Hematology Lecture 2: LMU – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
CBC
answer
Complete Blood Count
question
Y axis take off is caused by:
answer
-clotting specimen -clumping plts
question
CBC Components
answer
WBC: K/uL RBS: M/uL HgB: g/dL HCT: % MCV: fL(1x10x-15) MCH: pg (1x10x-12) MCHC: g/dL or % RDW: % PLT: K/uL Diff count : %
question
WBC ranges
answer
4.8 - 10.8 x 10x3 uL of whole blood (4,800 - 10,800 uL of whole blood) *High (leukocytosis) = bacterial infection *Low (leukopenia) = viral infection
question
RBC ranges
answer
males = 5.4 +/- 0.7 x 10x6 uL of whole blood (4.7 - 6.1 million uL of whole blood) females = 4.8 +/- 0.6 uL of whole blood (4.2 -5.4 million uL of whole blood)
question
Low RBC is characterisitc of:
answer
anemia
question
Hemoglobin (HgB)
answer
-measures the oxygen-carrying capacity of the RBC -When the _____ is below normal, the pt is anemic -males: 16+/- 2 g/dL -females: 14 +/- 2 g/dL
question
Hematocrit (HCT)
answer
-The % of RBCs in a volume of whole blood -aka: packed cell volume -A low ______ also signifies anemia -males: 46 +/- 5% -females: 42 +/- 5%
question
The H&H in Hematology
answer
The rules of three (under normal conditions) -RBC x 3 = HgB -HgB x 3 = HCT
question
If the HgB is 12, what is the expected HCT?
answer
HgB x 3 = HCT 12 X 3 = 36%
question
If the HCT is 45, what is the expected HgB?
answer
HgB x 3 = HCT HCT/3 = HgB 45/3 = 15g/dL
question
Exceptions to the "Rules of 3"
answer
-Severe dehydration --HgB is typically higher than what they actually are -Acute Blood Loss --The H/H reads lower than expected -IDA --The RBC usually higher than expected for the HgB
question
MCV: Mean Corpuscular Volume
answer
-Measures of the size/volume of RBCs *Most stable of all the CBC parameters* -Males: 87 +/- 7 fL -Females: 90 +/- 9 fL -Low ___: Mircocytic RBCs -High ___: Macrocytic RBCs -Normal ____: Suggests normocytic RBCs
question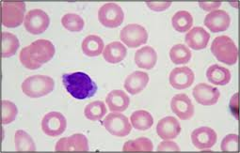
Microcytic RBCs

answer
MCV <80fL
question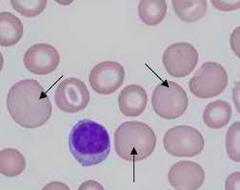
Macrocytic RBCs

answer
MCV >100fL
question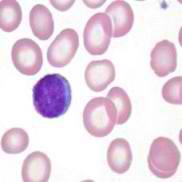
Normal RBCs

answer
MCV 80-100fL
question
MCH: Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin
answer
-Indicates the actual weight (in pg) of the hemoglobin in the RBCs -Normal range: 27 - 31 pg
question
MCHC: Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration
answer
-Expresses the ratio of the weight of HgB to the volume of the RBC -Determines the "chromasia" of the RBC -Low ___: hypochromic RBC -normal ___: Normochromic RBC -High ____: --True cases are very rare --commonly indicates an error in the HgB or RBC readings _____ cannot >= 40%
question
MCHC Normal value
answer
35 +/- 2 g/dL if 40 g/dL or higher, the blood specimen is most likely lipemic.
question
Calculations of RBC Indices
answer
MCV = HCT/RBC x 10 MCH = HgB/RBC x 10 MCHC = HgB/HCT x 100
question
RDW: Relative Distribution Width
answer
Normal Range: 11 - 13% -Indicates the variation of RBC size -HIGH ____: *Increased variation in RBC size, which is called anisocytosis *Population shows both big and small RBCs
question
Three Parameters that go Together
answer
*High RDW *"Broad Based" RBC histogram *Anisocytosis
question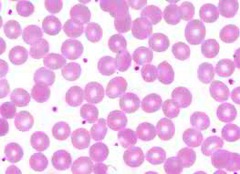
PLT:Platelet (Thrombocyte)

answer
Normal: 130,000 - 400,000 /uL Low ____: thrombocytopenia High ____: thrombocytosis
question
Critical Value, Med Alert Values, Panic values
answer
Defined as a value at such variance with normal as to represent a pathophysiological state to the patient which is or could potentially life-threatening unless immediate action is taken
question
What is used for a "Delta Check?"
answer
MCV
question
Examples of Critical Values:
answer
Hematology: -HgB: 50,000/ uL -Plt: <30,000/ uL
question
Types of Leukocytes in Normal Peripheral Blood
answer
Segs: 50-70% Bands: 0-5% Lymph: 20-40% Mono: 1-8% Eos: 0-5% Baso: 0-1%
question
Relative and Absolute Values
answer
The differential denotes the relative percetn of each type of white blood cells
question
Absolute Value Calculations
answer
(% on diff)(total WBC count) PT: 10,000 WBC/ uL Diff:60segs;5bands;30lymphs;5monos (.30)(10,000)=3,000 lymphs/uL WBC (absolute count)
question
Lymphocytosis
answer
Causes: Viral Infections;Mononucleosis;Whooping Cough
question
Neutrophilia
answer
Causes: Bacterial Infections; Appendicitis(Increased Bands)
question
Neutropenia
answer
-Decrease in neutrophils -This often occurs when there is a corresponding increase in lymphs
question
Monocytosis
answer
Tuberculosis Lupus Subacute bacterial endocarditis
question
Eosinosphila
answer
Allergies Parasitic Infections
question
Basophilia
answer
Chronic Myelogenous leukemia
question
Absolute Count Examples
answer
Slide 39 in Lecture 2
question
S.I. Units
answer
Conventional: WBC- 8.5 x 10x3 /uL RBC - 4.76 x 10x6 /uL HgB- 14.2 g/dL HCT- 43% Plt- 348 x 10x3 /uL S.I.: WBC- 8.5 x 10x9/L RBC- 4.76 x 10x12/L HgB-142g/L HCT- .43 L Plt- 348 x 10x9/L
question
Conversion factors
answer
1,000 uL = 1mL 1,000 mL = 1 L 1 L = 10x6 uL
question
What is a control?
answer
A material with a predetermined assay value that has the same matrix as the patient sample
question
What is a primary Standard?
answer
Reference material used to calibrate an instrument -Has a fixed known composition and is capable of being prepared in essentially pure form
question
What is a secondary standard?
answer
Reference material in which the analyte concentration has been ascertained reference to a primary standard
question
What is a calibrator?
answer
Preserved human cell suspension whose hematology parameters have been determined by multiple reference laboratories
question
Quality Control
answer
-Monitors the characteristics of the testing system(instrument)
question
Quality Assurance
answer
Much broader than QC -Looks at the overall process from chart to chart
question
Internal QC
answer
Done daily Run assayed known control samples with patient testing May include commercial controls as well as "patient" controls
question
External QC
answer
Proficiency Testing: Involves running unknown samples and sending in results for comparsion with other labs Not done daily
question
What is accuracy?
answer
The exactness of a mearsurement in comparsion with the true value
question
What is precision?
answer
Measures the reproducibility of an analyzer
question
What is a Delta Check?
answer
Comparing the result from the current analysis of a sample with the results from the previous sample for the same analyte for the same patient
question
CV: Coefficient of Variation
answer
SD/MEAN x 100% -The smaller the ___, the more precise the analytical method -A ____ of >5% is unacceptable.
question
What is sensitivity?
answer
Proportion of patients with the disease who have a positive test result -Screening test- -Used to rule out a disease
question
What is specificity?
answer
Proportion of the patients without the disease who have a negative test results -Confirmation test- -Used to confirm the presence of a disease
question
For our controls in hematology, the control result must fall into a acceptable range, which is typically the mean +/- ___ SD
answer
2
question
Levey-Jennings Control Charts
answer
95% of values should fall between +/- 2SD 99% of values should fall between +/- 3SD
question
Shifts on LJ Chart
answer
Sudden change of values from one level to another Causes: Erroneous reagents, controls, etc.
question
Trend on LJ Charts
answer
Drift of values in one direction over six or more consecutive values Causes: Deterioration of reagents, light sources, etc
question
Westgard Rules
answer
If any of these rules are broken, your instrument is "out of control" and your results are inaccurate and can't be reported
question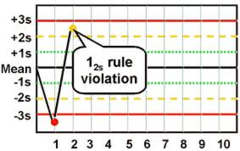
1 2s

answer
Considered a "warning." The run must be rejected if another Westgard rule is broken in addition to this rule. *1 control exceeds 2SD from the mean
question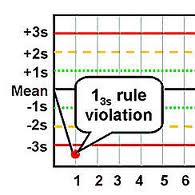
1 3s

answer
1 control result exceeds 3 SD from the mean
question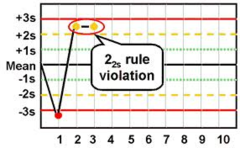
2 2s

answer
2 controls exceed 2SD on the same day of testing
question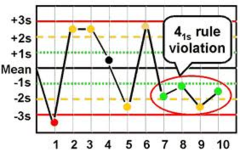
4 1s

answer
4 results exceed 1 SD in the same direction -Control values are beyond 1 SD for 4 consecutive days
question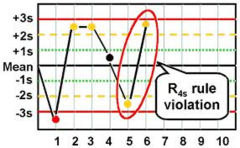
R 4s

answer
4 SD difference between controls in the same run *Most common reason: Picking up wrong control ; running it
question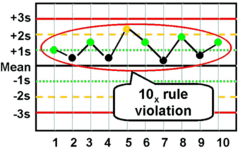
10x violation

answer
10 consecutive values fall on the same side of the mean
question
1 3s or R 4s
answer
*Indicate random error *Sample not mixed well, technical error, etc
question
2 2s, 4 1s, or 10x
answer
*Indicates systemic error *Deteriorating reagents, instruments needs cleaning, etc.
question
Limitations of Bulls Moving Average
answer
*Not sensitive to random errors *Very sensitive to patient population; a number of oncology patients culd affect the calculation in the absence of instrument malfunction *This method does not directly monitor the WBC and platelet counts



