Chapter 12 Social Cognitive Theory – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Bandura and Walters' work
answer
Social Learning & Personality (1959)
question
Bandura's work
answer
Social Foundations of Thought and Action (1986) -MONUMENTAL!
question
Walter Mischel's work
answer
-Personality and Assessment (1968) -"Perhaps the most influential volume in personality psychology in the past half century!!!"
question
Walter Mischel
answer
-Reason about the world using language -Contemplate present, past and hypothetical future events -Reflect on themselves (about self and own thinking)
question
Structure of personality
answer
-Competencies & skills -Beliefs & expectations -Goals -Evaluative standards
question
Competencies & Skills
answer
Ways of thinking about problems + behavioral skills in solving them -Declarative knowledge: involves knowing THAT something is the case -Procedural knowledge: involves knowing HOW to do something
question
Competencies & skills
answer
-Context specificity -Psychological change
question
Beliefs and expectancies
answer
Beliefs are about what the world is actually like -Expectations re: future -Situational variability -Highly idiosyncratic
question
Schemas
answer
-Self-schemas: validated by reaction time measures -"family of selves"
question
Self-efficacy beliefs
answer
Perceived self-efficacy: -Selection -Effort, persistence, performance -Emotion -Coping Situational
question
Outcome expectations vs. self-efficacy expectations
answer
Self-efficacy
question
Self-efficacy and anxiety
answer
*Perceptions* of low self-efficacy --> experience of high anxiety arousal
question
Perceived inefficacy and depression
answer
Prone to depression: -Impose excessively high goals & standards -Blame themselves for falling short of them
question
What is fundamental to anxiety? (not the threatening event)
answer
Perceived inefficacy in coping with it is fundamental to anxiety
question
Low self-efficacy
answer
-contribute to diminished performance --> falling even further below standards + additional self-blame
question
What causes depression
answer
when a person feels inefficacious in relation to a goal BUT believes the *goal to be reasonable*
question
What does not cause depression
answer
beliefs that goals are BEYOND one's capabilities because UNREALISTIC will lead to abandoning the goal and maybe apathy, *not depression*
question
Motives
answer
-Prefer to see ourselves as relatively stable 1) Self-enhancement motive: overcompensate self image, compare those less of us 2) Self-verification motive: seek those who validate our view of self
question
Self enhancement motive
answer
-biased towards positive views of the self -enhance self-image by comparing with those lesser to make us feel better -people tend to prefer positive feedback -overestimate positive attributes
question
Self-verification motive
answer
experience self as *consistent* and *predictable* -prefer feedback that validates how we feel about ourselves (even if it's negative) -seek out people who also validate us
question
Goals
answer
-Mental representation of action or course of action
question
How goals are organized
answer
Organized in a system and hierarchically -Vary by 3 factors: 1. Challenge: self-efficacy (higher self-efficacy, higher goals) 2. Proximity/distal: time frame 3. Subjective meaning
question
Goals are central to ____.
answer
Goals are central to *motivation*
question
Learning goals
answer
think about the task and all you can learn from it -improve/change -intrinsic/important to us
question
Performance goals
answer
aim to show: -how smart you are -avoid embarrassment when you don't know something -make a good impression
question
Personal standards (evaluative standards)
answer
fundamental/essential to motivation & performance
question
Self-evaluative reactions (evaluative standards)
answer
-Self-evaluative reactions (*emotional*) -respond in either satisfied or dissatisfied similar to expectations
question
Higgins
answer
"Ideal & ought" standards -*Actual & ideal self-discrepancies* lead to --> sadness (experience negative emotion if can't follow up) -*Actual & ought self-discrepancies* lead to --> anxiety (e.g. playing Fo4 when you should/ought to be studying)
question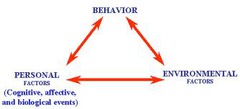
*Reciprocal determinism* (Bandura)

answer
ALBERT BANDURA -Developed for cause and effect -reciprocal in the sense that *actions of persons influence each other*
question
Mischel & Shoda
answer
-Broader view: environment and behavior -Cognitive Affective Processing System *(CAPS)*
question
CAPS
answer
-Cognitive Affective Processing System -by Mischel and Shoda 1. Cognitive and emotional linked (emotions --> thoughts) 2. 'Situational features' 3. 'Situational features' --> variable behaviors -Activate diff. parts of personality system -what causes us to vary behaviors due to diff. activation -Situation affects stability and variability
question
Mischel (if...then profiles)
answer
-Behavioral signatures: infinite profiles; tendencies to behave in similar situations -stable profiles in expressing behavior in groupos -Cognitive Affective Processing System (situational features and cognitive emotions)
question
Modeling (Bandura)

answer
Desired activities demonstrated by models who experience positive consequences -Complex behaviors broken down -*Learning can happen w/o reinforcement; by simply observing aka modeling*
question
Observational learning
answer
-Model (person that does the behavior) & Modeling (activities) (Bandura) -Internal mental representation -Acquisition and performance
question
Acquisition (deals with performance in modeling)
answer
Learning new skills and behaviors in the absence of reinforcement
question
Performance (deals with acquisition in modeling)
answer
Model and modeling in observational learning
question
Two main models (to observational learning; Bandura)
answer
1. Acquire new skills; acquisition 2. Self-regulation
question
Bobo Doll experiments (Bandura & Ross)
answer
-Aggressive behavior by model in 3 conditions: 1) No consequences --> control, just watched 2) Reward --> much more aggressive due to + reinforcement 3) Punishment: less *Bottom line*: kids imitated aggressiveness of adult
question
Vicarious conditioning
answer
Process of learning emotional reactions through observing others *Emotions are learned.*
question
Self-regulation
answer
2nd main point of Bandura observational learning -*Capacity to motivate oneself* e.g. Set goals, plan strats (RUSH B), Evaluate & modify behavior
question
What is motivation guided by?
answer
Our own *thinking processes* -Social cognitive theorists perspective
question
Bandura & Cervone
answer
-Research on goals (self-regulation) -4 groups of subjects w/ 4 conditions -*Goals and feedback shown to be most beneficial for performance* -Goals, feedback, and control groups actually nearly identical in performance
question
Mischel's Paradigm: Marshmallow test
answer
-Experiment involving 4 yr kids testing *delayed gratification* -found that children who were able to wait longer (stronger willpower) for the preferred rewards tended to have better life outcomes.
question
Stress
answer
when one views circumstances as taxing or exceeding resources & endangering well-being
question
Lazarus & Folkman
answer
1. *Primary appraisal*: "Is something at stake: Is there a threat or danger?" 2. *Secondary appraisal*: "What, if anything, can be done?"
question
Stress and coping (Lazarus & Folkman)
answer
1. *Problem-focused coping*: attempts to cope by altering features of stressful situation 2. *Emotion-focused coping*: attempts to improve internal emotional state
question
What are coping methods influenced by? (Lazarus & Folkman)
answer
Coping methods influenced by 1. *personality factors*...many strongly influence by 2. *situational context*
question
Stress and coping dynamic (Lazarus & Folkman)
answer
Greater level of stress and efforts to cope --> lead to poorer the physical health & greater the likelihood of psychological symptoms
question
Mastery and problem solving (Lazarus & Folkman)
answer
-Greater sense of *mastery* --> better physical and psychological health -Planful problem solving more adaptive than escape avoidance or confrontive coping
question
Bandura
answer
-Maladaptive behavior arises from dysfunctional learning -Dysfunctional expectancies -Dysfunctional self-evaluations -Self-efficacy beliefs
question
Modeling and guided mastery (Bandura)
answer
-Goal: change in self-efficacy -*Modeling*: observation of behavior + positive consequences -*Guided mastery*: observation + assistance
question
Ellis
answer
-Rational Emotive Therapy RET -*Beliefs about the events are what people respond to emotionally, not the events themselves.*
question
ABC of Rational-emotive therapy (Ellis)
answer
1) Activating event (A) may lead to consequence (C) like an emotional reaction 2) Beliefs (B) are created between A --> C 3) Beliefs (B) determine response to activating event B --> A so *Bottom line*: *Beliefs cause distress are irrational, it is the beliefs that cause reactions/consequences*
question
Aaron Beck
answer
Psychological difficulties are due to -Pattern of automatic thoughts -Dysfunctional assumptions -Negative self-statements
question
Beck's cognitive triad of depression
answer
1. Negative views of *self* (e.g. "I am inadequate, undesirable, worthless") 2. Negative views of the *world* (e.g. "The world makes too many demands on me & life represents constant defeat.") 3. Negative views of *future* (e.g. "Life will always involve the suffering & deprivation it has for me now.")
question
Faulty cognitions (Beck)
answer
Compared to non-depressed individuals, depressed persons: - focused more on themselves -had more accessible negative self-constructs -had bias toward pessimism rather than optimism in relation to self
question
Beck's cognitive therapy for depression (CBT)
answer
-Designed to identify and correct distorted conceptualizations and dysfunctional beliefs - 15 to 25 sessions at weekly intervals -interpretation and modification of distortions and dysfunctional beliefs
question
Highly specific learning environment
answer
-Monitor negative automatic thoughts e.g. catch yourself in the act "here I go again..." -recognize how these thoughts lead to problematic feelings and & behaviors
question
Cognitive Therapy for Depression (CBT by Aaron Beck)
answer
-Examine evidence for & against these thoughts -Substitute more reality based interpretations e.g. "Is that true" Questions+examines similar to 2 attorneys in a courtroom
question
Evaluation
answer
-Database is diverse -Highly testable -Comprehensive well defined constructs -Applicable = therapies! (-) Not tied well together so not very systematic (-) Falls short of biology methods in comprehension



