Marketing Management Ch 1 & 2 – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
production concept
answer
The idea that consumers will favor products that are available and highly affordable and that the organization should therefore focus on improving production and distribution efficiency :holds that consumers prefer products that are widely available and inexpensive. Managers concentrate on achieving high production efficiency, low costs, and mass distribution. (business in China with cheap labor as example)
question
Product Concept
answer
The idea that consumers will favor products that offer the most quality, performance, and features and that the organization should therefore devote its energy to making continuous product improvements (proposes that consumers favor products offering the most quality, performance or innovative features. However, a new or improved product will not be successful unless it's priced, distributed, advertised and sold properly.)
question
Selling Concept
answer
The idea that consumers will not buy enough of the firm's products unless the firm undertakes a large-scale selling and promotion effort
question
Marketing Concept
answer
A philosophy of conducting business that is based on the belief that all business activities should be aimed toward satisfying consumer wants and needs while achieving company goals. (holds that the key to achieving organizational goals is being more effective than competitors in creating, delivering, and communicating superior customer value to your target markets. Selling focuses on the needs of seller, marketing focuses on the needs of the buyer.)
question
Holistic Marketing Concept
answer
based on the development, design and implementation of marketing programs, processes and activities that recognize their breadth and interdependencies. "everything matters" can be thought of as an everything "stew" of marketing.
question
Marketing
answer
An organizational function and a set of processes for creating, communicating, and delivering value to customers and for managing customer relationships in ways that benefit the organization and its stakeholders :Marketing: identifying and meeting human and social needs => "meeting needs profitably"
question
Relationship Marketing
answer
Developing and maintaining effective customer relationships. Links organization to its individual customers/clients, employees, suppliers and other partners for their mutual long-term benefits :aims to build mutually satisfying long-term relationships with key constituents (customers, employees, marketing partners, and members of the financial community) in order to earn and retain their business.
question
Four P's
answer
product, place, promotion, and price, which together make up the marketing mix
question
Marketing Mix
answer
A unique blend of product, place, promotion, and pricing strategies designed to produce mutually satisfying exchanges with a target market. A combination of the product itself, the price of the product, the place where it is made available, and the activities that introduce it to consumers that creates a desired response among a set of predefined consumers.
question
Treating employees as customers and developing systems and benefits that satisfy their needs.
answer
People (The four P's of Modern Marketing Management )
question
Modern Marketing Management, the four p's
answer
people, processes, programs, performance
question
Creativity, discipline, and structure brought to marketing management
answer
The 2nd P of the 4 of Modern Marketing Management: Processes
question
Processes
answer
The 2nd P of Modern Marketing Management
question
People
answer
The first P of Modern Marketing Management
question
Programs
answer
The third P of Modern Marketing Management
question
Performance
answer
The fourth P of Modern Marketing Management
question
All firm's consumer-directed activities
answer
Programs (the four P's of Modern Marketing Management)
question
Captures the range of possible outcome measures that have financial and non financial implications.
answer
Performance, (the four P's of Modern Marketing Management)
question
Integrated Marketing
answer
is the practice of unifying all marketing communication messages and tools as well as the messages from the marketing mix decisions so that they send a consistent message promoting the brands strategy. For example, when a hospital buys an MRI from General Electric's Medical Systems division, it expects good installation, maintenance, and training services to go with the purchase. Integrated marketing is similar. It form of communication reinforces each other: radio, television, internet, print, ect.
question
Marketing Plan
answer
A document that describes the marketing environment, outlines the marketing objectives and strategy, and identifies who will be responsible for carrying out each part of the marketing strategy. : central instrument for directing and coordinating the marketing effort. Contains: executive summary, table of contents, situation analysis, marketing strategy, and financial projections.
question
Strategic Marketing Plan
answer
An approach whereby an organization allocates its marketing mix resources to reach its target markets : lays out the target markets and the firm's value proposition based on a analysis of the best market opportunities.
question
Tactical Marketing Plan
answer
How you implement your strategic market plan specifies the marketing tactics, like product features, promotion, merchandising, pricing etc.
question
Corporate Headquarters' Planning Activities
answer
1. Define Corporate's Mission 2. Establishing SBU's or Strategic Business Units 3. Assigning Resources to Each Strategic Business Unit 4. Assessing Growth Opportunities including planning new business, downsizing and terminating older businesses.
question
Strategic Business Units
answer
A division of the firm itself that can be managed and operated somewhat independently from other divisions and may have a different mission or objectives • Single business or a collection of related businesses that can be planned separately from the rest of the company • Has its own set of competitors • Has a manager responsible for strategic planning and profit performance.
question
Intensive Growth
answer
The increase of goods and services produced when business firms use EXISTING factors of production with greater efficiency
question
Integrative Growth
answer
growth achieved through backward integration (acquiring a supplier), forward integration (acquiring a distributor), or horizontal integration (acquiring a competitor)
question
Diversification Growth
answer
Concentric diversification strategy, Horizontal diversification strategy, conglomerate diversification strategy
question
Concentric Diversification Strategy
answer
A strategy used to add new businesses that produce related products or are involved in related markets and activities.
question
Horizontal Diversification Strategy
answer
A diversification growth strategy that involves seeking products that are technologically unrelated to a company's own products or business but appeal to the same target market
question
Conglomerate Diversification Strategy
answer
A strategy used to add new businesses that produce unrelated products or are involved in unrelated markets and activities.
question
Mission Statement
answer
A short, specific written statement of the reason a business exists and what it wants to achieve. : provides a shared sense of purpose, direction and opportunity. Characteristics of mission statement: Focus on a limited # of goals Stress the company's major policies and values Define the major competitive spheres Take a long-term view Short, memorable, and meaningful.
question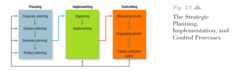
The Strategic Planning, Implementation, and Control Processes.

answer
The marketing plan is the central instrument for directing and coordinating the marketing effort. It operates at two levels: strategic and tactical. The strategic marketing plan lays out the target markets and the firm's value proposition, based on an analysis of the best market opportu- nities. The tactical marketing plan specifies the marketing tactics, including product features, promotion, merchandising, pricing, sales channels, and service. The complete planning, imple- mentation, and control cycle of strategic planning is shown in Figure 2.1.
question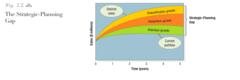
The Strategic Planning Gap.

answer
Figure 2.2 illustrates this strategic-planning gap for a major manufacturer of blank compact disks called Musicale (name disguised). The lowest curve projects the expected sales over the next five years from the current business portfolio. The highest describes desired sales over the same period. Evidently, the company wants to grow much faster than its current businesses will permit. How can it fill the strategic-planning gap? The first option is to identify opportunities for growth within current businesses (intensive opportunities).
question
The Business Unit Strategic-Planning Process.

answer
The business unit strategic-planning process consists of the steps shown in Figure 2.3. We examine each step in the sections that follow.
question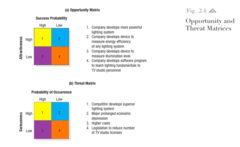
Opportunity and Threat Matrices.

answer
In the opportunity matrix in Figure 2.4 (a), the best marketing opportunities facing the TV-lighting-equipment company appear in the upper-left cell (#1). The opportunities in the lower-right cell (#4) are too minor to consider. The opportunities in the upper-right cell (#2) and the lower-left cell (#3) are worth monitoring in the event that any improve in attrac- tiveness and potential. An environmental threat is a challenge posed by an unfavorable trend or development that, in the absence of defensive marketing action, would lead to lower sales or profit. Figure 2.4 (b) illus- trates the threat matrix facing the TV-lighting-equipment company. The threats in the upper-left cell are major, because they have a high probability of occurrence and can seriously hurt the company. To deal with them, the company needs contingency plans. The threats in the lower-right cell are minor and can be ignored. The firm will want to carefully monitor threats in the upper-right and lower-left cells in the event they grow more serious.
question
Dog (Low Market Share, Low Growth Rate)
answer
Dogs - Dogs have low market share and a low growth rate and thus neither generate nor consume a large amount of cash. However, dogs are cash traps because of the money tied up in a business that has little potential. Such businesses are candidates for divestiture.
question
Question Marks aka Problem Child (High Growth Rate, Low Market Share)
answer
Question marks - Question marks are growing rapidly and thus consume large amounts of cash, but because they have low market shares they do not generate much cash. The result is a large net cash comsumption. A question mark (also known as a "problem child") has the potential to gain market share and become a star, and eventually a cash cow when the market growth slows. If the question mark does not succeed in becoming the market leader, then after perhaps years of cash consumption it will degenerate into a dog when the market growth declines. Question marks must be analyzed carefully in order to determine whether they are worth the investment required to grow market share.
question
Stars (High Market Share, High Growth Rate)
answer
Stars - Stars generate large amounts of cash because of their strong relative market share, but also consume large amounts of cash because of their high growth rate; therefore the cash in each direction approximately nets out. If a star can maintain its large market share, it will become a cash cow when the market growth rate declines. The portfolio of a diversified company always should have stars that will become the next cash cows and ensure future cash generation.
question
Cash Cows (High Market Share, Low Growth Rate)
answer
Cash cows - As leaders in a mature market, cash cows exhibit a return on assets that is greater than the market growth rate, and thus generate more cash than they consume. Such business units should be "milked", extracting the profits and investing as little cash as possible. Cash cows provide the cash required to turn question marks into market leaders, to cover the administrative costs of the company, to fund research and development, to service the corporate debt, and to pay dividends to shareholders. Because the cash cow generates a relatively stable cash flow, its value can be determined with reasonable accuracy by calculating the present value of its cash stream using a discounted cash flow analysis.
question
BCG Matrix
answer
X AXIS: Market Share Y AXIS: Growth Rate Q1: Star - High Market Share, High Growth Rate Q2: Question Mark/Problem Child - Low Market Share, High Growth Rate Q3: Dog - Low Market Share, Low Growth Rate Q4: Cash Cow - High Market Share, Low Growth Rate
question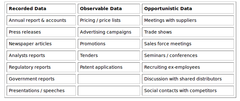
Sources of Competitive Information

answer
• Recorded data: this is easily available in published form either internally or externally. Good examples include competitor annual reports and product brochures; • Observable data: this has to be actively sought and often assembled from several sources. A good example is competitor pricing; • Opportunistic data: to get hold of this kind of data requires a lot of planning and organisation. Much of it is "anecdotal", coming from discussions with suppliers, customers and, perhaps, previous management of competitors.
question
Competition (as Environmental Force)
answer
Competition: competition refers to the numbers of similar competitive product brands' marketers in your industry, their size and market capitalizations. You as a marketer might not have direct influence on them, but it's important that you monitor their activities, and then design effective strategies using your controllable variables.
question
Governmental policies (as Environmental Force)
answer
Governmental policies: the government policies refers to the laws and legality that guilds the land, they go a long way to affect your business operations as a marketer. For instance, government restriction on the importation of a particular product might hinder the marketers playing in that particular field.
question
Natural forces (as Environmental Force)
answer
Natural forces: this refers to the physical environment, it comprises of the available or lacks of natural resources that can vacillated or hinder your production output.
question
social and cultural forces (as Environmental Force)
answer
social and cultural forces: the social and cultural forces refers to the structure and dynamics of individuals and groups and their behaviors, believes, thought patterns and lifestyles, friendship etc many of this trends goes a long way to affect your marketing operations.
question
Demographic factors (as Environmental Force)
answer
Demographic factors: demography refers to study of people, such as their age, sex, marital status, occupation, family size etc. Though, demography is uncontrollable because you cannot control the sex, age, marital status in your external environment, but accurate forecast of it goes a long way to enabling you as a marketer forecast future trend and consumptions of your product.
question
Technological changes (as Environmental Force)
answer
Technological changes: technology post much challenges to marketers, it affects the kind of product that you as a marketer can offer, For instance, technology have changed products like typewriting machines into a more proficient computer systems. You cannot stop the advancement of technology, but you can learn to adapt to it changes.



