Collin College, Dr. Rich Spring 2016 Biology 1407 Vocabulary for Practical 1
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Microevolution

answer
Evolutionary change below the species level through Mutation, selection, gene flow, and genetic drift. Example: Evolved Mosquito resistance to DDT
question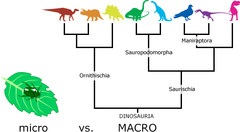
Macroevolution

answer
Evolutionary change above the species level. Includes the origin of a new group of organisms through a series of speciation events and the impact of mass extinction on the diversity of life. Example: Wales from land dwelling animals, Dinosaurs to Birds
question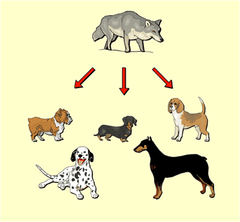
Artificial Selection

answer
Selective breeding of domesticated plants and animals to encourage the occurrence of desirable traits Example: Dogs
question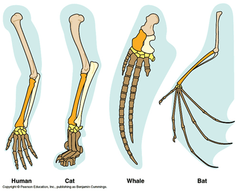
Homologous structures

answer
Structures in different species that are similar because of common ancestry but may have different function Example: Bat wing and human arm
question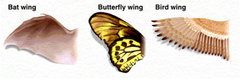
Analogous Structures

answer
Structures that are similar because of convergent evolution. Have the same function but different origins. Example: Insect wing and bat wing
question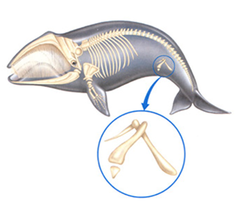
Vestigial Structures

answer
Feature of an organism that is a historical remnant of a structure that served a function in the organism's ancestors. Example: Wisdom Teeth, Coccyx
question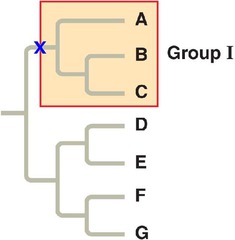
Clade

answer
Group of species that includes an ancestral species and all of its descendants. Example: Birds
question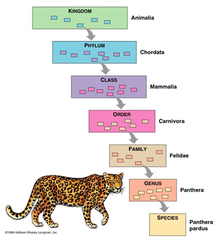
Taxonomy

answer
A scientific discipline concerned with naming and classifying the diverse forms of life using binomial nomenclature. Developed by Carolus Linnaeus.
question
Taxonomic Ranks

answer
Ranking system developed by Carolus Linnaeus in which organisms are grouped similarly. Taxon Ranks in order from most inclusive to least inclusive: Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Families, Genus, Species (Dirty kinky people can often find good sex)
question
Systematics
answer
Scientific discipline focused on classifying organisms and determining their evolutionary relationship.
question
Gametophyte
answer
In alternation of generations, the multicellular haploid form that produces haploid gametes by mitosis.
question
Sporophyte

answer
In alternation of generations, multicellular diploid form that produces haploid spores by meiosis
question
Zygote
answer
diploid cell produced by union of haploid gametes during fertilization. Fertilized egg
question
Gametes
answer
haploid reproductive cells egg and sperm
question
Gametangium
answer
Plant structure in which gametes are formed female = archegonia Male= antheridia
question
Spore

answer
haploid cell produced in the sporophyte by meiosis. (Fern)
question
Sporangium

answer
multicellular organ in which meiosis occurs and haploid cells develop
question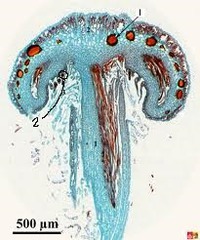
Archegonium

answer
female gametangium. Moist chamber in which female gametes develop
question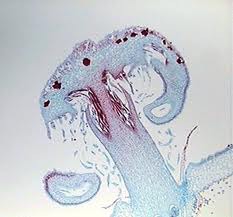
Archegoniophore

answer
Stalk or other outgrowth on a prothallum upon which archegonia are born
question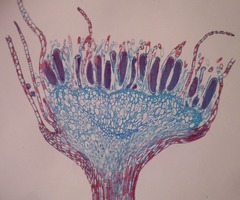
Antheridium

answer
the male gametangium. A moist chamber in which male gametes develop.
question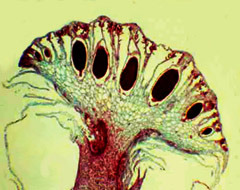
Antheridiophore

answer
Gametophore bearing antheridia only
question
Gemma Cup

answer
cup structure on mosses and iverwort used for asexual reproduction. Where Gemmae are born.
question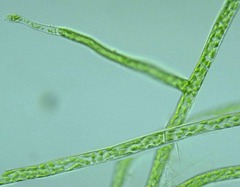
Protonema

answer
Thin photosynthetic filament which develops after spore germination and soon gives rise to a mature gametophyte.
question
thallus
answer
leaf-like lobed body found on thalloid liverworts.
question
Homosporous
answer
Referring to a plant species that has a single kind of spore, which typically develops into a bisexual gametophyte. Bryophytes
question
Heterosporous
answer
Referring to a plant species that has two kinds of spores: Microspores, which develop into male gametophytes, and megaspores, which develop into female gametophytes.
question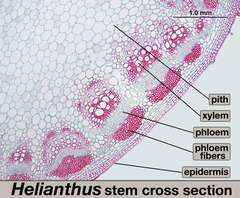
Xylem

answer
Vascular plant tissue which conducts water and dissolved minerals throughout the plant.
question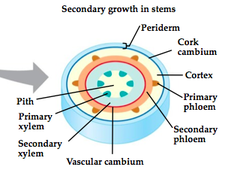
phloem

answer
Conducts nutrients, such as sucrose, hormones and other molecules throughout the vascular plant.
question
Cuticle

answer
waxy covering on the surface of stems and leaves used for protection against desiccation in a vascular plant.
question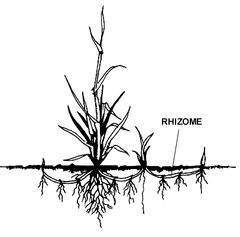
Rhizome

answer
An underground stem that branches horizontally, producing aerial stems and underground roots.
question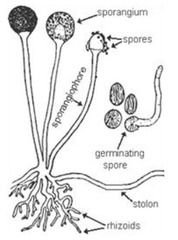
Rhizoid

answer
long, tubular single cell or filament of cells that anchors bryophytes to the ground.
question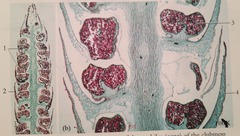
Sporophylls

answer
Reproductive sporangia - located on the surface of leaves.
question
Frond

answer
Fern leaves
question
Strobilus

answer
Cluster of sporophylls - cone shaped structure
question
Microphylls

answer
in lycophytes, small leaf with single unbranched vein. scalelike leaves
question
Fiddlehead

answer
young coiled fern leaves
question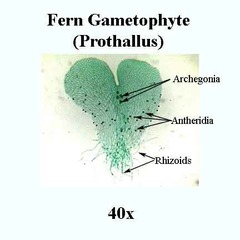
Prothallus

answer
heart shaped gametophyte of ferns and related plants
question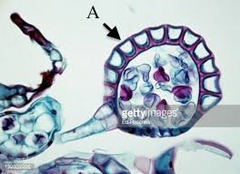
Annulus

answer
A fuzzy region of the Sorus which catapults mature spores.
question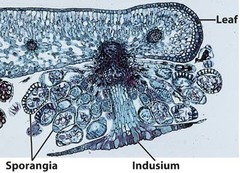
Indusium

answer
Protects the sori in a fern.
question
Sorus

answer
Cluster of sporangia on a fern sporophyll (distinct brown spots on the underside of a frond)
question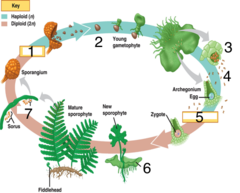
Fern life cycle

answer
Vascular plant, gametophytes are hermaphorditic. Sprophyte is diploid and dominant part of the plant cycle.
question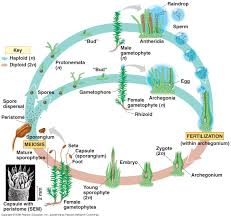
Moss life cycle

answer
Non-vascular plant, gametophyte is haploid, photsynthetic and dominant part of the plant life cycle.
question
Spermatophyte
answer
Seed plant, made up of gymnosperms and angiosperms.
question
Ovules

answer
structures of seed plants containing the female sex cells with the potential to develop into seeds
question
Pollination

answer
Pollen is carried from the male reproductive organs to the female reproductive organ in a number of ways, including wind, insects, and birds.
question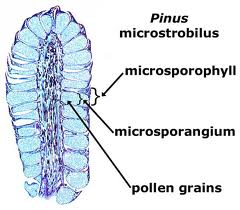
microsporophyll

answer
male plants produce pollen by leaf homologues. leaf-like structure that bears microsporangia
question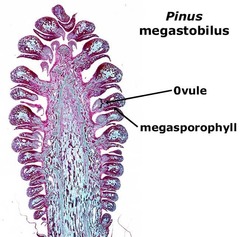
megasporophyll

answer
female plants produce ovules by leaf homologues. Leaf-like structure that bears megasporangia
question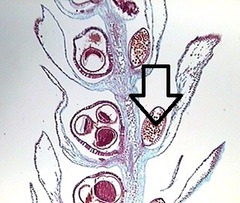
microsporangium

answer
a sporangium that produce spores that give rise to male gametophytes
question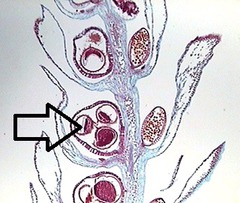
megasporangium

answer
female sporangia - structure in which megaspores are formed
question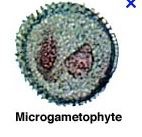
microgametophyte

answer
male gametophyte that develops from microspores of heterosporous plant
question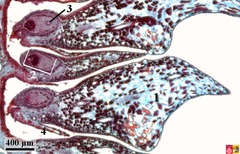
megagametophyte

answer
Embryo sac - the female gametophyte that arises from a megaspore of heterosporous plant
question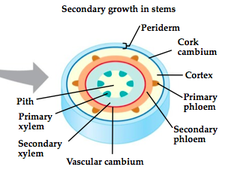
vascular cambium

answer
cylindrical layer of cambium that runs through the stem of the plant and undergoes secondary growth. (new xylem on the interior side and new phloem on the exterior side)
question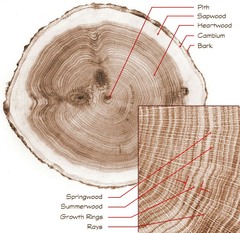
springwood

answer
Annual ring of wood: large, thin-walled cells, formed during the first part of the growing season (spring)
question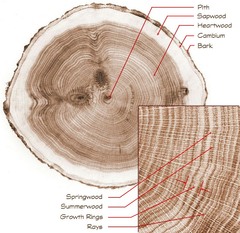
summerwood

answer
Annual ring of wood: compact, thick-walled cells formed during the later part of the growing season (summer)
question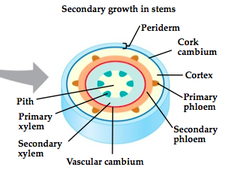
cork cambium

answer
Secondary growth - adds secondary dermal tissue. Replaces epidermis with a thicker, tougher periderm.
question
monocot

answer
Flowering plant whose seeds typically contain only one embryonic leaf
question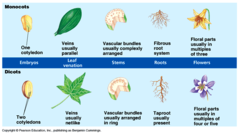
eudicot

answer
flowering plant having two cotyledons in the seed and normally having net-veined leaves.
question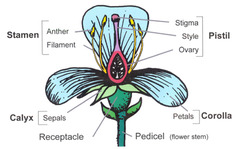
peduncle

answer
stalk where flower begins, stalk bearing a flower or fruit.
question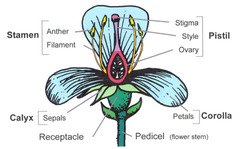
receptacle

answer
A swollen region that contains the other floral part arranged in whorls - formed by the peduncle or pedicels.
question
sepals
answer
The outermost whorl, leaflike, green petals
question
petals

answer
The most conspicuous part of the flower.
question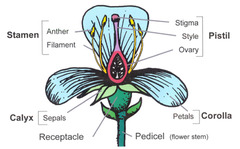
stamen

answer
The male portion of the flower which consists of a slender stalk, the filament, and the sac-like anther where pollen is produced.
question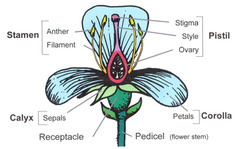
pistil (carpel)

answer
The most obvious female portion of the plant which is centrally located. Ovule producing part.
question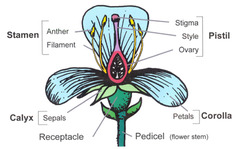
stigma

answer
a sticky knob that receives pollen, sits atop a slender tube called the style.
question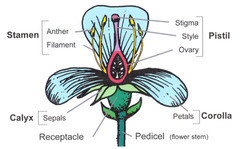
style

answer
long slender stalk that connects the stigma and the ovary.
question
ovary

answer
Enlarged basil portion of the pistil where ovules are produced.
question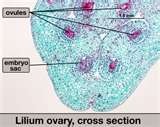
embryo sac

answer
female gametophyte of angiosperm
question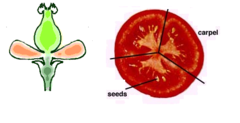
simple fruit

answer
Result of ripening of a simple or compound ovary in a flower with only one pistil.
question
multiple fruit

answer
Multiple carpels of many flowers
question
aggregate fruit

answer
One flower with many carpels



