Core Concepts Anesthesia Review – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Factors decreasing physiologic dead space include: 1. the supine position 2. anticholinergic agents 3. increasing age 4. emphysema
answer
1. the supine position Dead space is comprised of gases in non-respiratory airways (anatomic dead space) as well as in alveoli that are not perfused (alveolar dead space). The sum of the two is known as physiologic dead space. Certain factors affect dead space. The supine position is known to decrease dead space, whereas anticholinergics, β2-sympathomimetics, advancing age and COPD all increase dead space. pg. 599 Nagelhout, JJ, and Plaus, KL. Nurse Anesthesia. St. Louis: Elsevier, 2014. pg. 363 Longnecker, DE, Brown, DL, Newman MF and Zapol, WM. Anesthesiology. New York: McGraw Hill, 2012.
question
As compared with plasma osmolality, hypertonic crystalloid solutions include: 1. D5W 2. LR 3. D5 0.25NS 4. D5 0.45NS
answer
4. D5 0.45NS Normal plasma osmolality ranges between 280 - 290 mOsm/L. D5W is hypotonic in relation to plasma, with a tonicity of 253 mOsm/L. Both Ringer's lactate and D5 0.25NS are isotonic solutions, with tonicities of 273 and 355 mOSm /L respectively. D5 0.45NS is hypertonic with a tonicity of 406 - 432 mOsm/L. pg. 392 Nagelhout, JJ, and Plaus, KL. Nurse Anesthesia. St. Louis: Elsevier, 2014.
question
Pancreatic somatostatin producing cells in the islets of langerhans are: A. Alpha cells B. Beta cells C. Gamma cells D. Delta cells
answer
D. Delta cells Islets of langerhans are comprised of 4 cells types: alpha cells producing glucagon, beta cells producing insulin, delta cells producing somatostatin and PP cells producing pancreatic polypeptide Pg. 789 Nagelhout
question
Congenital heart diseases a/w right-to-left shunt include: (select 3) a. tricuspid atresia b. hypoplastic left heart syndrome c. aortopulonary window d. patent ductus arteriosus e. tetralogy of Fallot f. subvalvular aortic stenosis g. ventricular septal defects i. atrial septal defects
answer
a. tricuspid atresia b. hypoplastic left heart syndrome e. tetralogy of Fallot Right-to-left shunting (cyanotic) heart disease is a/w : TOF, pulmonary atresia, tricuspid atresia, transposition of the great vessels, trunks arterioles, single ventricle, double-oulte ventricle, total anomalous pulmonary venous return and hypoplastic left heart. With tricuspid atresia, blood can flow out of the right atrium only via patent foramen ovale (PFO). A PDA or VSD is necessary for the blood to flow from the LV to the pulmonary circulation Nagelhout pg. 1181
question
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors are used in the treatment of: a. acute glaucoma b. rental tubular acidosis c. diarrhea induced acidosis d. acidosis resulting from hypoventilation
answer
a. acute glaucoma Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors decrease the ability of the kidneys to reabsorb bicarbonate, resulting a hyperchloremic acidosis. As a result, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors would be avoided in patients with acidosis, especially a normal-anionic-gap acidosis. Because bicarbonate is filtered by the ciliary process in the formation of aqueous humor, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors reduce the formation of aqueous humor and can be used to decrease intraocular pressure. pg. 1211 Longnecker, DE, Brown, DL, Newman MF and Zapol, WM. Anesthesiology. New York: McGraw Hill, 2012.
question
Prior to pneumonectomy, split lung function testing is indicated in the patient with: a. an FEV1 of 2.2 L b. a PaCO2 of 49 mm Hg on room air c. a PaO2 of 54 mm Hg on room air d. a maximum VO2 of 21 mL/kg/min
answer
b. a PaCO2 of 49 mm Hg on room air Split lung function testing is indicated in patients requiring pneumonectomy, but not meeting the recommended laboratory criteria. Current recommendations for patients requiring pneumonectomy are: PaCO2 2 L Predicted postop FEV1 > 800 mL Maximum VO2 > 15 mL/kg/min FEV1/FVC > 50% of predicted pp. 663-665 Nagelhout, JJ, and Plaus, KL. Nurse Anesthesia. St. Louis: Elsevier, 2014.
question
Renal blood flow: (select 2) a. is largely determined by renal oxygen consumption b. accounts for 20 - 25% of the cardiac output c. is distributed mostly to juxtamedullary nephrons d. can be directed away from cortical nephrons by sympathetic stimulation e. is not autoregulated
answer
b. accounts for 20 - 25% of the cardiac output d. can be directed away from cortical nephrons by sympathetic stimulation The kidneys are the only organ for which oxygen consumption is determined by blood flow; the reverse is true in other organs. The kidneys receive 20 - 25% of the cardiac output with only 10 - 15% going to the juxtamedullary nephrons and 80% going to cortical nephrons. However, blood flow can be redirected to juxtamedullary nephrons by increased levels of catecholamines and angiotensin II. Autoregulation of RBF occurs between mean arterial pressures of 80 - 180 mm Hg. pp. 639-641 Butterworth, JF, Mackey, DC, and Wasnick, JD. Morgan & Mikhail's Clinical Anesthesiology. New York: Lange Medical Books/McGraw-Hill Medical Publishing Division, 2013.
question
The perception of an ordinarily non-noxious stimulus as pain is referred to as: a. allodynia b. anesthesia dolorosa c. dysesthesia d. hyperalgesia
answer
a. allodynia Allodynia is the perception of non-noxious stimuli as pain. Dysesthesia is an unpleasant sensation without a stimulus. Hyperesthesia is an increased response to a mild stimulus. Anesthesia dolorosa is pain in an area that lacks sensation. pp. 1649-1650 Barash, PG, Cullen, BF, Stoelting, RK, Cahalan, MK, Stock, MC, and Ortega, R. Clinical Anesthesia. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2013.
question
Venous irritation associated with the injection of diazepam and lorazepam is secondary to: a. the high degree of water solubility of these agents b. the presence of propylene glycol as a solvent c. the presence of metabisulfite as a preservative d. the low pH of these agents
answer
b. the presence of propylene glycol as a solvent The insolubility of diazepam and lorazepam in water requires that parenteral preparations contain propylene glycol, which has been associated with venous irritation. pg. 488 Barash, PG, Cullen, BF, Stoelting, RK, Cahalan, MK, Stock, MC, and Ortega, R. Clinical Anesthesia. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2013.
question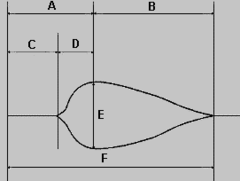
In the thromboelastogram below, clot strength is best represented by: a. A b. B c. E d. F

answer
c. E The maximum amplitude (E) is a measure of the strength of the fully formed clot. It reflects primarily platelet number and function although it also requires proper fibrin formation to achieve normal values. pg. 1519 Barash, PG, Cullen, BF, Stoelting, RK, Cahalan, MK, Stock, MC, and Ortega, R. Clinical Anesthesia. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2013.
question
In patients with a history of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, intraoperative management should include: a. a nitroglycerine infusion b. inotropic support c. afterload reduction d. maintenance of adequate preload
answer
d. maintenance of adequate preload In patients with outflow obstruction, myocardial depression and maintenance of preload and afterload are desirable. pp. 1083-1084 Barash, PG, Cullen, BF, Stoelting, RK, Cahalan, MK, Stock, MC, and Ortega, R. Clinical Anesthesia. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2013.
question
Correct statements regarding cerebral metabolism include: a. the brain can only utilize glucose as an energy source b. forty percent of brain glucose consumption is anaerobically metabolized c. hyperglycemia can reduce the damage from focal hypoxic injury d. the adult brain consumes approximately 50 ml/min of oxygen
answer
d. the adult brain consumes approximately 50 ml/min of oxygen The adult brain consumes about 20% of the total body oxygen (50 ml/min). Neuronal cells normally utilize glucose as their energy source, but can also utilize ketone bodies and lactate. Hyperglycemia has been shown to worsen global and focal hypoxic brain injury. pg. 576 Butterworth, JF, Mackey, DC, and Wasnick, JD. Morgan & Mikhail's Clinical Anesthesiology. New York: Lange Medical Books/McGraw-Hill Medical Publishing Division, 2013.
question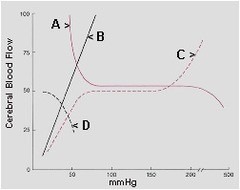
In the graph of cerebral blood flow below, PaO2 would best be represented by curve: a. A b. B c. C d. D

answer
a. A Curve A best represents the effects of changing oxygen tensions on cerebral blood flow. Hypoxemia causes a significant increase in CBF to meet the brain's metabolic demand. Hyperoxia, however, causes little change in CBF. pg. 999 Barash, PG, Cullen, BF, Stoelting, RK, Cahalan, MK, Stock, MC, and Ortega, R. Clinical Anesthesia. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2013.
question
Portal hypertension is defined as sustained portal vein pressure greater than: a. 5 mm Hg b. 10 mm Hg c. 20 mm Hg d. 25 mm Hg
answer
b. 10 mm Hg Portal hypertension is defined as a sustained portal vein pressure of 10 mm Hg or greater. This leads to the formation of portal-systemic collateral venous channels. pg. 1295 Barash, PG, Cullen, BF, Stoelting, RK, Cahalan, MK, Stock, MC, and Ortega, R. Clinical Anesthesia. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2013. pg. 793 Morgan, GE, Mikhail, MS, and Murray, MJ. Clinical Anesthesiology. New York: Lange Medical Books/McGraw-Hill Medical Publishing Division, 2006.
question
In patients receiving vecuronium, the greatest augmentation of neuromuscular blockade is seen with the use of: a. isoflurane b. sevoflurane c. desflurane d. nitrous oxide
answer
c. desflurane Volatile agents decrease the nondepolarizer dosage requirements. The degree of the augmentation of blockade depends on the inhalational agent, with desflurane > sevoflurane > isoflurane > nitrous oxide. pg. 213 Butterworth, JF, Mackey, DC, and Wasnick, JD. Morgan & Mikhail's Clinical Anesthesiology. New York: Lange Medical Books/McGraw-Hill Medical Publishing Division, 2013.
question
In the neuromuscular junction, acetylcholine receptor binding sites are found on the: a. α-subunits b. β-subunits c. δ-subunits d. ε -subunits
answer
a. α-subunits Each acetylcholine (ACh) receptor in the neuromuscular junction consists of 5 protein subunits. Only the α-subunits are capable of binding ACh molecules. If both binding sites are occupied, the channel briefly opens. The α-subunits are also the site of action of neuromuscular blockers. pg. 527 Barash, PG, Cullen, BF, Stoelting, RK, Cahalan, MK, Stock, MC, and Ortega, R. Clinical Anesthesia. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2013.
question
In the fetus, the percentage of cardiac output directed to the placenta is approximately: a. 10% b. 25% c. 50% d. 100%
answer
c. 50% In the fetus, the lungs receive little blood flow. The placenta receives nearly one-half of the fetal cardiac output and is responsible for respiratory gas exchange. pg. 836 Butterworth, JF, Mackey, DC, and Wasnick, JD. Morgan & Mikhail's Clinical Anesthesiology. New York: Lange Medical Books/McGraw-Hill Medical Publishing Division, 2013.
question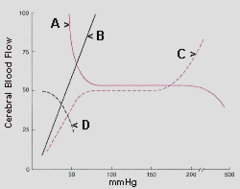
In the graph of cerebral blood flow below, PaCO2 would best be represented by curve: a. A b. B c. C d. D

answer
b. B Curve B best represents the effects of changing carbon dioxide tensions on cerebral blood flow. Between the ranges of 20 to 80 mm Hg a linear relationship exists between PaCO2 and CBF, such that a change in PaCO2 from 30 to 60 mm Hg will double CBF. pp. 998-999 Barash, PG, Cullen, BF, Stoelting, RK, Cahalan, MK, Stock, MC, and Ortega, R. Clinical Anesthesia. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2013.
question
Clinically significant histamine release has been associated with the use of: a. vecuronium b. rocuronium c. cisatracurium d. atracurium
answer
d. atracurium Atracurium has been a/w histamine release from mast cells and can result in bronchospasm, skin flushing and hypotension. pg. 535 Barash, PG, Cullen, BF, Stoelting, RK, Cahalan, MK, Stock, MC, and Ortega, R. Clinical Anesthesia. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2013.
question
Pathophysiologic changes associated with metabolic alkalosis include: (Select 2) a. compensatory hyperventilaton b. hypokalemia c. reduced tissue oxygen availability d. ionized hypercalcemia e. decreased digoxin effect f. arterial hypoxemia
answer
b. hypokalemia c. reduced tissue oxygen availability Metabolic alkalosis is associated with hypokalemia, ionized hypocalcemia, secondary ventricular arrhythmias, increased digoxin toxicity, and compensatory hypoventilation (hypercarbia). Alkalemia may reduce tissue oxygen availability by shifting the oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve to the left and by decreasing cardiac output. pg. 328 Barash, PG, Cullen, BF, Stoelting, RK, Cahalan, MK, Stock, MC, and Ortega, R. Clinical Anesthesia. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2013.
question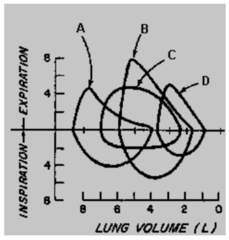
In the flow-volume loops below, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is best represented by: a. A b. B c. C d. D

answer
a. A Obstructive disease is best represented by flow-volume loop A, which demonstrates increased FRC and TLC with decreased expiratory flow. pg. 611 Nagelhout, JJ, and Plaus, KL. Nurse Anesthesia. St. Louis: Elsevier, 2013.
question
Drugs that bind to the proton pump of gastric parietal cell and inhibit hydrogen ion secretion include: a. ranitidine b. cimetadine c. famotidine d. omeprazole
answer
d. omeprazole Omeprazole (Prilosec) inhibits the proton pump of the parietal cells of the gastric mucosa, decreases hydrogen ion secretion and increase pH. Cimetidine, ranitidine and famotidine also increase gastric pH, however their mechanism is through blockade of the H2 receptor. pg. 283 Butterworth, JF, Mackey, DC, and Wasnick, JD. Morgan & Mikhail's Clinical Anesthesiology. New York: Lange Medical Books/McGraw-Hill Medical Publishing Division, 2013.
question
Respiratory parameters that are increased during pregnancy include: (Select 2) a. airway resistance b. tidal volume c. oxygen consumption d. plasma bicarbonate levels e. functional residual capacity f. PaCO2
answer
b. tidal volume c. oxygen consumption Respiratory/ventilatory effects of pregnancy include increased oxygen consumption, decreased airway resistance, decreased FRC, increased tidal volume and rate, increased PaO2, decreased PaCO2 and decreased serum bicarbonate. pg. 1129 Nagelhout, JJ, and Plaus, KL. Nurse Anesthesia. St. Louis: Elsevier, 2013.
question
Droperidol: a. has antiarrhytmic activity b. causes shortening of the QT interval c. causes peripheral vasoconstriction d. is effective for blood pressure control in patients with pheochromocytoma
answer
a. has antiarrhytmic activity Droperidol has mild alpha-blocking activity and causes vasodilation and has antiarrhythmic properties with prolongation of the QT interval. As a result of the prolongation of the QT interval, droperidol has been associated with torsades de pointes and should not be given to patients with QT intervals measuring more than 440 ms. Patients with pheochromocytoma should not receive droperidol because it can induce catecholamine release. pp. 190-192 Hemmings, HC, Talmage, DE. Pharmacology and Physiology for Anesthesia. Philadelphia: Elsevier, 2013.
question
The phrenic nerves arise from the: a. nucleus ambiguous b. C1 - C2 nerve roots c. C3 - C5 nerve roots d. C6 - T2 nerve roots
answer
c. C3 - C5 nerve roots The phrenic nerves arise from the C3 - C5 nerve roots. Unilateral phrenic nerve palsy only modestly reduces most indices of pulmonary function (about 25%). Bilateral phrenic nerve palsies produce more severe impairment, but accessory muscles may maintain adequate ventilation. Cervical cord injuries above C5 are incompatible with spontaneous ventilation. pp. 946-947 Barash, PG, Cullen, BF, Stoelting, RK, Cahalan, MK, Stock, MC, and Ortega, R. Clinical Anesthesia. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2013.
question
Sinus arrhythmia: a. is mediated through sympathetic innervation of the AV node b. causes an increase in heart rate with inspiration c. is indicative of SA node ischemia d. is the primary cause of premature atrial contractions
answer
b. causes an increase in heart rate with inspiration Sinus arrhythmia is a cyclic variation in heart rate that corresponds to ventilation, increasing with inspiration and decreasing with expiration. Sinus arrhythmia is a normal cardiac rhythm and is due to cyclic changes in vagal tone. pg. 1717 Barash, PG, Cullen, BF, Stoelting, RK, Cahalan, MK, Stock, MC, and Ortega, R. Clinical Anesthesia. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2013.
question
Of the following, the block associated with the highest blood level of local anesthetic per volume injected is the: a. epidural block b. spinal block c. intercostal block d. caudal block
answer
c. intercostal block Blood concentration of local anesthetic is dependent on the total volume and concentration injected. However, with the exception of airway blocks, the intercostal block results in the highest blood levels of local anesthetic per volume injected. pg. 569 Barash, PG, Cullen, BF, Stoelting, RK, Cahalan, MK, Stock, MC, and Ortega, R. Clinical Anesthesia. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2013.
question
In addition to providing analgesia, tramadol has been shown to: a. inhibit the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine b. inhibit cholinesterase c. significantly delay gastric emptying d. cause comparable respiratory depression to morphine
answer
a. inhibit the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine Tramadol is a synthetic opioid that also blocks neuronal reuptake of norepinephrine and serotonin. Tramadol is associated with significantly less respiratory depression and delay in gastric emptying as compared to other narcotics. pg. 186 Hemmings, HC, Talmage, DE. Pharmacology and Physiology for Anesthesia.. Philadelphia: Elsevier, 2013. pg. 1058 Butterworth, JF, Mackey, DC, and Wasnick, JD. Morgan & Mikhail's Clinical Anesthesiology. New York: Lange Medical Books/McGraw-Hill Medical Publishing Division, 2013.
question
Compensatory mechanisms generally present in patients with congestive heart failure include: a. decreased sympathetic tone b. decreased plasma renin levels c. decreased plasma aldosterone levels d. ventricular hypertrophy
answer
d. ventricular hypertrophy Major compensatory mechanisms present in patients with CHF include increased preload, increased sympathetic tone, activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, release of ADH and ventricular hypertrophy. pg. 367-368 Butterworth, JF, Mackey, DC, and Wasnick, JD. Morgan & Mikhail's Clinical Anesthesiology. New York: Lange Medical Books/McGraw-Hill Medical Publishing Division, 2013.
question
Neuromuscular blocking agents that undergo metabolism through the Hofmann elimination include: (Select 2) a. rocuronium b. vecuronium c. atracurium d. doxacurium e. cisatracurium f. succinylcholine
answer
c. atracurium e. cisatracurium Atracurium and cisatracurium are bisquaternary ammonium benzylisoquinoline compounds of intermediate duration of action. They are degraded via two metabolic pathways. One of these pathways is the Hofmann reaction, a nonenzymatic degradation with a rate that increases as temperature and/or pH increases. The second pathway is nonspecific ester hydrolysis. pp. 535-536 Barash, PG, Cullen, BF, Stoelting, RK, Cahalan, MK, Stock, MC, and Ortega, R. Clinical Anesthesia. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2013.
question
Opioids currently NOT approved for epidural or intrathecal use include: a. fentanyl b. sufentanil c. morphine d. remifentanil
answer
d. remifentanil Remifentanil is prepared in a solution of glycine, a known inhibitory neurotransmitter. Currently, remifentanil is not approved for epidural or intrathecal use. pg. 114 - 115 Stoelting, RK. Pharmacology and Physiology in Anesthetic Practice. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, 2006.
question
A 82-year-old female is scheduled for a total hip replacement under spinal anesthesia. She has been receiving enoxaparin for deep vein thrombosis prophylaxis. Current recommendations regarding the dosing of enoxaparin state that the drug be: a. continued without interruption as scheduled b. held for 4 - 6 hours prior to the spinal anesthetic c. held for 10 - 12 hours prior to the spinal anesthetic d. held for not less than 24 hours prior to the spinal anesthetic
answer
c. held for 10 - 12 hours prior to the spinal anesthetic Patients receiving fractionated low-molecular weight heparin are to be considered at increased risk of spinal hematoma. Patients receiving these drugs should have the drug held for 10 - 12 hours preoperatively according to the Consensus Statement from the American Society for Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine. pg. 929 Barash, PG, Cullen, BF, Stoelting, RK, Cahalan, MK, Stock, MC, and Ortega, R. Clinical Anesthesia. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2013.
question
A person acting as an amicus curiae: a. is not a party to the litigation b. gives expert testimony for the defense c. gives expert testimony for the plaintiff d. cannot file a written brief
answer
a. is not a party to the litigation Amicus curiae is a phrase that literally means 'friend of the court' -- someone who is not a party to the litigation, but who believes that the court's decision may affect its interest. An expert, not associated with either the defendant or plaintiff may, at the court's discretion, file a brief or give testimony to assist the court in decision making. "Amicus curiae." URL: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Amicus_curiae "Amicus curiae." URL: http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/amicus%20curiae
question
The first nurse anesthetist to be appointed to a university medical school faculty was: A. Alice Maude Hunt B. Agatha Hodgins C. Helen Lamb D. Alice Magaw
answer
A. Alice Maude Hunt In 1922, Alice became an instructor of anesthesia at the Yale university school of medicine and was later promoted to assistant professor. Hunt pioneered the use of nitrous oxide and oxygen as an anesthetic modality. Nagelhout, p. 16
question
Pulmonary effects of β2-adrenergic stimulation include: (Select 2) a. inhibition of hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction b. decreased bronchial secretions c. pulmonary vasoconstriction d. bronchodilation e. redirection of blood flow to lower V/Q alveolar units f. activation of type II pneumocytes
answer
b. decreased bronchial secretions d. bronchodilation The tracheobronchial tree receives sympathetic innervation form the T1 - T4 nerve roots. β2 stimulation causes bronchodilation and decreased secretions. The sympathetic nervous system has minimal effects on pulmonary vascular tone. However, α1 stimulation causes some degree of pulmonary vasoconstriction. pg. 492 Butterworth, JF, Mackey, DC, and Wasnick, JD. Morgan & Mikhail's Clinical Anesthesiology. New York: Lange Medical Books/McGraw-Hill Medical Publishing Division, 2013.
question
Portal hypertension leads to the development of portal-systemic venous collateral channels. These collateral sites commonly include the: a. hemorrhoidal veins b. pulmonary veins c. hepatic vein d. azygous vein
answer
a. hemorrhoidal veins Chronic portal hypertension leads to the development of portal-systemic collateral channels. Four major collateral sites are commonly recognized: gastroesophageal, hemorrhoidal, periumbilical and retroperitoneal. pg. 771 Nagelhout, JJ, and Plaus, KL. Nurse Anesthesia. St. Louis: Elsevier, 2013.
question
A nonselective α-antagonist used in the preoperative preparation of a patient with pheochromocytoma is: a. phenoxybenzamine b. doxazosin c. propranolol d. terazosin
answer
a. phenoxybenzamine Phenoxybenzamine is a nonselective α-antagonist used in the preoperative preparation of the patient with pheochromocytoma. Doxazosin and terazosin are selective α1-antagonists. Propranolol is a nonselective β-antagonist. In the preparation of patients with pheochromocytoma, α-blockade and intravascular volume replacement must precede β-blockade, so as to prevent the possibility of unopposed α-stimulation. pp. 745-746 Longnecker, DE, Brown, DL, Newman MF and Zapol, WM. Anesthesiology. New York: McGraw Hill, 2012.
question
The portion of the nephron responsible for concentration of urine via the countercurrent mechanism is the: a. glomerulus b. loop of Henle c. proximal convoluted tubule d. distal convoluted tubule
answer
b. loop of Henle The loop of Henle is responsible for formation of hypertonic fluid in the (renal) medullary interstitium via the countercurrent multiplier system. pg. 732 Nagelhout, JJ, and Plaus, KL. Nurse Anesthesia. St. Louis: Elsevier, 2013.
question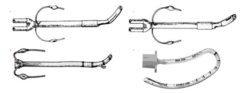
In the figure below, the Carlens tube is best represented by:

answer
Picture B The Carlens double-lumen tubes have a carinal hook to aid in proper placement and minimize tube movement after placement. Potential problems with carinal hooks include increased difficulty with proper placement, trauma to the airway, interference with bronchial closure, and break-off of the hook, which can become lost in the bronchial tree. pp. 395, 398 Dorsch, JA, Dorsch, SE. A Practical Approach to Anesthesia Equipment. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2011.
question
Parasympathetic preganglionic fibers are found in: (Select 3) a. cranial nerve IV b. cranial nerve VII c. cranial nerve IX d. cranial nerve XI e. thoracic nerve 9 f. thoracic nerve 11 g. sacral nerve 1 h. sacral nerve 2
answer
b. cranial nerve VII c. cranial nerve IX h. sacral nerve 2 Parasympathetic preganglionic fibers are found in cranial nerves III, VII, IX and X as well as sacral nerves 2, 3 and 4. pg. 363 Barash, PG, Cullen, BF, Stoelting, RK, Cahalan, MK, Stock, MC, and Ortega, R. Clinical Anesthesia. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2013.
question
During intraoperative fluoroscopy, the patient receives 32 mR at a distance of 1 foot from the fluoroscopy tube. The maximum radiation dose possible to the anesthesia provider, standing at a distance of 4 feet from the fluoroscopy tube is: (Enter numerical answer.) _______mR
answer
2 mR Increasing the distance from the source of radiation is a very effective means of reducing dose. Dose rates increase or decrease according to the inverse square of the distance from the source. Using the inverse square law formula: I1xD1^2 = I2xD2^2 I = intensity, D = distance (32 mR)(1 ft)^2 = (I2)(4 ft)^2; I2 = 2 mR pp. 880-881 Barash, PG, Cullen, BF, Stoelting, RK, Cahalan, MK, Stock, MC, and Ortega, R. Clinical Anesthesia. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2013.
question
Electrolyte containing irrigation solutions are avoided during transurethral resection of the prostate because they: a. interfere with the use of the cautery b. can precipitate severe hyponatremia c. can cause hyperglycemia in diabetic patients d. are associated with elevated ammonia levels postoperatively
answer
a. interfere with the use of the cautery Electrolyte containing solutions conduct electricity and interfere with cautery use during the resection of the prostate. Electrolyte solutions are commonly used in the postop period. Sorbitol solutions have been associated with hyperglycemia, especially in diabetic patients. Glycine solutions have been associated with elevated ammonia levels and transient postoperative visual syndrome. Sorbitol, glycine and distilled water have all been associated with TURP syndrome. pg. 1428 Barash, PG, Cullen, BF, Stoelting, RK, Cahalan, MK, Stock, MC, and Ortega, R. Clinical Anesthesia. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2013.
question
The speed in an inhalation induction is slowed by right-to-left shunting. The change in the rate of induction is LEAST pronounced when using: a. nitrous oxide b. sevoflurane c. isoflurane d. desflurane
answer
c. isoflurane With right-to-left shunting there is slowing of an inhalation induction. This effect is less pronounced with agents with high blood/gas solubilities. pg. 455 Barash, PG, Cullen, BF, Stoelting, RK, Cahalan, MK, Stock, MC, and Ortega, R. Clinical Anesthesia. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2013.
question
MAC-BAR is the: a. partial pressure of an anesthetic required to abolish movement in 50% of patients b. partial pressure of an anesthetic at which subjects will open their eyes c. partial pressure of an anesthetic at which autonomic blockade occurs d. partial pressure of an anesthetic at which amnesia occurs
answer
c. partial pressure of an anesthetic at which autonomic blockade occurs MAC-BAR is the minimum alveolar concentration that blocks autonomic reflexes. MAC-BAR is considerably greater than MAC, particularly in the absence of opioids. It has been estimated that MAC-BAR is approximately 50% above standard MAC. pg. 458 Barash, PG, Cullen, BF, Stoelting, RK, Cahalan, MK, Stock, MC, and Ortega, R. Clinical Anesthesia. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2013.
question
In a 6-year-old, the appropriate length of an endotracheal tube from distal tip to incisors is: (Enter numerical answer in box below. Click 'Next' when completed.) ________cm
answer
15-16.5cm Several formulas exist to estimate the length of ETT insertion in patients aged 2 to 12 years. One of the most frequently used is: Age/2 +12 or 3 x ETT size -> 3 x [(age/4) +4] pp. 1201-1202 Nagelhout, JJ, and Plaus, KL. Nurse Anesthesia. St. Louis: Elsevier, 2013.
question
Local anesthetic solutions that are isobaric with the cerebrospinal fluid include: (Select 2) a. tetracaine 0.5% in 5% dextrose b. bupivacaine 0.75% in normal saline c. procaine 10% in sterile water d. lidocaine 2% in normal saline e. bupivacaine 0.3% in sterile water f. lidocaine 5% in 7.5% dextrose
answer
b. bupivacaine 0.75% in normal saline d. lidocaine 2% in normal saline
question
An 82 year old female arrives to OR for open reduction of left intratrochanteric fracture. Significant past medical history includes hypertension, moderate aortic stenosis & dementia. The most appropriate anesthetic technique for this patient is: A. Opioid based general anesthesia B. Spinal anesthesia C. Volatile based general anesthesia D. Epidural anesthesia
answer
A. Opioid based anesthesia In patients with mild to moderate aortic stenosis, a primarily opioid-based technique results in minimal cardiac depression, less tachycardia and suppression of the sympathetic response to surgical stimulation. These are all desired effects as HTN and tachycardia may precipitate ischemia in these patients. Spinal or epidural anesthesia as well as a volatile-agent-based anesthesia can cause a fall in afterload with resulting severe hypotension. pp. 501-502 Nagelhout, JJ, and Plaus, KL. Nurse Anesthesia. St. Louis: Elsevier, 2014.
question
The formation of active metabolites has NOT been associated with the use of: a. vecuronium b. rocuronium c. pancuronium d. succinylcholine
answer
b. rocuronium The 3-OH metabolites of both vecuronium and pancuronium possess about 50% of the neuromuscular blocking activity of parent compound. Succinylcholine is metabolized to choline, succinic acid and succinylmonocholine. Succinylmonocholine also has some neuromuscular blocking activity. A small amount of rocuronium is metabolized to the 17-OH compound, which lacks activity. Most rocuronium is excreted by the kidneys and liver as intact drug. pg. 535-538 Barash, PG, Cullen, BF, Stoelting, RK, Cahalan, MK, Stock, MC, and Ortega, R. Clinical Anesthesia. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2013.
question
Selective adrenergic stimulation of the β2-receptor results in: a. increased heart rate b. increased insulin secretion c. detrusor muscle contraction d. pupillary constriction
answer
b. increased insulin secretion β2-receptor stimulation results in: increased insulin secretion, bronchodilation, increased salivary gland secretion, decreased upper GI motility, gluconeogenesis, pupillary dilation and detrusor muscle relaxation. Increased heart rate is a result of β1-receptor stimulation. Pupillary constriction (miosis) is the result of parasympathetic stimulation. pg. 187 Nagelhout, JJ, and Plaus, KL. Nurse Anesthesia. St. Louis: Elsevier, 2014.
question
The most consistent clinical manifestation of aspiration pneumonitis is: a. bronchospasm b. arterial hypoxemia c. pulmonary vasoconstriction d. tachypnea
answer
b. arterial hypoxemia Inhaled gastric fluid is rapidly distributed throughout the lungs, leading to destruction of surfactant-producing cells, damage to the pulmonary capillary endothelium and resultant atelectasis and pulmonary edema. Arterial hypoxemia is the most consistent clinical finding associated with aspiration pneumonitis. Tachypnea, bronchospasm and pulmonary vasoconstriction with secondary pulmonary hypertension may also be present. pg. 640 Nagelhout, JJ, and Plaus, KL. Nurse Anesthesia. St. Louis: Elsevier, 2014.
question
A full-term, 4.2 kg neonate is scheduled for a thoracotomy for resection of congenital lobar emphysema. The infant's starting hematocrit is 48%. Estimated allowable blood loss to maintain a hematocrit at or above 38% is: (Enter numerical answer in box below. Click 'Next' when completed.) ______mL
answer
70 - 110 mL The full-term neonate has approximately 85 ml/kg total blood volume. Therefore: 4.2 kg x 85 ml/kg = 357 ml (blood volume) MABL = Blood Volume x (HCT(starting) - HCT(final)) / HCT(average) 357 ml x (48 - 38) / 43 = 83 mL Please note that multiple formulas exist for the calculation of allowable blood loss, which may yield varying results. pp. 1165, 1171 Nagelhout, JJ, and Plaus, KL. Nurse Anesthesia. St. Louis: Elsevier, 2014.
question
The recommended maximum leakage current allowed in operating room equipment is: a. 5 μA b. 10 μA c. 1 mA d. 5 mA
answer
b. 10 μA 10 μA has been established as the recommended maximum allowable leakage current. This amount of current is below the threshold of perception (1mA) as well as below the threshold for risk of microshock. pg. 192 Barash, PG, Cullen, BF, Stoelting, RK, Cahalan, MK, Stock, MC, and Ortega, R. Clinical Anesthesia. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2013.
question
Causes of normal-anion-gap acidosis include: a. renal failure b. starvation c. diarrhea d. lactic acidosis
answer
c. diarrhea Normal-anion-gap acidosis is also called hyperchloremic acidosis and results from the selective loss of bicarbonate anion or the introduction of large amounts of chloride anion. Common causes include: diarrhea, hypoaldosteronism, renal tubular acidosis and increased intake of chloride containing acids sometimes found in hyperalimentation. pg. 461 Longnecker, DE, Brown, DL, Newman MF and Zapol, WM. Anesthesiology. New York: McGraw Hill, 2012.
question
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors are used in the treatment of: a. acute glaucoma b. renal tubular acidosis c. diarrhea induced acidosis d. acidosis resulting from hypoventilation
answer
a. acute glaucoma Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors decrease the ability of the kidneys to reabsorb bicarbonate, resulting a hyperchloremic acidosis. As a result, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors would be avoided in patients with acidosis, especially a normal-anionic-gap acidosis. Because bicarbonate is filtered by the ciliary process in the formation of aqueous humor, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors reduce the formation of aqueous humor and can be used to decrease intraocular pressure. pg. 1211 Longnecker, DE, Brown, DL, Newman MF and Zapol, WM. Anesthesiology. New York: McGraw Hill, 2012.
question
Hypoxemia during one-lung anesthesia is most effectively treated by: a. PEEP applied to the ventilated lung b. continuous oxygen insufflation to the collapsed lung c. changing tidal volume and rate d. periodic inflation of the collapsed lung
answer
d. periodic inflation of the collapsed lung The application of PEEP to the ventilated lung, changes in the ventilatory parameters and oxygen insufflation to the collapsed lung may offer marginal improvement in oxygenation. However, periodic inflation of the collapsed lung with oxygen, early ligation of the ipsilateral pulmonary artery and CPAP to the collapsed lung offer consistently effective improvement in oxygenation. pp. 678-679 Nagelhout, JJ, and Plaus, KL. Nurse Anesthesia. St. Louis: Elsevier, 2014.
question
A decrease in pseudocholinesterase activity has been associated with the use of: (Select 3) a. pancuronium b. esmolol c. droperidol d. vecuronium e. metoclopramide f. magnesium sulfate g. dantrolene h. rocuronium
answer
a. pancuronium b. esmolol e. metoclopramide The following drugs have been associated with a decrease in pseudocholinesterase activity: echothiophate, pyridostigmine, neostigmine, phenelzine, cyclophosphamide, metoclopramide, esmolol, pancuronium and oral contraceptives. Although both dantrolene and magnesium may alter the effects of neuromuscular blockers, neither causes inhibition of pseudocholinesterase. pg. 207 Butterworth, JF, Mackey, DC, and Wasnick, JD. Morgan & Mikhail's Clinical Anesthesiology. New York: Lange Medical Books/McGraw-Hill Medical Publishing Division, 2013.
question
During the delivery of an anesthetic in the radiology department, full E-cylinders of nitrous oxide and oxygen are being used. If a 3:2 mixture of nitrous oxide:oxygen is being delivered and the case has been proceeding for 60 minutes, the expected pressure in the nitrous oxide E-cylinder is: (Enter numerical answer in box below. Click 'Next' when completed.) psig
answer
745 - 750 psig Nitrous oxide has a critical temperature of 37oC. This allows nitrous oxide to exist as a liquid at room temperature. Full E-cylinders of nitrous oxide contain approximately 1590 L at a pressure of 745 psig. A sixty minute delivery of 3 L/min would result in a 180 L consumption, and this would be inadequate to consume all the liquid nitrous oxide in the tank. As a result, there would be no change in tank pressure Pg. 622 Longnecker, DE, Brown, DL, Newman MF and Zapol, WM. Anesthesiology. New York: McGraw Hill, 2012.
question
The synthesis of acetylcholine from acetylcoenzyme A and choline is catalyzed by: a. free acetate anion b. choline acetyltransferase c. acetyl cholinesterase d. pseudocholinesterase
answer
b. choline acetyltransferase The synthesis of acetylcholine occurs in the cholinergic nerve terminal. Acetyl Co-A and choline combine to form acetylcholine. This reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme choline acetyltransferase. pg. 819 Nagelhout, JJ, and Plaus, KL. Nurse Anesthesia. St. Louis: Elsevier, 2014.
question
Prior to pneumonectomy, split lung function testing is indicated in the patient with: A. an FEV1 of 2.2 L B. a PaCO2 of 49 mm Hg on room air C. a PaO2 of 54 mm Hg on room air D. a maximum VO2 of 21 mL/kg/min
answer
B. a PaCO2 of 49 mm Hg on room air Split lung function testing is indicated in patients requiring pneumonectomy, but not meeting the recommended laboratory criteria. Current recommendations for patients requiring pneumonectomy are: PaCO2 2 L Predicted postop FEV1 > 800 mL Maximum VO2 > 15 mL/kg/min FEV1/FVC > 50% of predicted Nagelhout pg 663-665
question
Mechanisms of renal compensation during acidosis include: a. decreased reabsorption of filtered bicarbonate b. decreased excretion of hydrogen ions c. increased production of ammonia d. increased elimination of carbon dioxide
answer
c. increased production of ammonia The renal response to acidemia is: increased reabsorption of bicarbonate anion increased excretion of hydrogen ion in the form of titratable acids increased production of ammonia Although increased carbon dioxide elimination is a compensatory mechanism in acidemia, it is accomplished by increased alveolar ventilation. pg. 734 Nagelhout, JJ, and Plaus, KL. Nurse Anesthesia. St. Louis: Elsevier, 2014.
question
Effects of lidocaine include: a. increased intracranial pressure b. increased refractory period of cardiac muscle c. decreased fibrinolysis d. myonecrosis
answer
d. myonecrosis Intravenous lidocaine decreases cerebral blood flow unless seizure activity develops. Lidocaine decreases the refractory period of cardiac muscle and decreases platelet aggregation while enhancing fibrinolysis. Local anesthetics have been shown to cause lytic degeneration and necrosis of muscle fibers when directly injected into the muscle (trigger point injections). pp. 270-274 Butterworth, JF, Mackey, DC, and Wasnick, JD. Morgan & Mikhail's Clinical Anesthesiology. New York: Lange Medical Books/McGraw-Hill Medical Publishing Division, 2013.
question
An increase in the plasma concentration & a prolongation of the elimination half-life of etomidate is seen with the concomitant administration of: a. midazolam b. rocuronium c. fentanyl d. succinylcholine
answer
c. fentanyl Fentanyl has been shown to increase the plasma level of etomidate as well as prolong the elimination half-life of the drug. pg. 185 Butterworth, JF, Mackey, DC, and Wasnick, JD. Morgan & Mikhail's Clinical Anesthesiology. New York: Lange Medical Books/McGraw-Hill Medical Publishing Division, 2013.
question
Correct statements concerning the use of benzodiazepines in the elderly include: a. volume of distribution is increased b. reduced pharmacodynamic sensitivity is observed c. the elimination half-life of diazepam, but not midazolam, is increased d. all of the above
answer
a. volume of distribution is increased Aging increases the volume of distribution for all benzodiazepines, effectively prolonging their elimination half-times. Enhanced pharmacodynamic sensitivity is also observed. The elimination half-times of both diazepam and midazolam are increased. pp. 902, 903 Barash, PG, Cullen, BF, Stoelting, RK, Cahalan, MK, Stock, MC, Ortega, R.,Sharar, SR, and Holt, NF. Clinical Anesthesia. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2017.
question
The highest incidence of muscle pain following the use of succinylcholine is seen in: a. infants b. octogenarians c. outpatients d. pregnant patients
answer
c. outpatients Myalgia following the use of succinylcholine is most commonly seen in females and outpatients. Pregnancy and extremes of age seem to be protective. pg. 170 Nagelhout, JJ, and Plaus, KL. Nurse Anesthesia. St. Louis: Elsevier, 2014.
question
The cardiovascular effects of pancuronium are caused by: (Select 3) a. vagal blockade b. stimulation of cardiac muscarinic receptors c. ganglionic stimulation d. decreased catacholamine reuptake e. direct myocardial stimulation f. blockade of cardiac slow calcium channels g. central thalamic stimulation
answer
a. vagal blockade c. ganglionic stimulation d. decreased catacholamine reuptake The cardiovascular effects of pancuronium are caused by the combination of vagal blockade and sympathetic stimulation. The latter is due to a combination of ganglionic stimulation, catecholamine release and decreased catecholamine reuptake. pp. 535,536 Barash, PG, Cullen, BF, Stoelting, RK, Cahalan, MK, Stock, MC, Ortega, R.,Sharar, SR, and Holt, NF. Clinical Anesthesia. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2017. pg. 217 Butterworth, JF, Mackey, DC, and Wasnick, JD. Morgan & Mikhail's Clinical Anesthesiology. New York: Lange Medical Books/McGraw-Hill Medical Publishing Division, 2013.
question
Anesthetic implications of multiple sclerosis include: a. the postponement of elective procedures during relapse b. exacerbation induced by peripheral nerve block c. exacerbation of symptoms secondary to hypothermia d. the presence of significant peripheral neuropathy causing severe hyperkalemia after succinylcholine administration
answer
a. the postponement of elective procedures during relapse Surgery and other physiologically stressful events should be avoided during episodes of relapse. Epidural and other regional techniques appear to have no adverse effect, especially in obstetrics; however a lower concentration of local anesthetic should be used. Demyelinated nerve fibers are extremely sensitive to hyperthermia, but conduction is usually improved by mild hypothermia. pp. 620, 621 Butterworth, JF, Mackey, DC, and Wasnick, JD. Morgan & Mikhail's Clinical Anesthesiology. New York: Lange Medical Books/McGraw-Hill Medical Publishing Division, 2013.
question
Local anesthetics with the potential to form methemoglobin include: (Select 3) a. EMLA topical anesthetic cream b. bupivacaine c. benzocaine d. ropivacaine e. prilocaine f. mepivacaine
answer
a. EMLA topical anesthetic cream c. benzocaine e. prilocaine EMLA cream contains both lidocaine and prilocaine. The metabolites of prilocaine can convert hemoglobin to methemoglobin. Benzocaine can also cause methemoglobinemia. pg. 140 Nagelhout, JJ, and Plaus, KL. Nurse Anesthesia. St. Louis: Elsevier, 2014. "Methemoglobin Risk with Benzocaine Containing Local Anesthetics" URL: http://www.upstate.edu/uha/pharmacy/newsletters/kidstuff_06/kidstuff_05_06.pdf
question
Ulnar nerve injury: a. results in wrist drop and loss of sensation in the web space between the thumb and index finger b. occurs more frequently in males c. manifests itself in the immediate postoperative period d. is most commonly seen in the patient with a BMI of less than 18
answer
b. occurs more frequently in males Three attributes which are highly associated with development of postoperative ulnar nerve injury are: 1) male sex - various reports suggest that 70 - 90% of patients with postoperative ulnar neuropathy are men 2) high body mass index - BMI > or = 38 3) prolonged postoperative bed rest. Many patients with postoperative ulnar neuropathy have a high frequency of contralateral ulnar nerve dysfunction, suggestive of a pre-existing abnormality. Patients may not develop symptoms of ulnar neuropathy until more than 48 hours postoperatively. Wrist drop and loss of sensation of the web space between the thumb and index finger are associated with radial nerve injury. pg. 815 Barash, PG, Cullen, BF, Stoelting, RK, Cahalan, MK, Stock, MC, Ortega, R.,Sharar, SR,
question
The potency of local anesthetics increases as the: a. lipid solubility increases b. pKa increases c. number of double bonds in the anesthetic molecule increases d. molecular weight decreases
answer
a. lipid solubility increases Local anesthetic potency correlates directly with lipid solubility. In general, lipid solubility increases with an increase in the total number of carbon atoms in the molecule and by adding a halogen to the aromatic ring. pg. 129 Nagelhout, JJ, and Plaus, KL. Nurse Anesthesia. St. Louis: Elsevier, 2014.
question
A decrease in cerebral blood flow is seen after the administration of: a. isoflurane b. propofol c. desflurane d. ketamine
answer
b. propofol The inhaled anesthetic agents and ketamine all increase cerebral blood flow (CBF). Benzodiazepines, etomidate, propofol and barbiturates all decrease CBF. pg. 701 Nagelhout, JJ, and Plaus, KL. Nurse Anesthesia. St. Louis: Elsevier, 2014.
question
The age group with the highest minimum alveolar concentration (MAC) of desflurane is: a. 2 - 3 months b. 1 - 2 years c. 25 - 30 years d. greater than 75 years
answer
a. 2 - 3 months The two-to-three-months-of-age group represents the highest MAC requirement. MAC subsequently decreases with advancing age. pg. 883 Butterworth, JF, Mackey, DC, and Wasnick, JD. Morgan & Mikhail's Clinical Anesthesiology. New York: Lange Medical Books/McGraw-Hill Medical Publishing Division, 2013.
question
The loss of ventricular filling as a result of acute atrial fibrillation is approximately: (Enter numerical answer in box below. Click 'Next' when completed.) _______%
answer
15-25% Passive flow accounts for about 75 - 85% of ventricular filling. The remaining 15 - 25% occurs as a result of atrial contraction, which is lost during atrial fibrillation. pg. 287 Barash, PG, Cullen, BF, Stoelting, RK, Cahalan, MK, Stock, MC, Ortega, R.,Sharar, SR, and Holt, NF. Clinical Anesthesia. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2017.
question
During surgical repair of a detached retina, 1 mL of sulfur hexafluoride is injected into the posterior chamber. If the patient is receiving 4% desflurane and a 2:1 ratio of N2O and O2, the pressure-volume relationship of the bubble will approximately: a. decrease by one third b. remain the same c. double d. triple
answer
d. triple A sulfur hexafluoride gas bubble is sometimes used to support the retina after detachment. Diffusion of nitrous oxide into the bubble will cause expansion as nitrous oxide equilibrates with the gas bubble. A sixty-seven percent nitrous oxide concentration will cause the bubble to triple in its pressure-volume relationship in about 30 minutes and may double the intraocular pressure (IOP). In addition, when nitrous oxide is discontinued, the bubble will return to normal size, causing a fall in IOP and possible extension of the retinal tear. For these reasons, it is recommended that nitrous oxide be discontinued at least 15 minutes prior to the injection of a posterior chamber bubble. pg. 762 Butterworth, JF, Mackey, DC, and Wasnick, JD. Morgan & Mikhail's Clinical Anesthesiology. New York: Lange Medical Books/McGraw-Hill Medical Publishing Division, 2013.
question
The postretrobulbar block apnea syndrome: a. is likely secondary to intravascular injection b. most commonly occurs during or immediately after injection c. is associated with unconsciousness d. carries a high morbidity and mortality
answer
c. is associated with unconsciousness The postretrobulbar block apnea syndrome is probably due to injection of local anesthetic into the optic nerve sheath, with spread into the CSF. The CNS is exposed to high concentrations of local anesthetic leading to apprehension and unconsciousness. Apnea occurs within 20 minutes and resolves within an hour. Treatment is supportive. pg. 766 Butterworth, JF, Mackey, DC, and Wasnick, JD. Morgan & Mikhail's Clinical Anesthesiology. New York: Lange Medical Books/McGraw-Hill Medical Publishing Division, 2013.
question
A 76-year-old man is scheduled for a hemicolectomy. His past medical history is significant for third degree heart block treated with a permanent pacemaker. Problems with electrocautery use in this patient can be minimized by: a. placing the grounding pad near the pacemaker b. using infrequent bursts of longer duration c. the use of a bipolar cautery d. reducing the surface area of the return electrode
answer
c. the use of a bipolar cautery Electrical interference from the electrocautery can be interpreted by the pacemaker as myocardial activity and suppress pacemaker activity. These problems can be minimized by limiting use to short bursts, placing the grounding pad as far from the pacemaker as possible and using a bipolar cautery. pg. 403 Butterworth, JF, Mackey, DC, and Wasnick, JD. Morgan & Mikhail's Clinical Anesthesiology. New York: Lange Medical Books/McGraw-Hill Medical Publishing Division, 2013.
question
The arteria radicularis magna, or artery of Adamkiewicz, most commonly arises from: a. T4 - T8 b. T8 - L2 c. L2 - L4 d. L4 - S1
answer
b. T8 - L2 A major complication of thoracic aortic surgery is paraplegia, occurring in up to 20% of elective cases, and is secondary to spinal cord ischemia. The arteria radicularis magna supplies blood to the anterior spinal artery. The arteria radicularis magna has a variable origin from aorta, arising between T5 - T8 in 15%, between T9 - T12 in 60% and between L1 - L2 in 25% of individuals. pg. 480 Butterworth, JF, Mackey, DC, and Wasnick, JD. Morgan & Mikhail's Clinical Anesthesiology. New York: Lange Medical Books/McGraw-Hill Medical Publishing Division, 2013.
question
Intracranial hypertension is defined as a sustained increase in intracranial pressure (ICP) above: a. 5 mm Hg b. 15 mm Hg c. 25 mm Hg d. 30 mm Hg
answer
b. 15 mm Hg Intracranial hypertension is defined as a sustained increase in intracranial pressure (ICP) above 15 mm Hg. Uncompensated increases in tissue or fluid within the rigid intracranial vault produce the sustained pressure elevations. pp. 871-874 Longnecker, DE, Brown, DL, Newman MF and Zapol, WM. Anesthesiology. New York: McGraw Hill, 2012.
question
Cholinesterase inhibitors that freely cross the blood-brain barrier include: a. neostigmine b. pyridostigmine c. physostigmine d. edrophonium
answer
c. physostigmine Physostigmine is a teritary amine and has a carbamate group, but no quaternary ammonium. Therefore, it is lipid soluble and is the only clinically available cholinesterase inhibitor that freely passes the blood-brain barrier. pg. 304 Barash, PG, Cullen, BF, Stoelting, RK, Cahalan, MK, Stock, MC, Ortega, R.,Sharar, SR, and Holt, NF. Clinical Anesthesia. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2017.
question
The most frequent manifestation of sickle cell disease is: a. pain b. splenic sequestration c. aplastic crisis d. right upper quadrant syndrome
answer
a. pain The most frequent manifestation of sickle cell disease is pain. The pain is thought to be secondary to tissue ischemia and usually affects the back, chest, extremities and abdomen. pg. 635 Barash, PG, Cullen, BF, Stoelting, RK, Cahalan, MK, Stock, MC, Ortega, R.,Sharar, SR, and Holt, NF. Clinical Anesthesia. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2017.
question
During the administration of general anesthesia for a radical prostatectomy, the rhythm strip below is obtained. The most appropriate therapeutic measures at this time would include: a. initiation of a nitroglycerine infusion b. administration of metoprolol c. requesting the use of a bipolar cautery d. engage the artifact filter on the ECG monitor
answer
c. requesting the use of a bipolar cautery This rhythm strip indicates a paced rhythm with clearly visible pacer spikes. Electrical interference from the electrocautery can be interpreted as myocardial activity and can suppress the pacemaker generator. The use of a bipolar cautery will reduce the electrical interference produced; if that is not possible, then pure cut is better than "blend" or "coag." pp. 125-126, 1722 Barash, PG, Cullen, BF, Stoelting, RK, Cahalan, MK, Stock, MC, Ortega, R.,Sharar, SR, and Holt, NF. Clinical Anesthesia. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2017.



