AP Biology: Genetics – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Gregor Mendel
answer
Austrian monk who conducted a quantitative study of inheritance using garden peas Why garden peas? alternate traits, true breeders, small and easy to grow, fertilization
question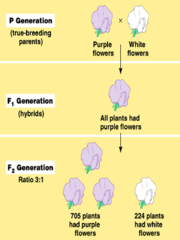
How did Mendel conduct his experiments?

answer
*1.* allowed plants to self fertilize for several generations- produced true breeders *2.* crossed true breeders *3.* allowed F1 generation to self fertilize *4.* counted numbers of offspring
question
What did Mendel reason for his experiments?
answer
*--*"factors" caused the traits *--*each organism had two factors for a trait *--*two factors for a trait came from parents *--*gametes contain only one factor from a parent *--*gametes have equal chance of having either factor
question
allele
answer
alternate form of a gene Ex. gene = flower color allele = purple or white
question
character
answer
heritable feature that varies among individuals
question
trait
answer
variant of a character
question
locus
answer
location of gene on chromosome
question
dominant
answer
allele that is expressed if present Ex. RR, Rr, rR
question
recessive
answer
allele that is "masked" by dominant **only seen if dominant is NOT present Ex. rr
question
genotype
answer
an organism's genetic make-up for a trait Ex. RR, Rr, rR, rr
question
homozygous
answer
having two identical alleles for a trait; purebred Ex. RR, rr
question
heterozygous
answer
having two different alleles for a trait; hybrid Ex. Rr, rR
question
phenotype
answer
a physical trait on an organism that can be "seen" Ex. blue eyes, green eyes
question
How do gametes play a role in genetics?
answer
Each gamete carries one allele. **Alleles come from parents' sex cells.
question
law of segregation
answer
alleles separate in meiosis so that only one allele from each pair is present in each gamete **random chance which allele goes into a gamete **results in genetic variation in gametes and offspring **ON DIFFERENT CHROMOSOMES
question
law of independent assortment
answer
alleles of one trait sort independently of the alleles of other traits **Exception: if genes are on the same chromosome, then they'll always be found together. **results in genetic variation in gametes and offspring **ON DIFFERENT CHROMOSOMES
question
law of dominance
answer
one of the alleles for a pair of inherited traits will be dominant and the other recessive
question
Punnett Square
answer
device used to predict possible outcome of a genetic cross *1.* List parents' genotypes *2.* Draw box *3.* Write allele(s) parents could donate to a gamete along top and side *4.* Combine alleles (gametes) into individual boxes
question
Multiplication Rule
answer
("AND" rule) - use when trying to find probability of 2 or more separate events occurring together.
question
Addition Rule
answer
("OR" rule) - use when trying to find probability of ONE of two or more mutually exclusive events occurring together.
question
monohybrid cross
answer
cross dealing with one trait
question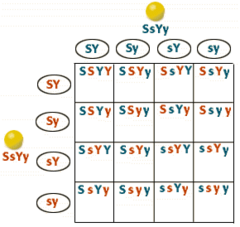
dihybrid cross

answer
cross dealing with two traits
question
Ratio for a dihybrid cross between 2 heterozygous parents
answer
9:3:3:1
question
test cross
answer
process used to determine the genotype of an unknown parent *1.* cross "unknown" parent with a recessive parent *2.* examine results >If any offspring show recessive trait, unknown parent was heterozygous.
question
incomplete dominance
answer
neither allele is completely dominant over the other **results in mixing *--*R = red, W = white *--*RR = red, WW = white *--*RW = pink
question
codominance
answer
more than one dominant allele **both expressed if present *--*B = black stripes, Br = brown stripes *--*BB = black stripes, BrBr = brown stripes *--*BBr = black and brown stripes
question
multiple alleles
answer
more than two alleles possible for a trait **organism only contains 2 Ex: human hair color Ex: blood type >AA or Ao = Type A >BB or Bo = Type B >AB = Type AB >oo = Type O
question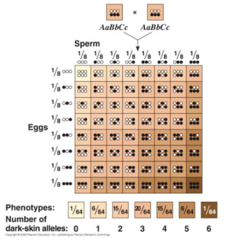
polygenic inheritance

answer
traits influenced by more than one gene Ex. human skin color, human height **occurs when multiple genes determine the phenotype of a trait
question
multifactorial
answer
when one or more genes + environmental factors influence a trait or disease **diabetes
question
pedigree
answer
family history tracing a particular trait Used to determine the pattern of inheritance: 1. Dominant/recessive 2. Autosomal/sex-linked 3. Monogenic or polygenic
question
sex linked genes
answer
genes carried on the sex chromosomes **usually the X chromosome Ex. colorblindness, hemophilia
question
glycoproteins
answer
on the surface determine blood type and is important in transfusions and transplants
question
codominant blood types?
answer
type AB
question
universial donor
answer
O negative
question
universal recipiant
answer
AB +
question
Rh factor
answer
another type of antigen which can be either present (+) or absent ( - ) on RBCs... **In general, Rh- blood is given to Rh- patients and Rh+ blood or Rh- blood may be given to Rh+ patients.
question
X-INACTIVATION...
answer
IN FEMALE MAMMALS **Most of one X chromosome in each cell is randomly inactivated by addition of methyl groups to DNA. **Becomes a condensed structure called a BARR BODY • **Thus males and females have same effective dose of most X-linked genes
question
EXTRANUCLEAR GENES
answer
**Exhibit a non-Mendelian pattern of inheritance **Extranuclear genes are found in cytoplasmic organelles (plastids and mitochondria) **Inherited from mother (in egg's cytoplasm)
question
Barr bodies
answer
inactivated X chromosomes found only in females (kind of like a "back-up" X chromosome) XX
question
sex linked traits
answer
traits determined by genes on the sex chromosomes **most are recessive
question
autosomes
answer
the 22 pairs of "non-sex" chromosomes
question
sex chromosomes
answer
the one pair of chromosomes that determine gender **two types: X and Y XX = female XY = male
question
Why does the almighty Y chromosome determine gender?
answer
contains SRY gene which causes testosterone to develop, creates a male
question
Why do sex linked traits show up in males much more often than females?
answer
males have only one X-sex chromosome, so they show the allele they have, and females have 2 X-sex chromosomes, so they have to be homozygous to show the trait
question
karyotype
answer
a picture of matched chromosomes (arranged in pairs by size and shape) 1. use blood cells 2. add chemicals to begin division and then stop in metaphase 3. chromosomes isolated and stained 4. chromosomes photographed, cut out, arranged in homologous pairs
question
genetic disorders
answer
these are due to either a "disease" gene or an incorrect number of chromosomes
question
genetic diseases
answer
these are caused by alleles but the chromosome number is correct
question
Autosomal genetic diseases:
answer
cystic fibrosis sickle cell anemia Huntington's
question
Sex-linked genetic diseases:
answer
hemophilia color-blindness muscular dystrophy
question
non-disjunction
answer
failure of chromosomes to separate during meiosis **results in abnormal chromosome # in egg or sperm, causes genetic disorders
question
How are autosomal genetic disorders caused?
answer
when autosomes fail to separate
question
trisomy
answer
genetic disorder in which there are extra autosomes Ex. Trisomy 21 (Down Syndrome)
question
monosomy
answer
genetic disorder in which there are missing autosomes **does not occur because you need all autosomes to develop properly
question
How are sex-linked genetic disorders caused?
answer
when sex chromosomes fail to separate
question
Sex chromosome disorders:
answer
Turner's Syndrome >sexually immature female Klinefelter's Syndrome >male w/ female characteristics XXX - normal female XYY - normal male OY - does not exist
question
linked genes
answer
genes found on the same chromosome usually inherited as a linked unit and associated with genes on the autosomes
question
Some traits are usually seen together (blonde hair, blue eyes). Why do variations of the expected combination occur?
answer
Variations of this expected combination occur due to crossing-over during meiosis.
question
How do you determine whether traits are linked?
answer
*--*Perform a cross with a parent recessive for both traits *--*Examine offspring *--*Examine the ratio of observed versus expected offspring
question
parental dominant
answer
offspring with same dominant traits as one of the parents
question
parental recessive

answer
offspring with same recessive traits as one of the parents
question
non-parental
answer
trait combination not seen in either parent
question
What affects how often genes cross-over?
answer
the distance the genes are from each other *--*genes closer together cross over less frequently *--*genes farther apart cross over more frequently **Crossing over frequency also affected by how close gene is to centromere
question
recombination frequency
answer
frequency in which a single chromosomal crossover takes place between two genes during meiosis **measure of genetic linkage used in the creation of a genetic linkage map (genes occurring together)
question
recombination mapping
answer
mapping of linkage groups with one map unit representing 1% recombination
question
null hypothesis
answer
there is no statistically significant difference between observed and expected results
question
autosomal dominant
answer
only need one dominant allele to be affected
question
autosomal recessive
answer
need two recessive alleles to be affected
question
x linked recessive
answer
females need two recessive alleles, males only need one allele to be affected
question
linked genes
answer
Genes located near each other on the same chromosome tend to be inherited together in genetic crosses
question
Genetic Recombination
answer
Production of offspring with combinations of traits that differ from those found in either parent.



