AQA (A) Geography Weather and Climate WML – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Climate
answer
The average weather conditions calculated based on recorded data from the past 30 or more years.
question
Weather
answer
The day-to-day conditions of the atmosphere involving, for example, temperature, cloud cover, wind direction and speed.
question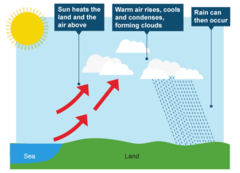
Convectional rainfall

answer
Intense rainfall often in the form of thunderstorms resulting from very high temperatures and rapidly rising cool air.
question
Relief rainfall
answer
Rainfall occuring over high land formed as air forced to rise, cool form clouds and rain.
question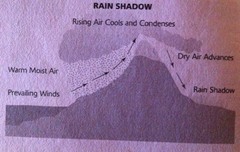
Rain shadow

answer
Area of lowland on the leeward (sheltered) side of highland. This area experiences less rainfall because it recieves dry air following relief rainfall on the highlands. eg. East Anglia
question
Latitude
answer
Determines the geographic North-South position of a point on the earth. 0 Degrees is at the equator and 90 Degrees are at the poles.
question
Prevailing winds
answer
The dominant or most common wind direction
question
Maritime influence
answer
The influence of the sea on climate (often makes an area humid and cloudy)
question
Continentality
answer
The influence of the sea on climate. Inland areas well away from the sea have a continental climate.
question
Altitude
answer
Height above sea level usually given in metres. Impacts on temperatures with 9.8 Degree C drop in temperature per 1000m gain in altitude. Upland areas also usually experience more precipitation.
question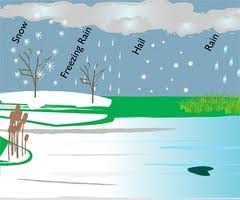
Precipitation

answer
The transfer of water from the atmosphere to the ground, eg. rain and snow.
question
Polar Continental
answer
An air mass formed over northern continental areas, usually cold but dry.
question
Polar Maritime
answer
An air mass formed over northern maritime areas, usually cold and wet.
question
Tropical Continental
answer
An air mass formed over southern continental areas, usually hot and dry.
question
Tropical Maritime
answer
An air mass formed over southern maritime areas, usually hot and wet.
question
Polar air mass
answer
An air mass formed over polar areas, often bitterly cold and bringing snow.
question
Anticyclone
answer
An area of high atmospheric pressure (greater than 1013 mb) usually bringing settled weather.
question
Depression
answer
An area of low atmospheric pressure (lower than 1013 mb).
question
Pressure (atmospheric)
answer
Pressure exerted on the earths surface my the mass of overlying atmosphere, measured in millibars (mb).
question
Front
answer
A boundary between warm and cold air.
question
Warm front
answer
A boundary with cold air ahead of warm air.
question
Cold front
answer
A boundary with warm air ahead of cold air.
question
Occluded front
answer
A front formed when the cold front catches up with the warm front.
question
Warm sector
answer
An area of warm air between a warm front and a cold front.
question
Frost
answer
The result of water vapour condensing and freezing when the temperature of the ground or the air drops below 0 degrees C.
question
Fog
answer
Water that has condensed close to the ground to form a dense low cloud with poor visibility.
question
Extreme weather
answer
A weather event which is record breaking, or significantly different from the average. eg. Flash flood or severe snowstorm.
question
Global warming
answer
An increase in average world temperatures as a result of the increase in greenhouse gasses in the atmosphere (eg. carbon dioxide, methane, CFC's and nitrous oxide). Brought about by human activities eg. burning fossil fuels or landfill sites and animal agriculture.
question
Climate change
answer
Long term changes in the climate such as cooling leading to an ice age, or the current trend of global warming.
question
Flash flood

answer
A sudden, violent flood that occurs within a few hours, or even minutes, of a storm.
question
Pleistocene period
answer
a geological time period lasting from about 2 million years ago until 10,000 years ago. Sometimes this is referred to as the Ice Age
question
Glacial retreat
answer
when glaciers melt, they appear to retreat up the valley from which they flow
question
Ice core
answer
A tube of ice cut from an ice cap. These can be used to sample gasses trapped in bubbles in the ice and from this data, calculate climate data for the past 400,000 years.
question
Ice age

answer
A period during which the world was dramatically colder than it is now, during which ice caps and glaciers would have covered huge swathes of the world.
question
Interglacial
answer
A period between ice ages, these are usually quite short. The current interclacial began around 10,000 years ago.
question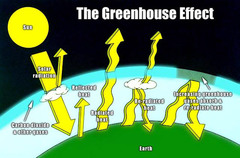
Greenhouse effect

answer
The blanketing effect of the atmosphere in retaining heat given off from the earths surface.
question
Short wavelength radiation
answer
Radiation of a short wavelength which originated from the sun and has a warming effect on the ground.
question
Long wavelength radiation
answer
Radiation of a long wavelength which originates from the earth as it gives off heat.
question
Enhanced greenhouse effect
answer
The increased greenhouse effect as a result of the greenhouse gasses added to the atmosphere by humans.
question
Greenhouse gases
answer
Gases which absorb long wavelength radiation and lead to a warming of the atmosphere. eg. carbon dioxide, methane, CFC's and nitrous oxides.
question
Recycling
answer
Using materials multiple times rather than discarding them. eg. glass and aluminium.
question
Congestion charging

answer
Charging vehicles to enter certain areas of cities eg. London, with the aim of reducing the use of vehicles. London currently charges £10 per day.
question
Kyoto Protocol
answer
An international agreement to try to reduce carbon emissions from industrialised countries.
question
Carbon credits
answer
A means of trading carbon between organisations or countries in order to meet an overall target.
question
Hurricane
answer
A severe storm that develops over tropical oceans and whose strong winds of more than 120 km/h spiral in toward the intensely low-pressure storm center
question
Eye (of the storm)
answer
The center of a hurricane- a core of warm, calm air with low pressure and light winds
question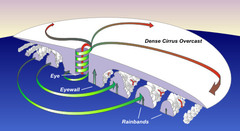
Eye wall

answer
The strongest winds of a hurricane surrounding the eye.
question
Track
answer
The path or course of a hurricane
question
Carbon Dioxide
answer
Greenhouse gasses formed by the burning of hydrocarbons eg. coal, oil and gas.
question
Methane
answer
A greenhouse gas which is more potent than carbon dioxide and is formed by anaerobic decomposition in landfill sites and by cattle.
question
Nitrous Oxide

answer
A very potent greenhouse gas (300 times more effective than carbon dioxide) which is created by car exhausts, power stations, agricultural fertilisers and sewage treatment.



