Eye Cancer- Orbit and Pterygium – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Benign orbit diseases
answer
-Graves' Disease -Orbital Pseudotumor -Pterygium
question
Malignant orbit diseases
answer
-Ocular Melanoma -Orbital Lymphomas -Metastasis to the Orbit
question
Eye epidemiology/etiology
answer
Graves' disease -More common in females than males -Occurs most often in middle ages (30-50) -Autoimmune disorder Melanoma is the most common primary intraocular malignancy -Average age is 55 -Metastatic disease to orbit is rare but more common than primary eye cancer -usually from breast or lung Primary intraocular cancer -2015 estimated in US, 2,580 adults (1,360 men and 1,220 women). -It is estimated that 270 deaths (140 men and 130 women) will occur this year. -Cancer that has spread to the eye from another place in the body (secondary eye cancer) is more common than primary eye cancer
question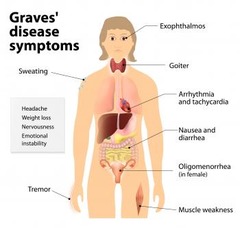
Clinical detection Graves Disease

answer
Caused by inflammation of extraocularmuscles and orbital tissues -Exophthalmos, opthalmoplegia, oculopathy, periorbitalswelling, corneal ulceration, optic nerve compression and opticatrophy
question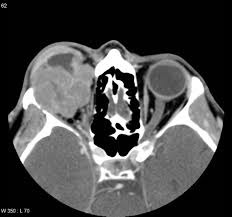
Clinical detection Orbital Pseudotumor

answer
Pain, conjunctiva redness, chemosis, edema, exophthalmoses, restriction of eye movement Can cause optic nerve atrophy, disc edema and vision loss
question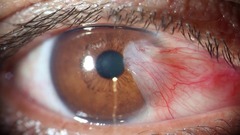
Clinical detection Pterygium

answer
Conjunctival growth over the sclera & cornea. -Causes visual and cosmetic impairment. -Common on nasal side of eye
question
Clinical detection Orbital Lymphomas
answer
Mass, Proptosis, Swelling, Inflammation, Diplopia, Pain
question
Diagnosis
answer
Eyelid -x-rays can detect bony invasion -incisional or excisional biopsy mandatory -Melanoma -biopsy not acceptable due to orbital spread -noninvasive imaging: CT, MRI, Nuclear Medicine, Ultrasound, opthalmoscopic exam
question
Mechanisms of Spread
answer
Melanoma -Can involve any organ via hematogenous spread, usually the liver -Lymphatic spread can occur, but not as common
question
Pterygium General Treatment Methods
answer
surgical excision -recurrence rate is 20 -40% Beta plaque irradiation postop can reduce recurrence rate to <5% -Strontium 90/yttrium-surface applicator -More commonly done after a recurrence -The second recurrence rate is 6% Can also use chemo or transplant for the recurrence -mitomycinC, thiotepa, flourouracil
question
Pterygium Radiation Treatment Plan
answer
Pterygium-decrease recurrence to less 5% Preferably within 24 hours of surgery, sterile plaque surface is placed in direct contact -10 -15 seconds delivers 5 -6 Gy surface dose -3 factions to 15 Gy w/ strontium 90 up to 10 Gy/60 Gy
question
Eye General Treatment Methods
answer
Melanoma -surgery (enucleation), RXT Lymphoma -chemo and RXT Graves Disease -steroids, surgery, RXT Orbital Pseudotumor -steroids, RXT Orbital Metastasis -RXT
question
Choroidal Melanoma Radiation Treatment Plans
answer
No lymphatics in the choroid Metastasis occur hematogenously unless local invasion 125 I of sufficient diameter to allow for a 2-3 mm margin. 100 Gy is given to the apex of 5-10 mm. 100 Gy at 5 mm is give for tumors 2.5 -5mm. Lesions contiguous with optic disk cannot be done due to radiation damage to optic nerve. Melanomas arising in the iris or ciliary body cannot be done due to damage to lens and cornea
question
Lymphoma of the Orbit Radiation Treatment Plans
answer
45* wedged pair 4-6 MV 1.8/25-30 Gy for low or intermediate grade 2/40 Gy for high grade Corneal dose is diminished if eye is open during treatment
question
Lymphoma of Conjunctiva Radiation Treatment Plans
answer
6-9 MeV electron beam Diameter to encompass conjunctiva Lens shielding a must -12 mm circular lead shield at least 4 mm thick 2 Gy per FX=30 Gy
question
Intraocular lymphoma Radiation Treatment Plans
answer
Rare, but may appear with CNS lymphoma Diffuse large cell found in immunosuppressed patients Field includes posterior 2/3 of eye 1.8 -2.0/40 -50 Gy Average survival is 12 months
question
Graves Disease Radiation Treatment Plans
answer
RXT for pts in whom steroids are contraindicated Efficacy of RXT related to radiation sensitivity of cellular infiltrates in the extraocularmuscles and retroorbitalconnective tissue Opposed pair using 4-6 MV Encompass both retrobulbarvolumes Anterior edge of beam at lateral bony canthus asymmetric jaws, or angle 5-7* posterior MIDLINE dose is 2 Gyper day, may produce initial swelling 20 GY total dose which will cause cataracts, so both lenses must be shielded
question
Orbital Pseudotumor Radiation Treatment Plans
answer
Nongranulomatousinflammatory disease 4 x 4 Electron beam with lens shield 9-16 MeV 10 -30 Gy
question
Orbital Metastasis Radiation Treatment Plans
answer
Metastasis uncommon to orbit, but metastatic tumors are the most common intraocular malignancy Commonly seen from breast cancer 4 x 4 field encompassing posterior portion of globe (posterior to lens) lateral beams using electron or 4-6 MV if treating both eyes Posterior angle to avoid contralateral lens 2-3/30-40 Gy will improve vision
question
Side Effects
answer
Dry eye cataract formation blindness Dose to produce cataract is 2 Gy
question
Parts of the eye TD5/5 Normal Tissue Tolerance
answer
lens 5 Gy retina 50 Gy cornea 50 GY optic chiasm & optic nerve 50 Gy
question
Parts of the Eye: least to most radiosensitive
answer
1. lens 2. conjunctiva 3. cornea 4. uvea 5. retina 6. optic nerve
question
Prognosis
answer
Generally about 75-80% of people with eye melanoma survive for at least 5 years. -Accurate survival rates for eye melanomas based on a specific stage are hard to determine because these cancers are fairly rare. Eye lymphoma is rare, so statistics for this cancer are hard to find. -Patients without HIV whose lymphoma was confined to the eye, about half of the patients were still alive 5 years after diagnosis.



