GERD and esophageal cancer – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
GERD
answer
-The condition that results when the reflux of gastric material into the esophagus or oropharynx causes symptoms, tissue injury, or both. -the free reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus composed of acid, non-acid secretions (bile, pancreatic enzymes, pepsin, mucus) and ingested gastric contents
question
Physiological reflux
answer
Type of reflux occurs many times each day with everyone during meals
question
Pathologic GERD
answer
-Typical or classic (heartburn/regurgitation) versus atypical symptoms -mucosal disruption description: erosive/ulcerative versus non-erosive -extent of reflux: esophageal versus laryngopharyngeal reflex
question
prevalence of GERD
answer
-40% of the US adult population has heartburn at least once per month -5 to 10% of the US population has episodes of heartburn at least once daily
question
Complications associated with esophageal reflux
answer
-Strictures -bleeding -Barrett's esophagus (intestinal metaplasia) -esophageal cancer -damage to the esophagus, pharynx, larynx, and respiratory tract
question
Classic symptoms of GERD
answer
-Heartburn (Pyrosis) -regurgitation or acid brash; gross reflex experienced with a sense of liquid passing up into the chest and sometimes the mouth -water brash; increased elevation caused by stimulation of esophageal reflux -chest pain; indistinguishable from cardiac angina -can be completely asymptomatic (25%)
question
2 symptoms that when they occur together are ;90% predictive of GERD
answer
Heartburn and regurgitation
question
Endoscopic or radiographic descriptions of reflux:
answer
Non-erosive reflux disease (NERD) erosive reflux disease
question
NERD

answer
-Imaging of esophageal mucosa is normal -most common pathologic reflux -50% with GERD sx -No visible damage -Must not have alarm symptoms/ conditions -Reassure and treat -Will not cause complications
question
Erosive reflux disease
answer
-Esophageal erosions noted on endoscopy or barium esophagram -may lead to the complications of reflux disease because of chronic inflammation -severity of symptoms does not necessarily correspond to severity of esophagitis
question
Atypical or extra esophageal manifestations of GERD presentation
answer
-Asthma -chronic cough -chronic coarseness -noncardiac chest pain -chronic hiccups -night sweats -a loss of dental enamel
question
Differential diagnosis of esophageal reflux symptoms
answer
-Infectious esophagitis -pill esophagitis -eosinophilic esophagitis -peptic ulcer disease -non-ulcer dyspepsia -biliary tract disease -coronary artery disease -esophageal motor disorders
question
Peptic strictures
answer
-form when chronic inflammation leads to scarring of the esophageal wall -compromises the viable diameter of the esophageal lumen -most commonly found near the gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) -patients present with difficulty swallowing; solids ;liquids -may result with acid suppression or may require endoscopic disruption would balloon dilation
question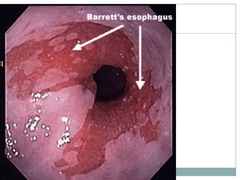
Intestinal metaplasia (Barrett's esophagus)

answer
-premalignant condition -Chronic reflux over many years leads to metaplastic change in the distal esophagus -squamous cells ? columnar epithelium -1/10 patients with chronic reflux develop this -has the potential to become adenocarcinoma of the esophagus; 1/200 patients with this develop cancer -monitor with biannual endoscopy with biopsy to monitor progression towards dysplasia
question
Upper esophageal sphincter
answer
-Striated muscle -close to prevent esophageal reflux into pharynx and aerophagia
question
Esophageal body
answer
-Striated muscle = proximal 5% -mix of striated and smooth muscle = proximal 1/3 -smooth muscle = distal 2/3 -25 cm long by 3 cm in diameter -within negative pressured thorax -primary and secondary peristalsis clears reflux materials
question
Lower esophageal sphincter
answer
-Smooth muscle -closed at rest to prevent reflux of gastric contents -distinct area of the esophagus and diaphragm -muscle is quite thick here -tonically contracted and relaxes with swallowing
question
Diaphragmatic sphincter
answer
Diaphragm squeezed into LES to further bolster pressure at GEJ
question
Epithelial resistance factors
answer
Salivary bicarb esophageal and gastric mucosal bicarbonate
question
pathophysiology of reflux
answer
-Multi-factorial = failure of reflux barrier -abnormal LES function -hiatal hernia -poor peristalsis of the esophagus leading to inadequate clearing of refluxate -caustic substances -reduced epithelial resistance
question
Abnormal LES function
answer
-Transient lower esophageal sprinkler relaxations (TLESR) believed to play a major role in initiating GERD -many stimuli increased frequencies of relaxations, including gastric this tension, burning zeal stimulation, stress, posture, and sleep -TLESR ? reflux and inflammation ? weakened LES
question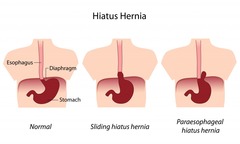
Hiatal hernia

answer
disrupts diaphragmatic positioning at LES
question
Reduced epithelial resistance
answer
Decreased bicarbonate from saliva and mucosa
question
Caustic substances
answer
-In addition to HCL secreted by the stomach, non-acid or weak acid refluxate includes the conjugated bile salts, pancreatic enzymes, pepsin, medications, or ingested foodstuffs that may be responsible for symptoms or damage
question
Diagnoses of GERD
answer
-Appropriate symptom complex (heartburn+reflux) -upper endoscopy with possible biopsy -esophagram or upper G.I. x-ray -24-hour monitoring -impedance plethysmography/24 hour ph
question
upper endoscopy with possible biopsy
answer
Gold standard for esophagitis Most sensitive test for seeing esophagitis, complications, and finding Barrett's esophagus
question
esophagram or upper G.I. x-ray
answer
Not sensitive for mild refluc Gives information about motility and amount of reflux
question
24 hour monitoring
answer
-Small tube place down the nose into the esophagus and stomach -acid sensor at the lower and quantifies the amount of reflux into the esophagus and correlates to reported symptoms
question
impedance plethysmography/24 hour ph
answer
-Sensors placed along the length of the probe to detect movement of fluid into the esophagus and to correlate to risk ported symptoms -Quantifies reflux -Helpful in patients unresponsive to empiric therapy and may have non-acid reflux
question
Lifestyle changes recommended for patients with GERD

answer
-Elevate head of bed at least 4-6 inches -stop smoking -decrease alcohol consumption -reduce fat intake -decreased size of meals -avoid bedtime snacks are eating 2 hours prior to lying down -avoid: tea, coffee, citrus, chocolate, mint, tomato juice, and cola -avoid these drugs as much as possible: anti-cholinergic, diazepam, theophyliine, calcium channel blockers, narcotics
question
Drug therapy for GERD
answer
-;80% of patients will require chronic reflux medications - antacids: neutralize acid in the esophagus and stomach -H2 receptor antagonists: decrease acid content of the gastric refluxate and make it less noxious to the epithelium -proton pump inhibitors: cause irreversible blockade of parietal cell hydrogen-potassium ATPase
question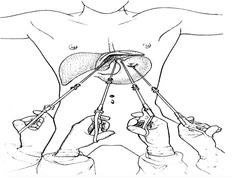
Nissen Fundoplication

answer
Surgery to reestablish the reflex barrier by wrapping the stomach around the GEJ to create a high-pressure zone
question
Incidence of esophageal cancer
answer
300,000 deaths/year worldwide -in China, annual rate is 130/100,000 -in the US, 90%
question
Symptoms of esophageal cancer
answer
-Dysphagia -GERD -thoracic back pain -bleeding -weight loss
question
Pathology of esophageal cancer
answer
-Rate of adenocarcinoma of the GEJ is increasing at a greater rate than any other malignancy in the Western world
question
Squamous cell cancer
answer
-Arises from the squamous lining of the upper esophagus -most common in the proximal esophagus -most common type of esophageal cancer in Asia
question
Risk factors for squamous cell cancer
answer
-Tobacco -alcohol -pickled foods and smoked meats -caustic injury of the esophagus -head and neck cancer -tylosis palmaris and plantaris
question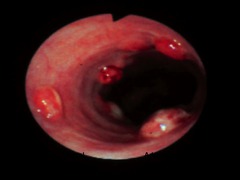
Adenocarcinoma

answer
-Currently the most common esophageal cancer in the Western world -fastest rising incidence of any solid tumor -found at or near the GEJ where columnar cells are found -Barrett's metaplasia is a precancerous change -reflux is the greatest risk factor for Barrett's changes -adenocarcinoma is more common with middle aged white men -adenocarcinoma is associated with obesity
question
Surviving esophageal cancer
answer
-Prognosis most closely correlates at this stage of the disease at the time of diagnosis -surgical esophagectomy remains the only cure for the disease; not offered to patients with advanced disease states
question
Staging esophageal cancer
answer
Step 1: thorough physical exam, keying in on sites prone to metastases including supraclavicular nodes, liver, lung step 2: PET/CT scan of chest and abdomen to evaluate for metastases step 3: endoscopic ultrasonography with possible fine needle aspiration biopsy -management is generally palliative -one discovered by symptoms (dysphagia, bleeding, weight loss) treatment is generally palliative
question
Goal of palliation in esophageal cancer
answer
to allow the patient to stay at home, allow oral intake, and control pain
question
Treatment of early disease stage
answer
Treated and cured with surgery only -endoscopic resection may be tried for stages 0, 1
question
Treatment of advanced esophageal cancer
answer
-Radiation, chemotherapy and surgery in combination
question
Treatment of metastatic disease
answer
-Endoscopic stenting or tumor ablation with photodynamic therapy, radiation and chemo palliation. -Surgery should be avoided
question
Photodynamic therapy
answer
-systemic injection of light-sensitive drug porfimer sodium. -local activation of low-power, red light laser -patients may remain light-sensitive for up to 8 weeks and must avoid the sun
question
Relief of dysphagia
answer
-Balloon dilation: effective but only last for a few days -stenting: ;15% risk of acute complications and 20-40% chance of late complications
question
Late complications of stenting
answer
Migrations, bleeding, fistula
question
Acute complications of stenting
answer
Perforation, bleeding
question
Specific treatment of esophageal cancer
answer
-Surgery -radiation -chemotherapy -palliation -thermal -chemical
question
Standard chemotherapy for esophageal cancer
answer
Cisplatin and 5 fluorouracil -response is 20-40% -there is no improved survival
question
things that aggravate heartburn
answer
alcohol caffeine chocolate citrus products fat peppermint spicy foods tomato products bending lifting meals before bed some medications obesity? pregnancy running smoking tight clothing
question
alarm symptoms of reflux
answer
Dysphagia Odynophagia GI bleeding and anemia Weight loss Chest pain Choking Recurrent pneumonia New onset...Age ; 45 yrs
question
LA grade A esophageal reflux

answer
One or more mucosal breaks no longer than 5 mm
question
LA grade B Esophageal reflux

answer
One or more mucosal breaks longer than 5 mm
question
LA grade C esophageal reflux

answer
Bridging of the tops of mucosal folds involving ;75% of the circumference
question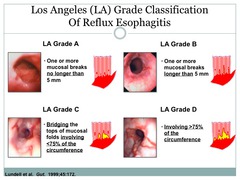
LA grade D esophageal reflux

answer
Involving ;75% of the circumference
question
GERD complications
answer
1. Esophageal reflux 2. Refractory erosive esophagitis -Persistent heartburn and chest pain 3. esophageal rings -Intermittent dysphagia 4. peptic strictures -Persistent dysphagia 5. Barrett's esophagus 6. esophageal adenocarcinoma -Progressive dysphagia
question
schatzki ring
answer
superficial mucosal scar
question
Strictures
answer
mucosal and submucosal scarring -most common complication of GERD -May occur in up to 25% *Decreasing severity due to PPI
question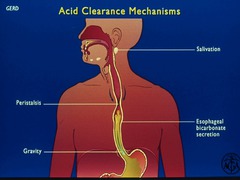
acid clearance mechanisms

answer
-salivation -peristalsis -gravity -esophageal bicarb secretion
question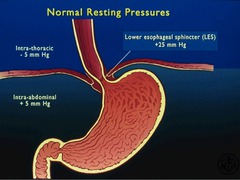
resting pressures

answer
intrathoracic = -5mmHg intraabdominal = +5mmHg LES = +25mmHg
question
progression to hypotensive LES
answer
TLESRs ? reflux and inflammation ? weak LES
question
Role Of Endoscopy In GERD
answer
-Rule out complications -Grade disease severity -Influence management? 50% with heartburn have no findings (NERD) severity of heartburn does not predict esophagitis lack of esophagitis does not predict an easier-to-treat subset of patients
question
when to perform an Esophageal 24 hr pH-Impedance Test
answer
Symptoms NOT responding to PPI: -Heartburn -Atypical chest pain -Extraesophageal manifestationsof GERD (e.g. laryngitis, chroniccough, adult-onset asthma) -Considering non-acid reflux
question
GERD treatment goals
answer
-Relieve symptoms -Heal esophageal injury -Prevent complications (eg, esophagitis,peptic strictures, Barrett's esophagus) -Maintain remission
question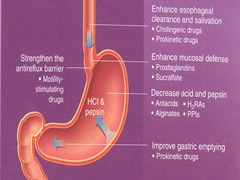
GERD Pathophysiology-based Pharmacologic Treatment

answer
1. enhance esophageal clearance and salivation -cholinergic and prokinetic drugs 2. enhance mucosal defense -prostaglandins and sucralfate 3. decrease acid and pepsin -antacids and alginates 4. improve gastric emptying -prokinetic drugs 5. strengthen the antireflux barrier -motility stimulating drugs
question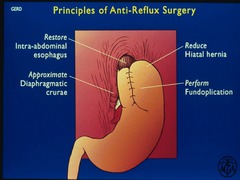
principles of anti-reflux surgery

answer
restore intra-abdominal esophagus approximate diaphragmatic crurae reduce hiatal hernia perform fundoplication
question
most effective treatment in the management of GERD
answer
PPIs
question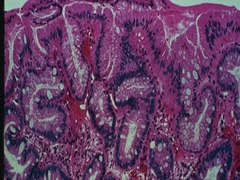
Barrett's histopathology

answer
Metaplastic changes of esophagus from GERD Specialized columnar epithelium Abundant goblet cells
question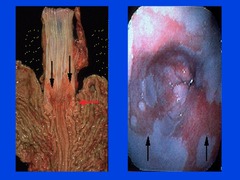
Barrett's Esophagus

answer
Change from squamous to columnar epithelium with goblet cell metaplasia is a risk factor for dysplasia and development of adenocarcinoma
question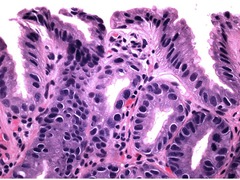
Barrett's w/ LG Dysplasia

answer
-Nuclear atypia, <50%, are large and have dark markings -Increased mitosis -Normal gland pattern (cells are grow in even rows).
question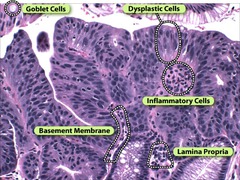
Barrett's with HG Dysplasia

answer
-Nuclear atypia with ;50% with dark nuclear spots -Abnormal glandular growth not beyond the lamina propria -Glands are branching, budding, and distorted -Increased mitosis -Cytoplasm may appear abnormal staining
question
Treating Barrett's ...(Preventing Adenocarcinoma)
answer
1. No clear evidence of reversal back to squamous 2. To prevent reflux-related inflammation: -PPI's - minimal effect -Antireflux surgery - some literature supports 3. Surveillence: every 2 years endoscopy + biopsies 4. Ablation for Barretts with dysplasia: -Radiofrequency Ablation Therapy -Photo Dynamic Therapy - more complications with a stricture rate 30%
question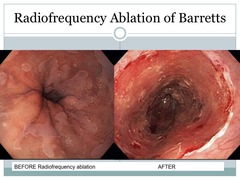
Radiofrequency Ablation for Barretts

answer
-Bipolar array -Devices are available in circumferential and focal configurations -Bipolar array technology, controlled ablation depth -Frictional heating of cellular water
question
adenocarcinoma risks
answer
1. Reflux-Barretts 2. Reflux risk factors: Obesity High fat diets Bile reflux
question
Esophageal Cancer - presenting symptoms occur late:
answer
Dysphagia to solids +/- liquids Weight loss Anemia/hemetemesis Chest pain Back pain Late presentation: -Esophagus is very distensible -Tumor must be large to cause dysphagia. -No adventitia layer thus CA spreads readily to surroundings.
question
Staging Esophageal Cancer
answer
1. Location: proximal vs. lower 2. Lymph nodes: regional vs. distant 3. Metastases: local vs. distant 4. Staging tests: CT scan of chest, abdomen, pelvis Endoscopic ultrasound PET scan



