General Psychology Chapter 3 Test – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Plasticity
answer
-The brain's special capability for change. -adaptable,changing
question
Afferent/Sensory Nerves
answer
-Nerves that carry information about the external environment to the brain and spinal cord via sensory receptors. -One way from outside into the brain A-Arrive
question
Efferent/Motor Nerves
answer
-Nerves that carry information out of the brain and spinal cord to other areas of the body. -From the Brain Out E- Exit
question
"One-Way Streets"
answer
Efferent and Afferent Nerves
question
CNS parts
answer
The Brain and Spinal Cord -Central Nervous System
question
Autonomic NS parts
answer
The body system that takes messages to and from the body's internal organs, monitoring such processes as breathing, heart rate, and digestion. -Two parts Sympathetic NS - arouses and Parasympathetic NS- calms the body
question
Mirror neurons
answer
a neuron that fires both when an animal acts and when the animal observes the same action performed by another
question
Types of cells in nervous system
answer
-Glial Cells -Neurons -Mirror Neurons
question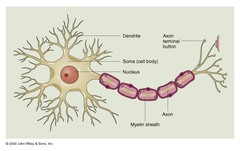
Parts of a neuron and functions

answer
-Cell Body -Dendrites -Axon -Myelin Sheath (only seen in peripheral nervous system >>> controls voluntary movement)
question
Flow of information in nervous system
answer
-Semipermeable - Ion Channels -Depolarization(Ion channels open) -Threshold -Action Potential -All-or-None Principle
question
Myelin
answer
A layer of fat cells that encases and insulates most axons. -surrounds the core of a nerve fiber or axon and that facilitates the transmission of nerve impulses, formed from the cell membrane of the Schwann cell in the peripheral nervous system and from oligodendroglia cells (Google Definition)
question
Resting potential
answer
The stable, negative charge of an inactive neuron.
question
Action potential
answer
The brief wave of positive electrical charge that sweeps down the axon.
question
All-or-Nothing principle
answer
-The principle that once the electrical impulse reaches a certain level of intensity -it's threshold-, it fires and moves all the way down the axon without losing intensity.(book definition) -A neuron will either fire or not fire, is either going to do something or nothing at all (Kardas Definition)
question
Synapse
answer
Tiny spaces between neurons; The gaps between neurons are referred to as synaptic gaps.
question
Neurotransmitters
answer
Chemical substances that are stored in very tiny sacs within the terminal buttons and involved in transmitting information across a synaptic gap to the next neuron.
question
Acetylcholine effects
answer
-ACH -Muscle actions, learning, memory -Black widow venom ^(up) Ach levels -Botox (botulin) | (down) Ach levels -Alzheimer's disease | (down) Ach levels
question
GABA function
answer
-Inhibitory neurotransmitter -Anxiety | (down) GABA levels -(fire,don't fire)
question
Runners high and endorphins
answer
-Natural opiates -Mediate feelings of pleasure and pain -The most obvious aspects to address with runner's high are the biological and psychological aspects that can be associated with it. When the body is put under stress the mind reacts accordingly.
question
Types of brain scans
answer
- X-Ray -CT Scan -PET (actively) -MRI (using magnetization vibrations) -fMRI (real time)
question
Medulla functions
answer
Controls breathing and heart rate, it also regulates reflexes
question
Hippocampus functions
answer
-Formation and recall of memories (place for horses) - The structures in the limbic system that has a special role in storage of memories ( book definition)
question
Thalamus functions
answer
-Relay station for much sensory information (everything except the nose) - The forebrain structure that sits at the top of the brain stem in the brain's central core and serves as an important relay station (book definition)
question
Hemispheres
answer
-The Cerebral cortex is divided in two halves -the two halves of the cerebellum
question
Corpus callosum
answer
-a broad band of nerve fibers joining the two hemispheres of the brain. -The large bundle of axons that connects the brain's two hemispheres, responsible for relaying information between the two sides.
question
Lobes of the cerebrum
answer
-Occipital lobe (vision)-- Structures located at the back of the head that respond to visual stimuli. -Temporal lobe (hearing, language processing, memory)--Structures in the cerebral cortex that are located just above the ears. -Frontal (intelligence, personality and the control of voluntary muscles)-- The portion of the cerebral cortex behind the forehead -Parietal(spatial location, attention, motor control)--Structures at the top and toward the rear of the head.
question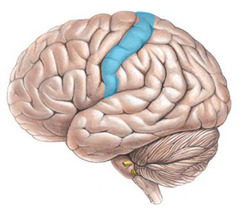
Somatosensory cortex

answer
-In parietal lobe -body sensations/ touch, detecting things -A region in the cerebral cortex that processes information about body sensations, located at the front of the parietal lobes (book definition)
question
"Split brain"
answer
a lay term to describe the result when the corpus callosum connecting the two hemispheres of the brain is severed to some degree. It is an association of symptoms produced by disruption of or interference with the connection between the hemispheres of the brain. (google definition)
question
Right hemisphere functions
answer
Spatial perception, visual recognition, emotion
question
Left hemisphere functions
answer
Verbal processing, speech, grammar
question
Hormones
answer
Chemical messengers that are produced by the endocrine glands and carried by the bloodstream to all parts of the body.



