal compartment syndrome

answer
a. Increased intraabdominal pressure leading to hypoperfusion and ischemia of the intestines
question
Autodigestive effects of pancreatic enzymes
answer
Trypsin/elastase - proteases - protein Edema Necrosis Hemorrhage Amylase - carbohydrates Hemorrhage Phospholipase A & Lipase - fat Fat necrosis
question
Acute pancreatitis- clinical manifestations
answer
Epigastric pain N/V Abdominal tenderness Low-grade fever Leukocytosis Hypotension Tachycardia Jaundice ?/absent BS Hypovolemia Grey Turner spots & Cullen's sign Seepage of bloodstained exudate from the pancrea
question
More about the pain
answer
Severe abdominal or epigastric Sudden onset Described as burning, or boring pain that radiates to the back Position changes don't help Consuming EtOH or fatty foods worsens the pain
question
Physical Assessment
answer
Firm, distended, diffusely tender abdomen Possibly rebound tenderness
question
Acute pancreatitis - complications
answer
Pseudocyst
question
Pseudocyst
answer
A cavity continuous or surrounding the outside of the pancreas Filled with necrotic products, plasma, pancreatic enzymes, inflammatory exudates Usually resolve spontaneously Rupture?peritonitis, stomach,
question
Pathology
answer
Pancreas is edematous and is enlarged. Pancreas can show acute inflammation, hemorrhage and or extensive necrosis. There can be extensive peripancreatic inflammation. Fluid can accumulate in lesser sac and pleural space Neutrophils infiltrate the edge of the necrotic areas and extend into the adjacent lobules of fat and produce fat necrosis. Calcification can be seen in chronic pancreatitis. Calcification in pancreas.
question
Potential complications
answer
- Abscess/pseudocyst - As liquefaction of necrotic pancreatic tissue progresses, it will gradually take on the appearance of localized fluid collection - pseudocyst. - This may be in the region of the pancreas or extend beyond the pancreatic region. - Pancreatic rupture/hemorrhage - Obstructive jaundice - Pulmonary complications in severely ill patients - ARDS - GI obstruction - Acute renal failure
question
Manifestations of pseudocyst
answer
Abdominal pain Palpable epigastric mass N/V Anorexia Serum amylase ?
question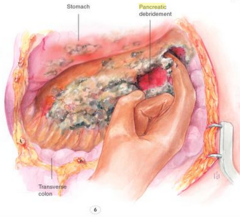
Treatment of pseudocyst

answer
Internal drainage procedure with an anastomosis between pancreatic duct and the jejunum
question
Acute pancreatitis complications
answer
Abscess Large fluid-containing cavity within the pancreas Becomes infected or perforate
question
Manifestations of abscess
answer
Upper abdominal pain Abdominal mass High fever Leukocytosis
question
Treatment of abscess
answer
Prompt surgical drainage to prevent sepsis
question
Acute pancreatitis - systemic complications
answer
Pulmonary Pleural effusion Atelectasis Pneumonia ARDS Cardiovascular (hypotension) Tetany (hypocalcemia)
question
Nursing Interventions: Pulmonary Complications
answer
Respiratory assessment ? Breath sounds Wheezes, crackles Pulse oximetry Encourage early ambulation Coughing, deep breathing, IS Change position q 2hr
question
Acute pancreatitis - lab values
answer
? Amylase - serum 3x the normal level ----- Elevated for 24 to 72 hours ----- Normal serum amylase *35 to 115* units/L ? Lipase - serum (more sensitive test of pancreatic function) ------- Levels rise in 3 to 4 hours, peak in 24 and stay high for up to 2 weeks ------- EtOH induced ------- Normal serum lipase* 32 to 80* units/L ? Amylase - urine may persist several days beyond the serum level
question
Other lab values
answer
Blood glucose - hyperglycemia ---------- ß-cell damage? ?insulin Serum calcium - hypocalcemia ---------- Ca++ binds with fatty acids Serum triglycerides - hyperlipidemia C-reactive protein - >150 mg/L 48 hrs after symptom onset reflects acute pancreatitis
question
Acute pancreatitis - nursing management
answer
Goals Relief/ ? pain Prevention or alleviation of shock Reduction of pancreatic secretions Maintain fluid/electrolyte balance Prevention/tx of infections Remove precipitating cause
question
Acute pancreatitis - pain control
answer
Demerol ----- Should be reserved for short course of therapy ----- Normeperidine - toxic metabolite - CNS irritant Morphine - longer ½ life May be combined with an antispasmodic Avoid atropine-like drugs when paralytic ileus is present
question
Nursing Interventions
answer
Assess pain frequently Use an objective pain scale Reassess effectiveness of pain regimen Nonpharmacological interventions Guided imagery Relaxation exercises May fear they will become addicted to opiods - support & teach
question
Acute pancreatitis - fluid resuscitation
answer
Generally require vigorous fluid replacement -------- Prevent hypovolemia r/t third-space losses and vomiting Shock Blood volume replacement - dextran or albumin Fluid replaced with LR or NS
question
Nursing Interventions
answer
Monitor I&O Weight and lab values Watch for signs of hypovolemia and/or third space loss ---------- ? skin turgor, cap refill ---------- Dry mucous membranes ---------- Thirst ---------- Hypotension, tachycardia
question
Acute pancreatitis - pancreatic suppression
answer
Bowel rest ---------- NPO ---------- NGT to LWS TPN Jejunal tube feeding
question
Chronic pancreatitis
answer
Progressive destruction of pancreas with fibrotic replacement of the tissue Strictures and calcifications may be present
question
Chronic pancreatitis - pathophysiology
answer
Chronic obstructive pancreatitis --------- Inflammation of sphincter of Oddi associated with cholelithiasis --------- Cancer may also contribute Chronic calcifying pancreatitis ---------- Ducts obstructed with protein precipitates
question
Chronic pancreatitis - clinical manifestations
answer
Abdominal pain ------- Recurrent months/years ------- Described as heavy, gnawing, burning, cramplike ------- Not relieved with food or antacids Symptoms of pancreatic insufficiency ------- Weight loss ------- Mild jaundice/dark urine ------- steatorrhea
question
Chronic pancreatitis - nursing management
answer
Diet ------ Bland, low fat, high carb ------ Total elimination of EtOH Replacement of pancreatic enzymes ---- Pancreatin (Viokase) ---- Pancrelipase (Cotazym) ---- Given with meals ---- Observe stool
question
Common disorders of biliary system
answer
Cholelithiasis ---------- Gall stones ---------- Lodged in neck or cystic duct Cholecystitis ---------- Inflammation of gall bladder
question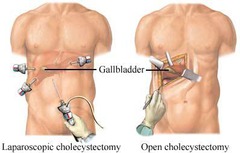
Cholecystectomy

answer
Gallbladder removal
question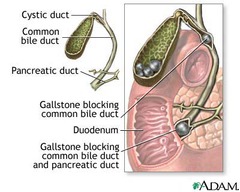
Choledocholithiasis

answer
Stone in the common bile duct
question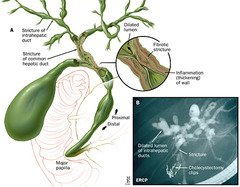
Cholangitis

answer
Inflammation of biliary ducts
question
Steatorrhea
answer
No bile salts in duodenum, preventing fat emulsion and digestion
question
Cholecystitis clinical manifestations
answer
Indigestion Pain - moderate to severe Fever Jaundice RUQ tenderness Restlessness Diaphoresis N/V
question
Cholelithiasis treatment
answer
Cholesterol solvents Drugs to dissolve stones Endoscopic sphincterotomy Extracorporeal shock-wave lithotripsy Surgery -------- Open chole ------- Lap chole
question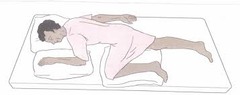
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy - post op care

answer
Bleeding Comfort Prepare for D/C Referred *pain to the shoulder* --------- CO2 irritation to phrenic nerve and diaphragm --------- Intervention - place in Sims' (left side with r. knee flexed)
question
Lap chole - post op care
answer
Deep breathing Movement ; ambulation Clear liquids Ambulation
question
Discharge teaching
answer
Dressings ---------- Dry ---------- Remove next day Minimal analgesics required Notify MD if fever, redness, increased pain, abd distention, vomit, oozing bile Resume normal activity 48-72 hours



