OAT Organic Chemistry Review – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Nomenclature:
answer
-How many carbons? -1 =Meth. -2 =Eth. -3 =Prop. -4 =But. -5 =Pent. -6 =Hex. -7 =Hept. -8 =Oct. -9 =Non. -10 =Dec.
question
Torsional Strain:
answer
-Electrons in bonds "push" away from each other.
question
Steric Hindrance:
answer
-Functional groups interfere with each other.
question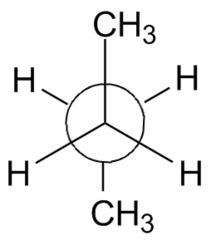
Staggered (anti):

answer
*Most favored conformation.
question
Totally Eclipsed:
answer
*Least favored conformation.
question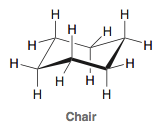
Chair Conformation:

answer
*Chair is more stable than boat.
question
Axial vs. Equatorial:
answer
-A single substituted group will always prefer to be in the equatorial position.
question
Axial vs. Equatorial (cont):
answer
-Between two substituents, the one with the larger electron cloud will be equatorial.
question
Ring Strain:
answer
-Instability of a ring due to angle strain or conformational strain. *Ideal angle is 109.5 degrees.
question
Fischer Projections:
answer
-Horizontal = out of the screen. -Vertical = into the screen.
question
Chiral Carbon:
answer
-A central carbon bonded to four different things.
question
Designating the Molecule as R or S:
answer
-(R) is clockwise. -(S) is counterclockwise.
question
Optical Activity:
answer
-R and S chiral centers rotate passing light in opposite direction.
question
Racemic Mixture:
answer
-A solution with equal amounts of two enantiomers has no net effect on rotating light. *NO net optical activity.
question
Meso Compounds:
answer
-have an internal plane of symmetry so it does not have enantiomers. -No optical activity. -Considered achiral.
question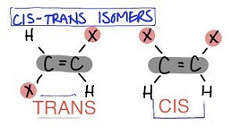
Cis-Trans Isomers:

answer
-Cis are on the same side of the double bond. -Trans are on the opposite side of the bond.
question
E-Z Isomers:
answer
-(Z) are on the same side of the double bond. -(E) are on the opposite side of the double bond.
question
Nucleophile:
answer
-Loves positive charge. -Negative, or electron-rich.
question
Electrophile:
answer
-Loves negative charge. -Positive, or electron-poor.
question
Leaving Groups:
answer
-Carries negative charge with it, therefore stabilizing negative charge halogens (Cl-, Br-, I-).
question
Substitution SN1:
answer
-1 stands for 1 thing only that matters: CARBOCATION. -SN1 stands for Unimolecular Nucelophilic Substitution. -Mechanism: Carbocation formation is rate determining step. -Kinetics: Rate = k[RX]. (1st order). -Substrates: 3 > 2 > 1 > CH3. -Nucleophiles: Does not require strong. -Leaving Groups: Good LG required (ex. Br-). -Solvents: POLAR PROTIC. -Stereochemistry: Not conserved.
question
Substitution SN1:
answer
-Leaving Group leaves. New nucleophile comes in.
question
Protic Solvent:
answer
-Able to form hydrogen bonds OR donate a proton. *Protic solvents form hydrogen bonds with the leaving group so it stays gone.
question
Substitution SN2:
answer
-Bimolecular Nucleophilic Substitution. -Mechanism: Concerted backside attack. -Kinetics: Rate = k[RX][Nu].m (2nd Order). -Substrate: CH3 > 1 > 2. -Nucleophile: Strong Nu required. (Ex. NaOH). -Leaving Groups: Good LG required. -Solvent: Polar Aprotic.
question
Substitution SN2:
answer
-Leaving Group refuses to leave. Nucleophile comes in and prevails over the LG, which leaves.
question
Aprotic Solvent:
answer
-Unable to form hydrogen bonds, avoids H-bonding nucleophile.
question
Elimination E1:
answer
-Elimination reaction creates a double bond. -First step of E1 and SN1 are the same. The second step is different. (Double bond formation for E1) (Substitution for SN1).
question
Elimination E1:
answer
-Mechanism: Carbocation formation is rate determining step. -Kinetics: Rate = k[RX]. -Substrates: 3 > 2. -Bases: Does not require strong. -Leaving Groups: Good LG. -Solvent: Protic. -Stereochemistry = most substituted product favored. -Competition: E1 and SN1 happen at the same time, but E1 is favored by heat. -
question
Elimination E2:
answer
-Mechanism: Concerted loss of H+ and LG. -Kinetics: Rate = k[RX][base]. (2nd order). -Substrates: 1, 2 or 3 but not CH3. -Bases: Strong base required. Large/bulky prevents SN2. -Leaving Groups: Good LG. -Solvents: aprotic is best. But the conjugate acid is used mostly. -Stereochemistry: Antiperiplanar. -SN2 and E2 occur together. SN2 inhibited with highly substituted substrates and bulky bases.
question
what is a tie breaker for right to left?
answer
alphabet and most substitutes
question
cyclo number
answer
least number and alphabet for tie
question
sec-butyl
answer
4 carbon
question
isobuyl
answer
y tail
question
central carbon TEE
answer
tert-butyl
question
cyclobutyl
answer
branch with a circle



