biology chapter 5 notes – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
the cell cycle
answer
5.1
question
interphases & mitosis
answer
cell cycle is split into two sections
question
g1, s phase, g2, mitosis
answer
4 stages
question
prophase pro-metaphase metaphase anaphase telophase
answer
mitosis 5 stages
question
when the cell membrane actually splits
answer
cytokinesis
question
G1 S-phase G2
answer
interphase
question
wrap around cell membrane and "pinch" it in half
answer
microtubules -
question
increases in size, replicates organelles, G1 check point (makes sure it is getting big enough to divide, signals other cells to see if division is necessary), where cells spend most of there time
answer
G1
question
DNA replication
answer
S phase (synthesis)
question
more growth, G2 check point (make sure that DNA is undamaged, checking size, checking that the need for cell division is still there, is everything there in order to divide) in animal cells the centrioles replicate
answer
G2
question
M check point (makes sure chromosomes are properly attached)- happens in the middle of mitosis, mitosis is the division of the nucleus and its content
answer
mitosis
question
same in every cell
answer
s phase, g1 and m phase take 12 hours
question
cells are still carrying out all metabolic functions but don't divide(ex. brain cells, heart cells)
answer
G sub 0
question
too little =cant contain all the organelles necessary to carry on there life processes too big = too big for things to diffuse around in effectively and efficiently
answer
cell size is limited
question
s-phase (synthesis)
answer
During which stage of the cell cycle is the DNA copied?
question
M-phases, S-phase, G2
answer
Which stages of the cell cycle generally require about the same amount of time in all human cells?
question
ratio of cell surface area to volume,too little =cant contain all the organelles necessary to carry on there life processes too big = too big for things to diffuse around in effectively and efficiently
answer
What limits the maximum size of a cell
question
in side of G1 somewhere because it would have to enter the cycle somewhere
answer
Suppose you were to draw a diagram representing the cycle of a neuron. Explain where and how you would represent G0
question
the cell would be one oversized cell with two nuclei and double every thing else, the microtubule belt wouldn't have been formed
answer
Suppose you treat cells with chemicals that block cytokinesis. describe what you think the cells would look like.
question
the cell division rate of the algae living in the sunny, nutrient-rich pond would have a higher rate then that of the algae living in the shady, nutrient-poor conditions. You could test that theory by creating two environments; one with good conations as the ones stated in the question, and one with bad conditions, as the ones stated in the question. Then introduce the same type of algae to both conditions and simply observe which one has a higher division rate.
answer
Predict how the rate of cell division would differ between single-celled algae living in a sunny, nutrient-rich pond verse algae living in a shady, nutrient-poor pond. How could you test your prediction?
question
mitosis and cytokinesis
answer
5.2
question
DNA and proteins condense, chromatin condenses into chromatids
answer
prophase
question
nuclear envelope breaks down, the centrioles move to opposite side of the cell microtubules(spindle fibers) form and attach to chromosomes at the centromere(on the kinetochore disk)spindle fibers start aligning the chromosomes
answer
pro-metaphase
question
the spindle fibers move chromosomes the middle of the cell and lines them up on the cell's equator, spindle fibers that don't attach to the chromosomes keep building microtubules and elongate cell= non-kinetochore spindle fibers that attach to chromosomes = kinetochore
answer
metaphase
question
chromatids are separate at centromere now called chromosome, pulls two chromatids apart, you are in anaphase until they are moved to opposite sides of the cell
answer
anaphase
question
chromosomes uncoil, nuclear membranes form, spindle fibers break down, nucleolus forms
answer
telophase
question
color
answer
croma-
question
one long continuous thread of DNA that consist of numerous genes along with regulatory information
answer
chromosome
question
protein that organizes chromosomes and around which DNA wraps, DNA packing
answer
histone
question
loose combination of DNA and proteins that is present during interphase, somewhat twisted
answer
chromatin
question
one half of a duplicated chromosome (each leg of a chromosome)
answer
chromatid
question
region of condensed chromosome that looks pinched; where spindle fibers attach during meiosis and mitosis
answer
centromere
question
repeating nucleotide at the ends of DNA molecules that do not form genes and help prevent the loss of genes, keep the end of chromosomes from attaching to each other, involved in how long the cell lives
answer
telomere
question
p - arm
answer
the area above the centromere
question
q- arm
answer
area below the centromere
question
when your a fetus it rebuilds telomere, when your born genes for makes telomerase turns off, in cancer cells it turns back on
answer
telomerase
question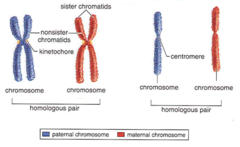

answer
draw what a chromosome looks like during metaphase. identify the chromatids and the centromere.
question
because the DNA is copied in synthesis and when they separate each cell gets the same exact DNA
answer
briefly explain why the daughter cells resulting from mitosis are genetically identical to each other and to the original cell.
question
prophase is when the chromosomes coil up and telophase is when they uncoil
answer
how do prophase and telophase differ?
question
spindle fibers, how the DNA is coiled(prokaryotic=circle shaped DNA, eukaryotic =X), membrane bound organelles
answer
using a light microscope, you observe a cell that has no nucleus. What features would you look for to determine whether it is a eukaryotic cell undergoing mitosis or a prokaryotic cell?
question
if the histones are not properly binding the DNA then the DNA will not be able to condense into chromosomes, which effects protein synthesis in the sense of speeding it up because it would make it easier for the enzymes to get to the DNA to cause transcription to take place
answer
for a cell to make proteins, enzymes must access its genes. When histones are modified with acetyl groups (-COCH3), their positive charge is neutralized, so they wrap DNA less tightly. How might this affect the rate of protein synthesis?
question
regulation of the cell cycle
answer
5.3
question
physical signals -cell-cell contact , in a eukaryotic cell that is behaving correctly when it touches another cell it stops dividing -cells need a surface to grow on (control) chemical signals - growth factors (growth hormone) - shuts off in girl 13-14, guys early 20s
answer
in eukaryotic cells there are both internal and external controls
question
move phosphate groups from one cell to another (phosphorylate) when you phosphorylate things they become higher energy
answer
kinases
question
create and destroys things rapidly
answer
cyclins
question
programmed cell death, external or internal signal tells the cell its time to die and the cell self destructs, the first thing that happens if the nucleus shrinks and disintegrates, cell becomes damaged, lysosomes rupture and spill digestive enzymes , immune system send phagocytic cell to eat the damaged cell, phagocytize
answer
apoptosis
question
cancerous
answer
technically any group of cells that are dividing uncontrollably is
question
encapsulated not invading other cells, stay in clusters, can be easily removed
answer
benign cancer
question
bad cancer, cells that metastasize break off and spread to other areas and grow there
answer
malignant caner
question
a hormone that stimulates growth and division of cells
answer
describe what a growth factor is and how it influences the cell cycle.
question
they don't follow the rules of cell to cell contact they divide uncontrollably they grow without growth factor they form tumors they can metastasize they don't contribute to any functions
answer
explain how cancer cells differ from healthy cells
question
benign tumors remain clustered, don't affect the surrounding tissues or cells malignant tumors can metastasize
answer
how do benign and malignant tumors differ?
question
no, because if the cell cycle is normal it would go against the direct definition of a cancerous cell which divides uncontrollably and doesn't follow any rules or doesn't need a growth factor
answer
suppose chromosomes in a single cell are damaged by ultraviolet radiation. if the damaged genes do not affect the cell cycle regulation, do you think the cell will become cancerous? explain.
question
because if spindle fibers are unable to form then mitosis couldn't happened and the cell couldn't divide
answer
some anticancer drugs prevent microtubules from forming spindle fibers. Why do you think these drugs might be effective treatment for cancer?
question
asexual reproduction
answer
5.4
question
about the exact same as mitosis
answer
binary fission
question
offspring are identical prokaryotes only option - have a circular DNA takes 4 hours for cells to divide
answer
asexual reproduction
question
numbers(exponential growth) no variation no struggle of finding a mate more efficient keep genes out ex. plants(budding), bacteria(binary fission) if your healthy, offspring should be healthy if your well adapted, offspring are well adapted
answer
advantages
question
no genetic diversity don't handle big changes in environment well (less adaptable) if there is a problem with the parent cell then there will be a problem with the offspring
answer
disadvantages
question
very costly attracting a mate mother has to labor over offspring advantage genetic diversity
answer
sexual reproduction
question
ex. hydra, yeast offspring grows off parent cells
answer
budding
question
ex. starfish parent cell breaks off and each piece becomes a new organism
answer
fragmentation
question
mitosis occurs exclusively in eukaryotic cells. prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a process called binary fission
answer
explain how mitosis differs from binary fission
question
each piece would become a new flat worm not kill it(fragmentation)
answer
briefly explain why cutting a flat worm into pieces wouldn't kill it.
question
sexual reproduction - allows for change in DNA of an organism, which leads to a stronger species asexual reproduction - ensures the species will carry on - no struggle of finding a mate
answer
how does an organism benefit by being able to reproduce both sexually and asexually
question
the dish that stops growing is the one that was treated with the chemical that blocks DNA replication
answer
yeasts are growing in two dishes. you treat one dish with a chemical that blocks DNA replication but you forget to label it. How can you identify the treated dish?
question
an environmental change that causes the larger but unadaptable species to die off
answer
two populations live in the same habit and complete for food. the first group is larger and multiplies through asexual reproduction; the second group reproduces sexually. What could happen to cause the second group to outnumber the first?
question
multicellular life
answer
5.5
question
a bunch of similar cells performing a similar function= tissue, a bunch of different types of tissues preforming complimentary functions= organ, a number of organs preforming related services
answer
multicellular
question
we can specialize our cells, reason why we got so big in single celled organism that one cell does everything
answer
benefit to being multi cellular
question
embryonic stem cells- all of the cells of an embryo,each cell has the potential to become anything =totipotent pluripotent stem cells - can grow into any cell except for totipotent stem cells, can grow into almost anything multipotent stem cells can grow only into cells of a closely related cell family
answer
stem cell classifications
question
they divide and renew themselves for a long period of time remain undifferentiated in form can differentiate into a variety of specialized cell types
answer
uniqueness's of stem cells
question
found everywhere in body, not as flexible as embryonic stem cells, partially differentiated, non controversial disadvantages not easy to find not easy to grow
answer
adult stem cells
question
the cells can communicate to each other and "tell" each other what needs to be done so that they can maintain the body's temperature, PH level, etc.
answer
how does communication between cells help maintain homeostasis
question
it's important to the development of multicellular organisms because if there was no cell differentiation, how could muscle and nerve cells form? so basically, cell differentiation is important because it decides whether a cell is a muscle cell, or a nerve cell, and what structure and function it preforms in a multicellular organism
answer
why is cell differentiation an important part of the development of a multicellular organism?
question
1. they divide and renew for long periods of time 2. they remain undifferentiated in form 3. they differentiate into a variety of specialized cell types
answer
what are the defining characteristics of stem cells?
question
a bunch of similar cells performing a similar function= tissue, a bunch of different types of tissues preforming complimentary functions= organ, a number of organs preforming related functions
answer
describe how cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems are related.
question
it determines how the stem cell will differentiate
answer
what role does the location of a cell in a developing embryo play in cell differentiation?
question
this is a matter of opinion, of course, but I believe the most important factor to be considered in whether stem-cell research should be legally and federally funded is the potential for curing some of our most baffling diseases
answer
explain which factor you think is most important in deciding whether stem research should be legal and government-funded
question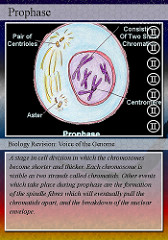
DNA and proteins condense, chromatin condenses into chromosomes, centrosomes move to opposite sides of the and spindle fibers start forming

answer
1.prophase
question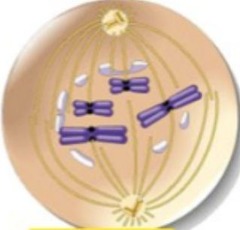
nuclear envelope breaks down, the centrioles move to opposite side of the cell microtubules(spindle fibers) form and attach to chromosomes at the centromere(on the kinetochore disk)spindle fibers start aligning the chromosomes

answer
2.pro-metaphase
question
the spindle fibers move chromosomes the middle of the cell and lines them up on the cell's equator, spindle fibers that don't attach to the chromosomes keep building microtubules and elongate cell= non-kinetochore spindle fibers that attach to chromosomes = kinetochore

answer
3.metaphase
question
chromatids are separate at centromere now called chromosome, pulls two chromatids apart, you are in anaphase until they are moved to opposite sides of the cell

answer
4.anaphase
question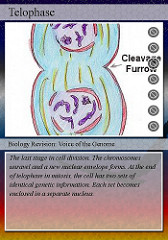
chromosomes uncoil, nuclear membranes form, spindle fibers break down, nucleolus forms, chromosomes begin uncoiling and forming back into chromatin

answer
5.telophase
question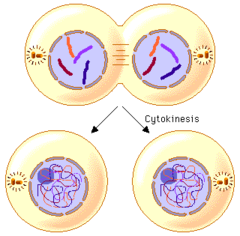
when the cell membrane actually splits

answer
6.cytokinesis
question
the "waist" of the chromosome that looks pinched, the point at which the spindle fibers attach to the chromatin
answer
7.centromere
question
a repeating nucleotide at the ends of the chromatin, that keep genes from "fraying"
answer
8.telomere
question
telophase is the end of mitosis the telomere is at the end of the chromatid
answer
9.the prefix telo- means "distant, far, or end." How does this meaning relate to the words telophase and telomere?
question
G1-increases in size, replicates organelles, G1 check point (makes sure it is getting big enough to divide, signals other cells to see if division is necessary), where cells spend most of there time S-phase- DNA replication G2-more growth, G2 check point (make sure that DNA is undamaged, checking size, checking that the need for cell division is still there, is everything there in order to divide) in animal cells the centrioles replicate M-phase-M check point (makes sure chromosomes are properly attached)- happens in the middle of mitosis, mitosis is the division of the nucleus and its content, chromosomes are separated and distributed to the two new cells
answer
11.the cell cycle has four main stages-G1, s, G2, and M. What occurs in the cell during each stage?
question
the DNA strands wrap around the histones, which helps the DNA from getting tangled = DNA packing
answer
14.you know that a chromosome is a very long, continuous strand of DNA. how do proteins help condense chromosomes?
question
mitosis is the process of making double of everything in the cell(DNA, organelles, size, nuclei cytokinesis is the division of the cytoplasm
answer
16.how does the process of cytokinesis differ from the process of mitosis?
question
the presence of a growth factor is going to increase cyclin levels because growth factor is a hormone that makes the cell want to divide
answer
17.increased levels of cyclin help trigger a cell to divide. Do you think a growth factor would increase or decrease cyclin levels? explain.
question
both result in two genetically equal cells binary fission happens in prokaryotic cells mitosis happens in eukaryotic cells
answer
19.list one similarity and one difference between binary fission and mitosis.
question
asexual reproduction, mitosis is happening in the roots to make them grow
answer
20.you pull a leaf from a plant and place it in a cup of water. After a week, roots start to grow from the leaf. what type of reproduction has occurred, and what role does mitosis play in it?
question
1. they divide and renew for long periods of time 2. they remain undifferentiated in form 3. they differentiate into a variety of specialized cell types
answer
22.list three characteristics of all stem cells
question
benefits- huge yield it going to be faster to propagate risks- no genetic diversity so if a virus comes around everything will die wouldn't be able to grow in other palaces price would go down because there are so many
answer
25.a scientist wants to use asexually reproducing vegetables to increase crop yields. he plans to distribute budding potatoes and teach farmers how to separate them into new plants. what are some potential benefits and risks that could result form this situation?
question
because by mutating they can adapt to there environment better
answer
26.the rates of DNA mutations in bacteria are know to increase when they are under stressed environmental conditions. why do you think this is important for an organism the reproduces asexually?
question
48, because the DNA multiplies in S phase
answer
27.suppose an organism usually has 24 chromosomes in its nucleus. how many chromatids would it have just are the S phase of the cell cycle?
question
interphase, because that's where cells spend most of there time
answer
29.in what stage of the cell cycle are most of these cells? explain.
question
by looking how degraded the telomere is, longer=younger shorter= older, new cells are smaller, nucleus takes up more space in cell=younger
answer
30.how can you visually distinguish between newly formed cells and older cells?
question
c, the compound killed the treated cells
answer
1.scientist researching anticancer drugs treat a cell culture with a compound. following treatment, they notice that the culture stopped growing. untreated cells from the same culture, however, have continued to grow. these results indicate that the compound blocks the normal cell cycle. what else could have caused these results?
question
b, it carries the code from which each type expresses specific genes.
answer
2.which describes the role of DNA in cell differentiation?
question
b, outer layer
answer
3.one environmental factor that plays a key role in cell differentiation in multicellular organisms is the location of the developing cell with respect to other cells. in human development, from which cell layer in the emryo will a nerve cell develop?
question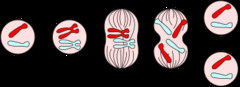
c, 6 each

answer
4.in the diagram above, cell A is undergoing mitosis. if cell A has 6 chromosomes, how many chromosomes will cells B and C have?
question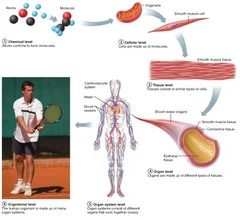
c, organs

answer
5.the figure above represents some levels of organization in multicellular organisms. which term fits in the box marked "X"?
question
d, both types of cells have the same DNA, but each cell uses only part of the DNA message
answer
6 .unlike stem cells, most body cells cannot form different types of cells. for example, skin cells can only make skin cells, and nerve cells can only make nerve cells. which statement best explains why skin cells will never become nerve cells?



