Human Geography FInal: KSU – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Ester Boserup
answer
>Boserup identified 5 basic stages in the reduction of fallow farmland: • Forest fallow (left fallow for >20 yrs.) • Bush fallow (up to 10 yrs.) • Short/Field fallow (up to 2 yrs.) • Annual cropping (rotation - fallow for a few months) • Multi-cropping (used several times in a year, climate permitting)
question
Challenges in Defining States
answer
Disagreement exists about actual number of sovereign states as a result of historical disputes involving more than one claim to a territory
question
Korea:challenges defining state
answer
>Leaders of both countries want one Korea > Korean Peninsula was a colony of Japan from 1910 to 1945 >After WWII, the country was divided >N Korea invaded S Korea in 1950 > Korean Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) roughly follows the 38th parallel (160 miles long); established in 1953
question
China and Taiwan: One State or Two?
answer
>Most other countries consider China (People's Republic of China) and Taiwan (Republic of China) as separate and sovereign states >China's government considers Taiwan a part of China >Civil war between the Nationalists and the communists during the 1940s • After losing in 1949, the Nationalists fled to Taiwan > Taiwan lost its UN member 1971
question
Western Sahara: challenges defining state
answer
>Most African countries consider Western Sahara a sovereign state (103,000 sq. mi with a population of about 600,000) >Morocco claims the territory and has built a 1,700 mi wall around it to keep rebels out >The legal status of the territory and the question of its sovereignty remains unresolved >It is considered a non-self-governed territory by the United Nations
question
Physical Boundaries
answer
>coincide with significant features of the natural landscape
question
Desert Boundary
answer
type of physical boundary. >Desert boundaries are common in Africa and the Middle East. >Unmarked border between Mali and Mauritania runs through the Sahara Desert > Desert boundaries effectively divide two states, because deserts are hard to cross and sparsely inhabited
question
Mountain boundaries
answer
Type of physical boundary. >effectively divides two states because mountains are difficult to cross - also sparsely populated. >The Andes serve as the boundary between Argentina and Chile.
question
Water Boundary
answer
Type of physical boundary. >Examples include rivers, lakes, and oceans (usually in the middle of the water) >Less permanent overall than mountain boundaries because of tendencies of water levels to change in bodies of water and river channels to move over time. > especially common in East Africa
question
Geometric Boundaries
answer
>Regular, often perfectly straight lines drawn without regard for physical or cultural features
question
Cultural Boundaries
answer
>Ethnic boundaries are based on one or more cultural characteristics >A relic boundary is basically a boundary that doesn't exist but still has an effect on the present-day area
question
Enclave
answer
Part of a country that is completely separated from the main land of the country
question
Compact
answer
>distance from the center to any boundary does not vary greatly. >Seems to be the easiest to manage, based on close proximity of the government to the rest of the country/good communication (+) >Easier to defend war (small borders and small area to cover) (+) >Fewer amounts of resources due to the smaller land size (-)
question
Elongated
answer
>A long narrow shape. >Encompasses a large area of and variety of landscapes, adds biodiversity and resources (+) >Difficult to govern peripheral areas and maintain communications (-)
question
Prorupted
answer
>Compact with a large projecting extension. >More of a chance to have resources(+) >Issues with "devolution" sometimes (-) >Can disrupt communications between different regions (-)
question
Fragmented
answer
>A state includes several discontinuous pieces of territory >More area covered means more resources for the country (+) >Lack of communication between different segments (-) >Rebellions in segments that are farther from the capitol could be effective (-)
question
Perforated
answer
A country that completely surrounds another country
question
Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ)
answer
is a seazone (up to 200 nautical miles) over which a state has special rights over the exploitation and use of marine resources, including production of energy from water and wind
question
Unitary State
answer
>An independent state in which power is highly concentrated in the central government >Highly centralized government where the capital city serves as a focus of power >Appropriate for states with few internal cultural contrasts and smaller size Weaknesses: •Slow at making decisions because there are so many to make •Governs too big of an area •Bureaucracy and no balance of power
question
Federal State
answer
>A state in which considerable autonomy and power are given to individual provinces and the Central Government is relatively weak > Federalism distributes powers to its territorial sub-divisions (e.g. states and provinces) >Most of the world's largest states are federal >Federalism functions differently depending on the context
question
Centripetal and Centrifugal Forces
answer
>Richard Hartshorne described the forces within the state that unify the people and the forces that divide them >Existence, stability, and development of a country depend on the balance between these two forces
question
Centripetal Force
answer
Any factor that supports the internal unity of a state(pull)
question
Centrifugal Forces
answer
Any factor that disrupts the internal order of a state (push)
question
Gerrymandering
answer
Drawing voting districts to benefit one group over another
question
Wasted vote
answer
type of gerrymandering >spreads opposition supporters across many districts but in the minority •Break up concentration of voters •Mix with different voter groups •Dilute their voting power
question
Excess vote
answer
type of gerrymandering >concentrates one group together in a district • Minimize their impact in other districts • This guarantees them some representation - but weaken them overall
question
Stacked vote
answer
type of gerrymandering >links distant areas of like-minded voters through oddly shaped boundaries • Remove much competition from elections • Often done by incumbents to ensure continued election
question
Terrorism
answer
is a threat or deliberate use of violence against civilians, groups, or even governments
question
Al-Qaeda
answer
•Founded around 1990 by Osama bin Laden(Killed on May 2, 2011) •Laden moved to Afghanistan during the mid-1980s •joined Mujahideen force in Pakistan in 1979 • Declared war against the USA in 1996 • 9/11 attack
question
Islamic State (ISIS/ISIL)
answer
•Originated in 1999 and became an affiliate of al-Qaeda in 2004 and separated from it in 2014 •Comprises of Sunni Muslims who seek to impose strict Islamic laws
question
Boko Haram
answer
•Founded in 2001
question
Southwest Asia(crop hearth)
answer
barley, wheat, lentil, and olive
question
East Asia(crop hearth)
answer
rice and millet
question
Sub-Saharan Africa(crop hearth)
answer
sorghum,yams, millet, and rice
question
Latin America(crop hearth)
answer
beans, cotton, potato, and corn
question
Southwest Asia(animal hearth)
answer
Cattle, goats, pigs, sheep (between 8,000 and 9,000 yrs. ago), and dogs (12,000 yrs. ago)
question
Central Asia
answer
horses
question
Agriculture
answer
cultivation of plants and raising of animals to obtain sustenance and/or economic gain
question
Subsistence agriculture
answer
>the production of food primarily for consumption by the farmer's family. >Practiced primarily in developing countries >A typical subsistence farm has a range of crops and animal needed by the family to eat during the yea
question
Commercial agriculture
answer
>the production of food primarily for sale off the farm >Features that distinguish itself from subsistence agriculture include: lower percentage of farmers in labor force, highly mechanized, and larger farm size
question
Diets differ because of:
answer
1) level of development 2) physical (climatic) conditions 3) cultural preferences
question
Dietary energy consumption
answer
>the amount of food that an individual consumes >The unit of measurement of dietary energy is the kilocalorie (kcal) or Calorie in the United States
question
What do most humans derive most of their kilocalories through consuming
answer
cereal grain
question
What three cereal grains account for nearly 90% of all grain production
answer
wheat, rice, and corn
question
Protein
answer
>a nutrient needed for growth and maintenance of the human body >Developed and developing regions typically differ most in their primary sources of protein consumed <Developed Countries - leading source of protein is meat (beef, pork, and poultry) products <Developing Countries - leading source of protein is cereal grains
question
Pastoral Nomadism
answer
•It is based on the herding of domesticated animals on a seasonal basis •Various approaches combine some reliance on sedentary agriculture with the herding of livestock •It is practiced in dry climates, where planting of crops is impossible:Saudi Arabia, North and East Africa, Turkey, Central Asia, and Mongolia • About 15 million pastoral nomads, but they occupy about 20% of Earth's land area - number is declining
question
Shifting Cultivation
answer
A migratory, field rotation system found in areas of Tropical Rainforests climate •Characterized by two distinctive features: - Farmers clear land for planting by slashing vegetation and burning the debris - burn puts nitrogen into the soil - Farmers grow crops on a cleared field for only a few years, until soil nutrients are depleted, and then leave it fallow for many years so the soil can recover •Farmers return to a fallow site as few as 6 years later or as many as 20 years later
question
Plantation Farming/Agriculture
answer
•A large estate in tropical or subtropical areas devoted to the production of a single cash/export crop •Intensive commercial agriculture •The average plantation is much larger in size than the average farm in the USA • Mostly owned by multinational corporations • Each plantation tends to specialize in one (cash or luxury) crop (monoculture) • Climate is the vital element in the production of plantation crops - usually grown in the humid tropics with heavy rainfall
question
Dairy Farming
answer
• Located outside the large cities because of transportation factors • Ring surrounding a city from which milk can be supplied is known as the milkshed area • Challenges: labor intensive and winter feed •cool climate
question
Grain Farming
answer
•Distinguished from mixed crop and livestock farming, because crops are grown primarily for human consumption •Farms sell their output to manufacturers of food products, such as breakfast cereals and bread • Characteristics of a typical grain farm: heavily mechanized; farms large in areal extent; and oriented to consumer preferences •often grown in temperate grass lands
question
Mediterranean Agriculture
answer
•Every site practicing this form of agriculture borders a sea, and most are on west coasts of continents •Prevailing sea winds provide moisture and moderate the winter temperatures -moist winter • Along the Mediterranean Sea, olives and grapes are two most important cash crops • Approximately half of the land here is used to grow cereals
question
von Thünen's Model
answer
• Farm products would be grown in a series of concentric zones outward from a city (market center) •a closed model -totally unaffected by outside influence, no trade connections with the outside world
question
Organic Farming
answer
•Crops grown without application of herbicide and pesticides to control weeds •Worldwide 75 million acres or 1% of all farms (2013) •Australia, Argentina, and USA/China
question
Development
answer
>implies a process of of improving the material conditions of people through diffusion of knowledge and technology > process of improving a person's prospects of leading a long and healthy life, acquiring knowledge, and obtaining adequate resources
question
Three basic dimensions of human development
answer
health, education, and living standards
question
Human development index(HDI)
answer
>measures the level of development of every country Four variables: <The GNI (PPP) per capita <life expectancy at birth, <the adult literacy rate < the gross enrollment in education as a % of the total school-age population
question
Gross national income (GNI)
answer
the market value of all final goods and services produced in a country in a given year, including money that leaves (-) and enters the country (+)
question
Gross domestic product (GDP)
answer
similar except it doesn't account for money entering and leaving the country
question
Purchasing power parity (PPP)
answer
>an adjustment made to the GNI to account for differences among countries in the cost of goods. >PPP determines the relative value of two currencies
question
Economic Structure
answer
Primary sector:(basic production) agriculture, forestry, mining, fishing. Secondary sector:(production of goods) industry, construction, craft. Tertiary Sector:(services) trade,banks, transport,culture,education,health
question
Indicators of development
answer
>Access to Knowledge: UN considers years of schooling to be the most critical measure of the ability of an individual to gain access to knowledge needed for development. >A Long and Healthy Life: UN considers good health to be an important measure of development. Main health indicator contributing to the HDI is life expectancy at birth.
question
Inequality-Adjusted HDI (IHDI)
answer
•IHDI modifies the HDI to account for inequality within a country • The lowest score means highest inequality •HDI=IHDI means perfect equality (0 for Norway and Australia)
question
Gender Inequality Index(GII)
answer
•Considers: empowerment (2), laborforce (1), and reproductive health (2) >GII values range from 0 to 1 • Zero value = No inequality between men and women • One = highest inequality between men and women (i.e., women fare as poorly as possible in all three measures)
question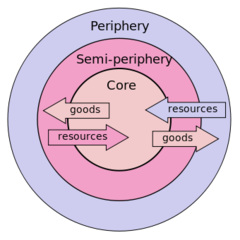
Core and Periphery

answer
•developed by Immanuel Wallerstein in 1974
question
Self-sufficiency (balanced growth) Path
answer
•Countries encourage domestic production of goods, discourage foreign ownership of businesses and resources, and protect domestic businesses form international competition •Most popular for most of 20th century •Promote self-sufficiency by setting barriers that limit the import of goods from other countries - Fixing quotas, imposing high taxes, requiring licenses • Businesses are not forced to compete with international corporations
question
Problems with self-sufficiency
answer
•Inefficiency - have little incentive to improve quality, lower production cost, reduce prices, or increase production •Large bureaucracy - encourage abuse and corruption
question
International trade Path
answer
•Countries open themselves to foreign investment and international markets •Became more popular beginning in the late 20th century • Calls for a country to identify its distinctive or unique economic assets • The sale of these products in the world markets brings needed funds for development
question
Problems with International Trade Path
answer
•Uneven resource distribution •Increased dependence on developed countries •Market decline
question
ROSTOW MODEL
answer
•In 1960, Walt W. Rostow proposed a five-stage model of development known as Modernization Model or The Classical Model of Development Five stages *Traditional Society *Preconditions to Take-off *Take-off: *Drive to Maturity *Age of High Mass Consumption
question
Traditional Society:
answer
First stage. This stage is characterized by a subsistence, agricultural based economy, with intensive labor and low levels of trading, and a population that does not have a scientific perspective on the world and technology.
question
Preconditions to Take-off
answer
Second stage. Here, a society begins to develop manufacturing, and a more national/international, as opposed to regional, outlook.
question
Take-off
answer
Third Stage. Rostow describes this stage as a short period of intensive growth, in which industrialization begins to occur, and workers and institutions become concentrated around a new industry.
question
Drive to Maturity:
answer
Fourth Stage. This stage takes place over a long period of time, as standards of living rise, use of technology increases, and the national economy grows and diversifies.
question
Age of High Mass Consumption
answer
Fifth stage. At the time of writing, Rostow believed that Western countries, most notably the United States, occupied this last "developed" stage. Here, a country's economy flourishes in a capitalist system, characterized by mass production and consumerism.



