Biochemistry | Chapter 1 | Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Non polar, Nonaromatic Side Chains
answer
-Glycine -Alanine -Valine -Leucine -Isoleucine -Methionine -Proline
question
Glycine
answer
3 Letter Abbreviation: Gly 1 Letter Abbreviation: G -Single H atom as side chain -Achiral
question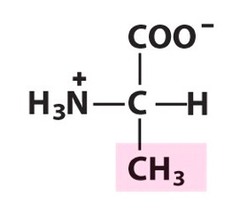
Alanine

answer
3 Letter Abbreviation: Ala 1 Letter Abbreviation: A
question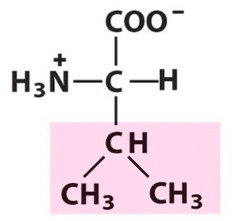
Valine

answer
3 Letter Abbreviation: V 1 Letter Abbreviation: Val
question
Leucine
answer
3 Letter Abbreviation: Leu 1 Letter Abbreviation: L
question
Isoleucine
answer
3 Letter Abbreviation:Ile 1 Letter Abbreviation: I
question
Methionine
answer
3 Letter Abbreviation: Met 1 Letter Abbreviation: M - One of only 2 amino acids that has a Sulfur atom in its side chain
question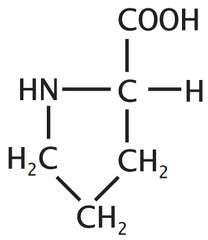
Proline

answer
3 Letter Abbreviation: Pro 1 Letter Abbreviation: P - Unique, forms a cyclic amino acids - The ring --> LESS flexibility --> Strains its role in secondary structure
question
All chiral amino acids used in Eukaryotes are __-amino acids
answer
L. NOT D.
question
Aromatic Side Chains
answer
-Tryptophan -Phenylalanine -Tyrosine
question
Tryptophan
answer
3 Letter Abbreviation: Trp 1 Letter Abbreviation: W - Largest aromatic A.A.
question
Phenylalanine
answer
3 Letter Abbreviation: Phe 1 Letter Abbreviation: F - Nonpolar
question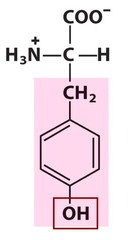
Tyrosine

answer
3 Letter Abbreviation: Tyr 1 Letter Abbreviation: Y - Polar
question
Polar, Non-aromatic Side Chains
answer
-Serine -Threonine -Asparagine -Glutamine -Cysteine
question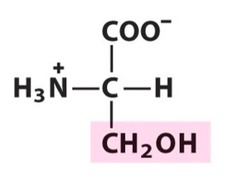
Serine

answer
3 Letter Abbreviation: S 1 Letter Abbreviation: Ser -Highly Polar & Able to participate in H bonding
question
Threonine -
answer
3 Letter Abbreviation: Thr 1 Letter Abbreviation: T -Highly Polar & Able to participate in H bonding
question
Asparagine
answer
3 Letter Abbreviation: Asn 1 Letter Abbreviation: N - Amide side chain
question
Glutamine
answer
3 Letter Abbreviation: Gln 1 Letter Abbreviation: Q -Amide side chain
question
Cysteine -
answer
3 Letter Abbreviation: Cys 1 Letter Abbreviation: C -Thiol side chain - THE ONLY AMINO ACID THAT IS NOT "S"
question
Negatively Charged (Acidic) Side Chains
answer
-Aspartic Acid -Glutamic Acid
question
Aspartic Acid (Aspartate = Deprotonated form)
answer
3 Letter Abbreviation: Asp 1 Letter Abbreviation: D
question
Glutamic Acid (Glutamate = Deprotonated form)
answer
3 Letter Abbreviation: Glu 1 Letter Abbreviation: E
question
Positively Charged (Basic) Side Chains
answer
-Lysine -Arginine -Histidine
question
Lysine
answer
3 Letter Abbreviation: Lys 1 Letter Abbreviation: K
question
Arginine
answer
3 Letter Abbreviation: Arg 1 Letter Abbreviation: R
question
Histidine
answer
3 Letter Abbreviation: His 1 Letter Abbreviation: H
question
Hydrophobic Amino Acids
answer
Long alkyl side chains -Alanine -Valine -Leucine -Isoleucine -Methionine -Tryptophan -Tyrosine -Phenylalanine
question
Hydrophilic Amino Acids
answer
Charged Side chains (+) -Histidine -Arginine -Lysine (-) -Glutamate -Aspartic acid Amides -Asparagine -Glutamine
question
Amphoteric Species
answer
Can either accept or donate a proton
question
pH and pKa relationship
answer
pKa = The pH at which half of the molecules in that substance are protonated Soooooooooo...... [HA] = [A-] [Pronated form] = [Deprotonated form]
question
If the ph is smaller than the pka
answer
A higher percentage of the species will be pronated
question
If the pH is larger than the pKa
answer
A lower percentage of the species will be pronated
question
pKa's of amino acid componenets
answer
The carboxyl group = ~pKa = 2 The amino group = ~pka = 9-10
question
Amino Acids @ low pH's (pH = 1) (<-- Stomach acid)
answer
So the pH is lower than pKas--> protonated (+) Charged!
question
Zwitterions @ Normal pH (~pH=7.4) (<-- Blood)
answer
The carboxyl = Is NOT protonated The amino = IS protonated
question
Amino Acids @ high pH's (pH = 10.5) (;--milk of magnesia)
answer
So the pH is higher than pKas---> un-protonated (-) Charged!
question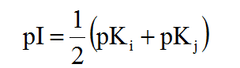
Isoelectric point formula
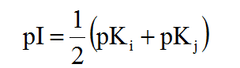
answer
pKi = pKa of NH3 pKj = pKa of COOH If acidic, replace NH3 with R group If basic, replace COOH with R group
question
Amino acid side chains and PI values relationship
answer
Acidic Sides chains = pI values below 6 Basic side chains = pI values above 6
question
Peptides are composed of amino acids subunits called ______
answer
Residues
question
The residues are joined together through ________ ________
answer
Peptide bonds
question
Peptide bonds
answer
-Covalent -Water is a byproduct
question
1° Structure
answer
-Linear arrangement of amino acids -N-terminus --> C-terminus -Encodes all the information for folding at the higher levels of structure -1° Structure can be determined by a technique called sequencing
question
2° Structure
answer
-Result of H-bonding - 2 most common structures - Alpha helix - Beta pleaded sheet AA with proline -RARE in alpha helix -ALTHOUGH, could be the starting residue -RARE in the middle of B sheet also - Found in the turns between he chains
question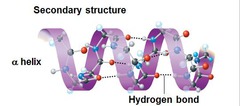
Alpha Helix

answer
- Stabilized: Intramolecular hydrogen bonds between carbonyl's O and and the amide's H four residues down the chain - Side chains point AWAY from the cord - IMPORTANT comp. of keratin
question
Beta pleaded sheet
answer
- can be PARALLEL or ANTIparallel - To accommodate the most hydrogen bonds, this is PLEADED - R groups --> Point ABOVE & BELOW the plane IMPORTANT comp. of Fibroin
question
3° Structure
answer
- The 3D shape Determined by : --Hydrophilic and hydrophobic interactions between the R groups (Phobic = Inside the protein) --H bonds --Disulfide bonds
question
Disulfide Bonds
answer
-When two CYSTEINE molecules are oxidized, they from CYSTINE - These disulfide bonds that are formed from this process create loops in the protein shape
question
Molten Globules
answer
Intermediate stage between secondary and tertiary
question
Solvation layer
answer
A protein is most stable when the hydroPHILIC side chains are on the outside of the protein. This increases entropy, and as a result deems this as spontaneous, and more STABLE
question
4° Structure
answer
-Not all proteins have this -Exists for proteins with more than 1 polypeptide chain -Combination of subunits, and the FUNCTIONAL form of a protein
question
Advanteges to having a 4° Structure
answer
-Stable, because reduces surface area -Reduce the amount of DNA needed to encode the complex -Bring catalytic sites together, allow intermediates from one reaction to be directly shuttled to a second reaction -COOPERTIVITY, or ALLOSTERIC effects
question
Conjugated Proteins
answer
-Function stems from prosthetic groups -Proteins with lipid, carb, or nucleic acid prosthetic groups are lipoproteins, glycoproteins, nucleoproteins
question
Prosthetic groups
answer
-Vitamins -Metals, such as Iron -Heme
question
Heme
answer
Iron group at core Binds to oxygen
question
Denaturation ; Heat
answer
Temp increases kinetic energy. BUT, when temp gets TOO high, the hydrophobic compounds in the middle of the compounds, unfold
question
Denaturation ; Solutes
answer
Solutes can disrupt the disulfide bonds in cystine, resulting in two cysteine residues, and NO quat/tert structure



