atomic structure and nuclear chemistry – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
democritus
answer
all matter is made out of tiny, indivisible particles (atomos). no experimentation, no explanation of chemical behavior.
question
aristotle
answer
did not believe in atoms. All matter is continuous, composed of air, water, fire and earth. his;refs weren't challenged until the age of experimentation in the 18th century.
question
john dalton
answer
proposed an atomic theory based on experimentation, observed that elements combine in simple, whole number ratios, meaning that the smallest piece of the combining elements had to a particle (atom)
question
dalton's atomic theory
answer
1) elements are composed of tiny, indivisible particles called atoms 2) atoms of the same element are identical, and different from atoms of any other element. 3) atoms of different elements can be mixed together, or they can chemically combine with atoms of another elements in simple, whole number ratios to form compounds. (law of Definite Proportions) 4) atoms of one element can never change into atoms of another element.
question
JJ thompson
answer
cathode ray tube experiments. named the particle an electron, did not depend on the type of gas, therefore they were in all elements. Plum pudding. (bulk was positive, electrons dispersed like raisins)
question
cathode ray tube experiment
answer
jj thompson- passed an electric current through gases at a low pressure, the resulting "rays" were attracted to the positive plate, so they must be negatively charged.
question
Robert Millikan
answer
oil drop experiment determined the mass and charge of the electron.
question
ernest rutherford
answer
"father of nuclear physics" proved that alpha radiation was a stream of helium nucleii. gold foil experiment: atoms must be mostly empty space. positive charge and mass concentrated on the nucleus. discovered the proton
question
gold foil experiment
answer
directed a beam of alpha particles at thin gold foil. most went straight through, a few were deflected
question
niels bohr
answer
planetary model of the atom, nucleus was the center and electrons orbit around it. electrons move in discreet energy levels.
question
james chadwick
answer
discovered the neutron
question
quantum theory
answer
electrons do not orbit the nucleus like planets electrons do exist in discreet energy levels, defined by regions of probability it is impossible to determine the exact location of an electron at any time most of the mass is in the nucleus
question
protons
answer
P+, charge: +1, relative mass: 1u, found in the nucleus
question
electrons
answer
E-, charge: -1, relative mass: 0u, found in energy levels ("shells") around the nucleus
question
neutron
answer
N^0, charge: 0, relative mass: 1u, found in the nucleus
question
atomic number
answer
# of protons = # of electrons in a neutral atom
question
mass number
answer
# of protons + # of neutrons (always a whole number bc it counts particles)
question
isotope
answer
atoms of the same element that have different masses. # of protons is the same and # of neutrons is different.
question
protium-1
answer
hydrogen isotope 1 protron, 0 neutrons, mass # 1
question
deuterium-2
answer
1 proton, 1 neutron, mass # 2
question
tritium
answer
1 proton, 2 neutrons, mass # 3
question
hyphen notation
answer
"hydrogen-3"
question
symbol notation
answer
"^3H"
question
relative atomic mass
answer
atomic mass unit (AMU) or u, based on the isotope carbon-12. 1 amu = 1/12 the mass of carbon-12 atom.
question
average atomic mass
answer
a weighted average of al the isotopes of the element. the mass listed on the periodic table. (rarely a whole number)
question
relative abundance
answer
percentage of this isotope found on earth compared to other isotopes of the same element
question
andre henri
answer
discovered radioactivity when he observed that uranium emitted radiation without an external source of energy.
question
marie and pierre curie, becquerel
answer
won the nobel prize in physics
question
radioactivity
answer
the process by which an atomic nuclear gives off radiation
question
radiation
answer
penetrating rays emitted by a radioactive source.
question
radioisotopes
answer
unstable nucleii, loses energy by spontaneously emitting radiation.
question
radioactive decay
answer
an unstable nucleus spontaneously emitting radiation, ne way transmutation
question
nuclide
answer
an atom of an isotope
question
stable nuclides
answer
always have at least as many neutrons as protons odd/odd are unstable except for hydrogen-2, boron-10, lithium-6, and nitrogen-14 all nuclides with atomic number greater than or equal to 84 are unstable
question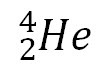
alpha emission
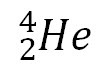
answer
the atom loses an e=alpha particle: helium nuclei 2 protons, 2 neutrons, charge: +2 atomic number decreases by 2 and mass number decrease by 4 don't travel far bc of mass most dangerous if ingested stopped by paper
question
beta emission
answer
fast moving electrons formed when a neutron decomposes into a proton and an electron. ejected electron. atomic number increases by 1, mass stays the same charge: -1 smaller, more penetrating than alpha particles, stop by aluminum foil, thin wood and lead
question
gamma emission
answer
high energy electromagnetic radiation emitted from a nucleus as it changes from an excited state to a ground energy state. no charge or mass extremely penetrating, stopped by lead, concrete
question
radioactive series (decay chain)
answer
the decay of a radioactive isotope into other radioactive isotopes through a series of alpha, beta or gamma emissions. will continue until a stable isotope is found.
question
parent nuclide
answer
heaviest nuclide in the series
question
daughter nuclide
answer
the nuclide produced by the decay of the parent
question
3 natural decay series
answer
uranium-238, uranium-235, and thorium-232
question
uranium-235
answer
first five steps in decay: a, b, a, a, b
question
positron emission
answer
a particle with the mass of an electron but with a positive charge, formed when the proton changes into a neutron. occurs when neutron;proton ratio is too small. atomic number decreases by 1 (1 less proton), mass doesn't change charge: +1 stopped by lead
question
electron capture
answer
an inner orbital electron is captured by the nucleus of its own atom, combines with a proton, and forms and neutron. k-capture. atomic number decreases by 1 (proton to neutron), mass stays the same
question
nuclear transmutation
answer
occurs when a nuclear reaction transforms an isotope of one element into the isotope of another element.
question
nuclear bombardment
answer
occurs when high energy particles (protons, neutrons, alpa particles) bombard the nucleus of an atom
question
particle accelerators
answer
accelerate the bombarding particles to speeds close to the speed of light by use of electromagnetic fields
question
transuranium elements
answer
elements with an atomic number > 92 none occur in nature all are radioactive synthesized in nuclear rectors and particle accelerators
question
half life
answer
time required for half the atoms of a radioactive nuclide to decay symbol: t1/2 the longer the half-life, the more stable the isotope
question
carbon-14
answer
t1/2= 5730 years all living things go through the carbon cycle when an organism dies, the amount of carbon-14 begins to decline as it decays an is not replenished by a living organism beta emission
question
uranium-238
answer
t1/2=4.5x10^9 years
question
decimal fraction of radioactive atoms remaining
answer
1/2n, where n = number of half lives
question
number of half lives elapsed
answer
total time elapsed/length of half-life
question
remaining mass of an isotope
answer
(initial mass of an isotope)x (decimal amount remaining)
question
fusion
answer
occurs when two light nucleic combine to produce a nucleus of heavier mass, accompanied by the release of a large amount of energy. occurs in all stars high temps required products mostly stable possible energy source
question
hydrogen bomb
answer
occur due to the fusion of two deuterium nuclei, initiated by the detonation of a fission bomb.
question
fission
answer
occurs when isotopes are bombarded with neutrons splits the nucleus into smaller fragments releases neutrons and large amount of energy can be controlled heat used to generate steam to drive a turbine, spinning turbine provides electricity.
question
suitable coolant
answer
removes energy given off as heat from the reactor core
question
neutron moderation
answer
water or carbon slows down neutrons so they can be captured by the reactor fuel to continue the chain reaction.
question
neutron absorption
answer
rods made of some type of neutron-absorbing material (usually cadmium) are extended into the rector o pulled out of the reactor to control the rate of fission into=absorb neutron=slows down out=absorb fewer neutron=speeds up
question
methods of detecting radiation
answer
geiger counter scintillation counter film badge
question
geiger counter
answer
primarily beta
question
scintillation counter
answer
coated screen detect radiation particles
question
film badge
answer
several layers of photographic film encased in a holder. detect beta and gamma
question
radioisotopes in medicine
answer
imaging soft-tissue organs special detectors are placed around the body after radioisotopes are administered to detect gamma radiation tomography half life requirements: should use lowest dose with shortest half-life. longer half-lives prevent reducing too often (tumor treatment) tracers
question
tomography
answer
computer analysis of information, 3D image of the organ
question
tracers
answer
iodine-131 : used to check for thyroid cancer cobalt-60 and cesium-137: radiation sources for cancer treatment



