Neurology Shelf Review – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
What is a lacunar stroke?
answer
Small non cortical infarcts caused by occlusion of a single penetrating branch of a large cerebral artery. -Branches arise at acute angles from the large arteries of the circle of willis and stem from the MCA or the basilar artery.
question
What are the common locations of lacunar strokes?
answer
Internal capsule Pons Thalamus
question
What type of lacunar syndrome presents with unilateral motor deficit (face, arm and to a lesser extent, leg); mild dysarthria; No sensory, visual or higher cortical function dysfunction?
answer
Pure Motor hemiparesis
question
What is the underlying pathology of pure motor hemiparesis?
answer
Lacunar infarct in the posterior limb of the internal capsule (carries descending corticospinal and corticobulbar tracts or basis pontis)
question
What type of lacunar syndrome presents with unilateral numbness, parathesias and hemisensory deficit involving the face, arm, trunk and leg?
answer
Pure sensory stroke
question
What is the underlying pathology of a pure sensory stroke?
answer
Stroke in the ventroposteriolateral nucleus of the thalamus. (infarct usually in the contralateral thalamus)
question
What type of lacunar syndrome presents with weakness that is more prominent in the LE, along with ipsilateral arm and leg incoordination?
answer
Ataxic hemiparesis
question
What is the underlying pathology of ataxic hemiparesis?
answer
Lacunar infarction in the anterior limb of the internal capsule (contains fibers running form the thalamus to the frontal lobe, fibers connecting the lentiform and caudate nuclei, fibers connecting the cortex with the corpus striatum and fibers passing from the frontal lobe through the medial fifth of the base of the cerebral peduncle to the nuclei pontis) .
question
What lacunar syndrome presents with Hand weakness, mild dysarthria and NO sensory abnormalities?
answer
Dysarthria-clumsy hand syndrome
question
What is the underlying pathology in dysarthria-clumsy hand syndrome?
answer
Lacunar stroke at the basis pontis.
question
What are some body positions and actions that someone can do to increase their ICP?
answer
Leaning forward valsalva cough
question
What are some sxs of elevated ICP?
answer
HA (worse at night) n/v mental status changes (decreased level of consciousness, cognitive dysfunction)
question
What does the Cushing reflex suggest?
answer
Brainstem compression
question
What are the 3 hallmarks of Cushing reflex?
answer
Hypertension Bradycardia Respiratory depression
question
What can cause momentary vision loss that varies according to changes in head position?
answer
Papilledema-can cause visual blind spot at the head of the optic nerve because it enlarges.
question
What is amaurosis fugax?
answer
Painless, transient monocular blindness that lasts a few seconds. It is usually vascular (ie. embolus to opthalmic artery) in origin.
question
What condition should be considered as a diagnosis in a pt with parkinsonism who experiences orthostatic hypotension, impotence, incontinence or other autonomic symptoms?
answer
Multiple system atrophy (Shy-Drager syndrome)
question
What are the three components of multiple system atrophy?
answer
1. Parkinsonism 2. Autonomic dysfunction 3. Widespread neurologic signs.
question
What disease is AR seen in predominantly children of Ashkenazi Jewish ancestry. Characterized by gross dysfunction of the ANS with severe orthostatic hypotension.
answer
Familial dysautonomia (Riley-Day syndrome)
question
What are the sxs of hypothyroidism?
answer
weight gain, fatigue, constipation, hoarseness, and memory changes.
question
Pt presents with progressive ascending paralysis over hours-days. the paralysis is more pronounced in the legs although there is some paralysis in the arms. Sensation is normal, there is no autonomic dysfunction and CSF exam is normal. What is this pt suffering from?
answer
Tick borne paralysis
question
Pt has a peripheral neuropathy characterized by weakness affecting the LEs first, progressing superiorly to the arms and facial muscles; any sensory loss presents as loss of proprioception and areflexia. What is this pt suffering from?
answer
GBS
question
What is a tremor?
answer
Uncontrolled uncoordinated unwanted movement of the limbs, extremities or trunk.
question
What is the cause of Parkinson's disease?
answer
Loss of the DA nerves in the substantial nigra
question
What is the fundamental problem is parkinson's disease?
answer
bradykinesia
question
Pt with parkinson's disease have what symptoms?
answer
Pill rolling tremor Cogwheel rigidity Mask-like facies unsteady gait shuffling steps
question
How is parkinson's disease diagnosed?
answer
CLinical -can do an autopsy
question
If a parkinson's disease pt is functional, how do you treat if <60?
answer
Use dopamine agonists like Bromocriptine
question
If a parkinson's disease pt is functional, how do you treat if >60?
answer
Use anti-cholinergic SEs of Amantadine
question
If a parkinson's disease pt has non-functional status, how do you treat ?
answer
Add levodopa-carbidopa
question
If a parkinson's disease pt is non-functional, and the levodopa and carbidopa stop working, how do you treat?
answer
Use the "capones", Selegiline and other DA-agonists
question
What is essential tremor?
answer
A familial disease -pt has no tremor at rest that worsens with movement -typically <30 -(+) FHx -EtOH makes this tremor improve
question
Pt is <30 yo M with a family history of tremor and notices that when he picks up the remote to watch tv, his hand seems to shake. What type of tremor is this?
answer
Essential tremor
question
What is essential tremor diagnosed?
answer
clinical
question
How do you treat essential tremor?
answer
Beta-blockers, particularly propranolol.
question
What is cerebellar dysfunction tremor?
answer
-Another tremor that is absent at rest and worsens with movement -Occurs in anyone with a cerebellar lesion (Wernickes encephalopathy or cerebellar ischemia)
question
what is distinct about cerebellar dysfunction tremor?
answer
As pt gets closer to the object that they intend to touch, the tremor will get worse and will not be so bad if they are far away. -Additionally these pts are usually old >40 (in comparison to essential tremor) -EtOH makes this tremor worse.
question
How can you diagnose cerebellar dysfunction tremor?
answer
clinical -can do an MRI to see loss of brain cerebellar tissue
question
How can you treat cerebellar dysfunction tremor?
answer
There is no treatment
question
What is delirium tremens?
answer
Withdrawal from EtOH or benzos
question
Pt comes into the ED and reports a negative history of chronic alcohol abuse. After 48-72 hrs pt begins to get anxious, have a tremor and start seeing things. What is this pt suffering from?
answer
DT -signs that they are about to have a seizure.
question
What are the sxs of DT?
answer
Tremor at rest anxiety elevated HR and elevated BP -if pt is actively hallucinating-->seizure!!!
question
How is DT diagnosed?
answer
Clinically
question
How do you treat DT?
answer
Before pt starts to seize, give them a long acting benzo such as chlordiazepoxide or lorazepam
question
What is huntington's disease?
answer
Genetic Caused by a trinucleotide repeat (CAG) and exhibits anticipation.
question
What are the sxs of huntington's disease?
answer
Chorea and dementia
question
How do you diagnose?
answer
Clinically but can do a DNA scan
question
How can you treat Huntington's dz?
answer
There is no treatment.
question
What type of tremor is the following: -resting tremor (4-6hz) that decrease with voluntary movement -usually involves legs and hands -Facial involvement is less common
answer
Parkinson's disease tremor
question
What type of tremor is the following: -bilateral action tremor of the hands, usually without leg involvement -possible isolated head tremor without dystonia -usually no other neurologic signs -relieved with alcohol in many cases
answer
Essential tremor
question
What type of tremor is the following: -Usually associated with ataxia, dysmetria or gait disturbance -tremor increases steadily as the hand reaches its target
answer
Cerebellar tremor
question
What type of tremor is the following: -Low amplitude (10-12 hz) not visible under normal conditions -acute onset with increased sympathetic activity (ie. drugs, hyperthyroidism, anxiety, caffeine) -usually worse with movement & can involve the face and extremities.
answer
Physiologic tremor
question
What are some sxs of cerebellar dysfunction?
answer
-Chronic alcoholism -progressive gait disorder-->frequent falls -truncal ataxia -nystagmus -intention tremor -dysmetria (limb-kinetic tremor when attempting to touch a target) -impaired rapid alternating movements (dysdiadochkkinesia) -muscle hypotonia -->pendular knee reflex (more than 4 swings is abnormal)
question
Where is the brain lesion that presents as: -unilateral motor impairment -no sensory or cortical deficits -no visual field abnormalities
answer
Posterior limb go the internal capsule (lacunar infarct)
question
Where is the brain lesion that presents as: -Contralateral somatosensory & motor deficit (face, arm & leg) -Conjugate eye deviation toward side of infarct -Homonymous hemianopia -Aphasia (dominent hemisphere) -Hemineglect (nondominant hemisphere)
answer
MCA occlusion
question
Where is the brain lesion that presents as: -Contralateral somatosensory & motor deficit, predominately in lower extremity -Abulia (lack of will or initiative) -Dyspraxia, emotional disturbances, urinary incontinence
answer
ACA occlusion
question
Where is the brain lesion that presents as: -Alternate syndromes with contralateral hemiplegia & ipsilateral cranial nerve involvement -possible ataxia
answer
Vertebrobasilar system lesion (supplying the brain stem)
question
Pt presents with HA, low grade fever, and periorbital edema days later. Pt further reports vomiting and papilledema is present on PE. What is this pt likely suffering from?
answer
Cavernous sinus thrombosis
question
How is cavernous sinus thrombosis diagnosed?
answer
MRI with MRV
question
How is cavernous sinus thrombosis treated?
answer
broad spectrum IV antibiotics and prevention or reveal of cerebral herniation.
question
What is a diagnosis for the following: -In a child: liver disease with asymptomatic ALT elevation leading to fulminant hepatic failure -In young adult: Neuropsychiatric disease ranging from tremor & rigidity to depression, paranoia and catatonia.
answer
Wilson's disease
question
How is Wilson's disease diagnosed?
answer
Confirmed by presence of low serum ceruloplasmin (particularly <20mg/dL) in conjunction with increased urinary copper excretion of Kayser-Fleischer rings
question
What is included in the primary HA category?
answer
Brain parenchyma itself or vasculature which leads to pain: -Migraines -Cluster -Analgesic rebound -Tension HA
question
What is included in the secondary HA category?
answer
Dangerous & require emergent evaluation. Come from outside brain parenchyma and lead to irritation: -SAH -meningitis -abscess -tumor -temporal arteritis
question
What is the cause of analgesic rebound HA?
answer
Withdrawal of medications such as NSAIDs and Tylenol
question
How do you treat analgesic rebound HAs?
answer
Discontinue the medications
question
What type of HA is characterized by muscular pain: -Bilateral vice-like pain that radiates to the neck
answer
Tension HA
question
How do you diagnose tension HAs?
answer
clinically
question
How do you treat tension HAs?
answer
OTC meds -NSAIDs -acetaminophen
question
What is the cause of cluster HAs?
answer
Primarily vascular in nature
question
Pt reports that they have been asymptomatic for months and then they had multiple attacks -(30-60) clusters in 1-3 days. -attacks usually occur at night -lasts ~2 hours -(+) ipsilateral Horner's syndrome -lacrimation -conjuctival injection -scleral injection -(+) red, hot painful eye (periorbital or retro-orbital) . What are they suffering from?
answer
Cluster HA
question
How do you treat cluster HAs?
answer
O2 (acute attack) +subcutaneous sumatriptan -because it is vascular you can treat it similar to migraines. ie. treat with ergots or prophylax with CCBs. -can be prevented with verapamil, lithium
question
How often do cluster HAs occur?
answer
Last 20-30 minutes long and so can happen 8-20 times per day.
question
If you find someone with cluster HAs, what further testing should you perform?
answer
Brain imagining.
question
What is the underlying pathology in migraine HAs?
answer
Vascular in nature (vasodilation)
question
Pt presents with HA & photophobia, phono phobia. Usually there is a trigger. -may present with an aura -HA may last for multiple days -if pt falls asleep, HA will abort and they will wake up hungover. What are they suffering from?
answer
Migraine
question
How do you treat migraine if caught early?
answer
NSAIDs
question
If pt has mild-moderate migraines, how do you treat?
answer
Ergots Triptans (watch out for coronary artery disease) -Prochlorperazine (an antiemetic-effective acute treatment and can be giving in IV form which is often necessary due to pts tendency towards vomiting)
question
How can you prophylax migraines?
answer
CCBs and beta-blockers
question
What can you prescribe a pt with a migraine who complains on nausea?
answer
Prochlorperazine (an anti-emetic
question
What further study should you order if pt has migraines?
answer
Brain imaging
question
What is the underlying pathology of Idiopathic Intracranial HTN (pseudo tumor cerebri)?
answer
Elevated ICP (Can be due to hypervitaminosis A, etc.)
question
Pt presents with intense HA, may have some neurologic deficit, typically young women 20-30s with normal CT scan. LP revealed elevated opening pressure and relief of HA and deficits with LP. What is pt suffering from?
answer
Idiopathic intracranial HTN (pseudotumor cerebri)
question
How do you treat Idiopathic intracranial HTN (pseudotumor cerebri) ?
answer
Stop OCPs if on them repeated LPs VP-shunt acetazolimide
question
Pt presents with lightening shocks down the side of the face. What are they suffering from?
answer
Tic douloureux (trigeminal neuralgia)
question
How do you treat tic douloureux?
answer
Carbamazepine
question
Pt presents with HA that lasts 2-10 minutes, and so happen 50-100 times per day. What are they suffering from?
answer
Paroxysmal hemicrania
question
How do you treat Paroxysmal hemicrania?
answer
They are aborted with indomethicine and prevented with verapamil
question
Pt presents with HAs that last seconds and so happen 1000s of times per day. What are they suffering from?
answer
SUNCT/SUNA
question
How do you treat SUNCT/SUNA HAs?
answer
They are so short that they dont get aborted (but people wouldn't mind ending their life since there isn't anything they can do about 1000 shocks of daily pain). They are prevented with Lamotrigine
question
What are the red flags associated with secondary HAs?
answer
-Fever + HA -Focal neurologic deficit +HA -Progressive HA + n/v in morning (developing tumor) -New onset at age >50yo (risk for tumor) -Sudden onset (thunderclap HA)
question
Pt reports fever, HA and a stiff neck. What is the likely diagnosis?
answer
Meningitis
question
What are the known causes of meningitis?
answer
-Commonly bacterial (TB, RMSF, Lyme, Cryptococcus,) -Viral
question
Pt reports fever, HA, and focal neurological deficit. What is the likely diagnosis?
answer
Brain abscess or cancer
question
Pt reports fever, HA and some altered mental status. What is the likely diagnosis?
answer
Encephalitis (because it causes encephalopathy)
question
What are the common caused of encephalitis?
answer
West Nile virus St. Louis virus Equine virus ... -->Tx is supportive for those above **Only one that matters in herpes (because you can treat it)
question
What is the criteria that demonstrates an LP is contraindicated?
answer
"FAILS" Focial Neurologic Deficit Altered Mental Status Immunosuppressed Lesion over site of needle placement Seizures -->if increased ICP -->brain herniation
question
If pt satisfies any of the FAILS criteria what test would you perform?
answer
Give empiric antibiotics + CT scan -if CT is negative get an LP
question
LP shows 1000s PMNs. What is the likely diagnosis?
answer
Bacterial meningitis
question
What antibiotics do you start to treat empirical bacterial meningitis?
answer
Ceftriaxone Vancomycin Steriods (if immunosuppressed, add on ampicillin)
question
LP does not show many PMNs at all. What is the likely diagnosis?
answer
Not bacterial
question
Pt presents with fever, rash that moves from the arms to the trunk and has a history of recent camping. What is their likely diagnosis and what would you see on CSF?
answer
RMSF -see antibodies on CSF
question
How do you treat RMSF?
answer
Ceftriaxone
question
Pt presents from recent travel to CT. They have a targeted rash with arthralgias, and an arrthymia. What is their likely diagnosis?
answer
Lyme Disease (invasive) -See lyme antibody
question
How do you treat Lyme disease?
answer
Ceftriaxone
question
Pt with a history of AIDs presents with fever and HA. Their LP revealed >20cmH2O opening pressure. What is the likely diagnosis?
answer
Cryptococcal meningitis -cryptococcal antigen is positive
question
How do you treat cryptococcal meningitis?
answer
amphotericin B
question
Pt presents with night sweats, weight loss, hemoptysis and symptoms of meningitis. They report that they are homeless. What is the likely diagnosis?
answer
TB meningitis -others at risk are homeless, in prison and from endemic areas
question
How do you treat TB meningitis?
answer
RIPE therapy -Rifampin -Isoniazid -Pyrazinamide -ethambutol
question
Pt with a history of primary chancre, secondary erythema multiforme and now presented with neurologic sxs. What is the likely diagnosis?
answer
Neuro syphilis -get CSF RPR or CSF antibodies
question
Pt presented with fever, HA and altered mental status. LP revealed lymphocytes. What is the likely diagnosis and treatment?
answer
encephalitis -supportive therapy or if it is HSV, treat with acyclovir.
question
Pt's LP revealed temporal lobe bleeding or hemorrhagic tap. What should you be thinking?
answer
HSV
question
How do you diagnose HSV encephalitis?
answer
HSV PCR
question
What are the alarm symptoms of back pain?
answer
h/o cancer fever urinary symptoms (retention or incontinence) -sexual dysfunction (priapism or inability to achieve erection) sensory deficit LE weakness
question
If a pt presents with an alarm symptom of back pain, what is the likely diagnosis?
answer
Cord compression
question
If you suspect cord compression in a pt, what should you immediately treat them with?
answer
Dexamethasone -the earlier the pt gets steroids, the more likely they will recover with normal neurologic function
question
What imaging should be obtained if you suspect a pt has cord compression?
answer
X-ray then MRI for confirm
question
If pt complains of back pain without any alarm sxs and a relatively negative PE, what should you recommend?
answer
Non-urgent back pain -NSAIDS -Exercise -tell them to return in 4-6 weeks
question
If pt with non-urgen back pain improves in 4-6 weeks on conservative therapy, what was the likely cause?
answer
MSK
question
If pt with non-urgen back pain does not improve in 4-6weeks on conservative therapy and although they still do not have any alarm symptoms but have a positive PE, what is the next step?
answer
Urgent back pain -X-ray followed by MRI -Dx and tx with surgery likely.
question
What is the underlying pathology of msk back pain?
answer
Muscular strain
question
Pt presents with a history of heavy lifting, <40 yr old. they describe their pain as a belt-like pain without any point of tenderness, no step-off on palpation and no neurologic sxs. What is the likely next step?
answer
MSK back pain -Tx with NSAIDs and exercise DO NOT get x-ray or MRI
question
What is the underlying pathology of disc herniation?
answer
Nucleus pulposus pops out and pinches a nerve.
question
Young person with history heavy lifting currently complains of sciatic (lightening pain) down back of leg, particularly when he coughs or has hip flexion (+) straight leg raise What other tests should be done?
answer
-Ankle plantar flexion to check the nerve root S1 & S2 -Ankle dorsiflexion to check the nerve root L4 & L5 -Check these regions for disc herniation.
question
What is the work up for a pt that is suspected to have disc herniation?
answer
1st: X-ray 2nd: MRI to visualize the bulging disc
question
How do you treat disc herniation?
answer
-at 6 mo. neurosurgery is better than conservative treatment -after 6mo, neurosurgery and conservative treatment have the same efficacy.
question
What is the underlying pathology of osteophytes?
answer
Bone spur that grows into the exit of the nerve and pinches it.
question
How does a pt with osteophytes present?
answer
Pt is typically older (>40) -all symptoms of sciatica -NO history of heavy lifting
question
How do you diagnose pt with osteophytes?
answer
X-ray (1st) MRI (best)
question
How do you treat a pt with osteophytes?
answer
Surgery
question
What is the underlying pathology of a compression fracture?
answer
Osteoporosis
question
Pt with a history of osteoporosis recently fell on her butt and not complains on pinpoint tenderness and on exam has vertebral step-offs and neurologic sxs. What is the likely diagnosis?
answer
Compression fracture
question
How do you diagnose a compression fracture?
answer
X-ray (1st) MRI (Best)
question
How do you treat a compression fracture?
answer
Surgery Tx osteoporosis
question
What is the underlying pathology of spinal stenosis?
answer
When a bone grows into the vertebral canal and compresses the cord.
question
Pt can exercise and walk upright normally but complains of an intense burning pain in hips, buttocks and thighs. However, if they lean forward, it relieves sxs. What is the likely diagnosis?
answer
SPinal stenosis
question
How do you diagnose spinal stenosis?
answer
X-ray (1st) MRI (best)
question
How do you treat spinal stenosis?
answer
Surgery (laminectomy)
question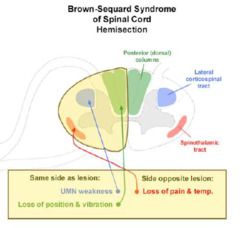
What is the result of damage to the lateral spinothalamic tracts?

answer
Brown-Sequard syndrome -causes contralateral loss of pain and temperature sensation beginning two levels below the level of the lesion. (Involves ipsilateral hemiplegia with contralateral pain and temp deficits due to the decussating fibers of the spinothalamic tract)
question
What drug has been proven to decrease the frequency of relapse and reduce disability in pt with the relapsing-remitting form of MS?
answer
Interferon-beta
question
If a parent presents with myasthenia gravis, what scan would likely be abnormal?
answer
CT scan of the chest--because 15% of pt have a coexisting thymoma.
question
What type of intracranial hemorrhage presents with occipital HA, vomiting, gaze palsy or nystagmus, neck stiffness and gait ataxia?
answer
Cerebellar hemorrhage
question
What type of intracranial hemorrhage presents with deep coma & total paralysis within minutes as well as pinpoint reactive pupils?
answer
Pons hemorrhage
question
What is thought to be the underlying pathology is lacunar strokes?
answer
A combination of microatheroma and lipohyalinosis.
question
Pt >40 complains of rapid onset severe eye pain and reports seeing halos around lights. The eye looks injected and the pupil is dilated and poor responsive to light. The pt further complains of tearing and HA with some n/v. What is this pt suffering from?
answer
Acute angle closure glaucoma. -typically affects the Asian and Inuit populations and individuals with farsightedness.
question
What type of medication is trihexyphenidyl?
answer
an anticholinergic agent that can be used to treat early stage Parkinson's tremor in younger patients where tremor is the predominant symptom.
question
65yo pt presents with weakness that is more pronouced in the bilateral UEs than in the LEs. What is he suffering from?
answer
Central Cord syndrome -pt typically complain of burning pain and paralysis un UEs with relative sparing of LEs.
question
What is central cord syndrome?
answer
Typically occurs with hyperextension injury in elderly pts with preexisting degenerative changes in the cervical spine. -Causes selective damage to the central portion of the anterior spinal cord, specifically the central portions of the corticospinal tracts and the decussating fibers of the lateral spinothalamic tract.
question
Pt presents with contralateral hemiparesis & hemisensory loss, homonymous hemianopsia and gaze palsy. Where is the likely location of their intracerebral hemorrhage?
answer
Basal ganglia
question
How can you treat exertional heat stroke?
answer
1. rapid cooling: ice water immersion preferred; can consider high flow cool water dousing, ice/wet towel rotation, evaporative cooling 2. Fluid resusicitation 3. Electrolyte correction 4. Management of end organ complications 5. No role for antipyretic therapy
question
Pt presents with ipsilateral ataxia, tends to sway to one side when standing with legs together, and exhibits titubation. Other findings are nystagmus, intention tremor, ipsilateral muscular hypotonia and marked difficulty in coordination and performing rapid alternating movements. What is this pt suffering from?
answer
Cerebellar tumor -Obstruction of CSF flow may occur leading to increased ICP leading to presentation of HA, n/v and papilledema. Titubation: forward and backward movement of the trunk
question
What are some early side effects of treatment with levodopa +carbidopa?
answer
Somnolence, confusion, agitation, hallucinations and nausea
question
What are some "late" side effects of treatment with levodopa +carbidopa?
answer
Involuntary movements (dyskinesia & dystonia) typically occur after 5-10 years of therapy in nearly 50% of pts.
question
Pt presents with subcutaneous neurofibromas, hyper pigmented cafe-au-lair spots, deafness due to acoustic neuromas. What is the diagnosis?
answer
NF2 -AD -caused by a mutation in the tumor suppressor gene located on Chr22. The severe variant, Wishart, is caused by a frameshift or nonsense mutation and misreading of the nucleotide code downstream or early termination of the translation process occurs.
question
What MMSE score is suggestive of dementia?
answer
24/30
question
Pt presents with total loss of motor function below the level of a burst fracture of the vertebra and loss of pain and temperature on both sides below the lesion. What is this pt suffering from?
answer
Anterior Cord syndrome
question
What is the most common site of hypertensive hemorrhage?
answer
30% occur in the putamen -the internal capsule that lies adjacent to the putamen is almost always involved, leading to contralateral dense hemiparesis.
question
Pt presents with flushing, anhidrosis/dry mouth, hyperthermia, mydriasis/vision changes, delirium/confusion and urinary retention/constipation. They additionally complain of HA, dizziness and tachycardia. What are they experiencing?
answer
Anticholinergic excess.
question
What are the sxs of hypokalemia?
answer
weakness fatigue muscle cramps -when severe can lead to paralysis and arrhythmia -EKG: U waves, flat and broad T waves and premature ventricular beats.
question
How do you treat narcolepsy?
answer
Modafinil and armodafinil address excessive, uncontrollable daytime sleepiness. Amphetamine stimulants have been used for treatment. Sodium oxybate reduces cataplexy.
question
What are the typical neuroimaging findings in autism?
answer
Increased total brain volume
question
What are the neuroimaging findings in OCD?
answer
Abnormalities in orbitofrontal cortex & striatum
question
What are the neuroimaging findings in panic disorder?
answer
Decreased volume of amygdala
question
What are the neuroimaging findings in PTSD?
answer
Decreased hippocampal volume
question
What are the neuroimaging findings in schizophrenia?
answer
Enlargement of cerebral ventricles.
question
What is transient global amnesia?
answer
A clinical syndrome of reversible anterograde amnesia accompanied by repetitive questioning that occurs in middle aged and elderly individuals. -etiology is obscure & prognosis is benign
question
What other conditions is transient global amnesia associated with?
answer
Migraines
question
What do you treat transient global amnesia?
answer
There is no specific therapy indicated
question
What are the three cardinal findings in brain death?
answer
unresponsiveness absence of brainstem reflexes apnea
question
What tests can be used to assist in diagnosis of brain death?
answer
Cerebral angiogram EEG MRI transcranial Doppler
question
What labs findings are associated with MS?
answer
mild CSF pleocytosis (rarely containing PMNs) normal CSF glucose CSF protein is mildly elevated CSF IgG CSF oligoclonal bands
question
What are the benefits of using lamotrigine to treat a generalized seizure in a female of reproductive age?
answer
It appears to have a lower incidence of inducing birth defects than other anticonvulsants. -Frequency of cognitive side effects is low
question
What nerve is expected to be pinched with a C5-C6 disc prolapse?
answer
C5 nerve lies above C6 vertebra and a C5-C6 disc prolapse will compress the 6th cervical nerve.
question
What are the side effects of common migraine medications: Topiramate Propranolol Valproic acid Verapamil Amitriptyline
answer
Topiramate: can cause renal stones Propranolol: can exacerbate asthma Valproic acid: is potentially hepatotoxic Verapamil: 2nd line for migraine Amitriptyline: can cause drowsiness
question
What are general causes of paroxysmal focal symptoms?
answer
TIA: aburpt onset & cause loss of function w/ no residual deficit Seizures: usually last 2-3mins migraine auras: cause positive phenomenon that progress over 15-30mins (commonly visual but tingling also possible)
question
What portion of the brain is responsible for visuospatial functioning?
answer
Largely the nondominent parietal lobe
question
What lobe of the brain is responsible for semantics?
answer
Lateral temporal cortex of the dominant hemisphere
question
What region of the brain is necessary for facial recognition?
answer
the inferior occipitotemporal cortex (fusiform gyrus) -bilateral dysfunction of this region produces prosopagnosia (inability to recognize familiar faces)
question
What muscles does the musculocutaneous nerve supply?
answer
The biceps brachial, brachialis, and coracobrachialis
question
Where does the musculocutaneous nerve receive sensory information from?
answer
The lateral cutaneous nerve of the forearm.
question
Which tract travels from the cerebellar cortex and projects to the ipsilateral deep grey nuclei of the cerebellum which in turn project via the superior cerebellar peduncle to the contralateral red nucleus and gives rise to this tract that crosses and travels ipsilaterally to the cerebellar cortex?
answer
Rubrospinal tract.
question
What is TRAP for PD stand for?
answer
resting tremor rigidity akinesia postural instability



