Epidemiology: Surveillance and Outbreak Investigations: THE JON SNOW STORY (L20) – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Why is Jon Snow a BFD (Big F*ing Deal)?
answer
Showed that public health interventions based on epi info can proceed and be effective even with imperfect knowledge of the etiological agent of a disease! • Removing the pump handle saved hundreds of lives, despite the fact that Snow did not know the cause of cholera Also: Voted best Doctor EVER (take that Hippocrates!) Invented anesthesia
question
Importance of the Snow maps
answer
• Each bar on map is a death, shows a clustering of cases near the broad street pump • Houses near the OTHER pump only had 10 deaths; of those, 5 victims always drank water from the Broad St. pump • Took sample from the pump, examined it under microscope, saw white, flocculents • Mapping allowed him to support his theory the pump was the source of cholera
question
Surveillance
answer
an active disease accounting process intended to monitor the overall disease and health status of a population continuously and systemically - in vet med: based on PREVALENCE SURVEYS
question
Uses of Surveillance
answer
o Way to define the normal limits for disease (expected frequency) o Detect outbreaks/epidemics in their early stages o Track longer term "secular changes" o Certify that disease is absent o Evaluate the efficacy of public health interventions
question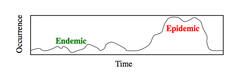
How outbreaks are detected

answer
• When the incidence of disease in a given time period is above the normal range • Generally suspected when rates of occurrence (incidence) exceed limits defined by 95% confidence intervals around time averaged means
question
Time series analysis

answer
detection description and measurement of periodicities from temoporal disease occurrence data; example: moving average
question
Time series analysis: Trend Types

answer
• Secular trends: overall, long term increases or decreases in rate of occurrence (Height, obesity) • Seasonal fluctuations: regular changes in occurrence with periods shorter than a year (Flu season) • Cyclic changes: regular changes in occurrence with period longer than a year (Outbreak of dz every few years in mumps: due to children being born, getting it, herd immunity protects for a bit, then the cycle occurs again when herd immunity lost) • Irregular variation: random or unpredictable changes in occurrence over time
question
Case Definition
answer
based on clinical signs, microbio and serologic features etc. Necessary to an outbreak investigation to accurately classify cases vs non- cases.
question
Population at Risk
answer
must also be defined for an outbreak investigation. Who is at risk? = Denominator
question
Index Case
answer
first case to be brought up to a public health official (not necessarily first case of outbreak)
question
Primary Case
answer
A case that gets infected from exposure to the souce of the dz/agent (not first case either)
question
Secondary Case
answer
Case that gets dz from exposure to a primary case
question
Primary Attack Rate
answer
Recall from Exam 1. Measures initial speed of outbreak "How BAD the situation is"
question
Secondary Attack Rate
answer
Recall from Exam 1. Measured *ongoing* speed of outbreak. = # individuals that become diseased in *subsequent* period/(initial PaR - primary cases)
question
Exposure Specific Attack Rates
answer
compare attack rates from sick vs non sick animals to figure out if factor is associated with the dz.
question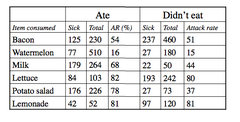
Multiple Exposure Specific Attack Rates: Identifying causal factors

answer
Causal factors will have: - higher attack rates in exposed groups than unexposed - greatest difference between attack rates - relative risk >1 for exposed groups - Confidence Intervals that don't cross 1 - nonexposed level=endemic dz level.
question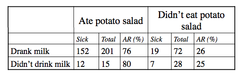
Cross Tablulation

answer
used for single exposure outbreaks (one cause, like the potato salad!) - can be done by hand in the field, using exposure specific attack rates.
question
Quarantine
answer
Quarante Giorno (40 days!) to prevent spread of black plague. *Quarantine period should be longer than incubation period.* • Quarantine individuals coming into the population to prevent reintroductions of the disease agent • Quarantine individuals leaving the population to prevent the spread of disease
question
Common Intervention strategies
answer
• Limit access by people • Clean and disinfect equipment: beware fomites! Equipment includes vehicles • Call appropriate officials (state vet, especially for reportable dz) • Adopt a generous "down time" policy for health professionals serving multiple clients and herds (beware iatrogenic transmission)
question
Disease prevention, control, eradication
answer
*Prevention*: exclude a disease from an unaffected popln -->Requires continuous effort and vigilance for as long as the possibility remains that a disease may occur *Control*: reduce the frequency or cost of dz to some socially or economically acceptable level *Eradication*: the complete elimination of an infectious agent from a geographic region. Ex. Rinderpest (smallpox)
question
Common Tactic for Dz control/management
answer
• Mass treatment: treat all (food/water) • Mass immunization • Slaughter • Environmental hygein: prevent contact with contam environ (disinfection) • Biological control ("applied ecology"): reduce the vector or reservoir • Education: essential but can be ineffective
question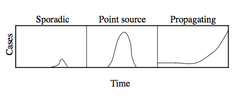
Epidemic types displayed by Epidemic Curve

answer
Sporadic Point Source Propagating
question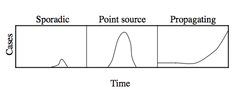
Epidemic Curve

answer
graph of the times of onset of cases - Y axis = raw number of cases; X axis = different time points Contains info about: o Avg # secondary infections causes by a primary infection (early curve) o Time between exposure and onset of dz (incubation period) o Types of epidemic (sporadic, point source, propagating)
question
Case fatality rates
answer
Probability of dying if you get the disease • # deaths due to disease/total # of cases of dz • CFR = "honest" measure of severity of an outbreak



