Pearson Anatomy & Physiology (Tenth Edition) Ch. 1 – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Anatomy
answer
The study of body structure
question
Physiology
answer
Study of function
question
Macroscopic Anatomy
answer
Study of relatively large structures (ex organs and organ systems)
question
Microscopic Anatomy
answer
deals with structures too small to be seen with the naked eye
question
Cytology
answer
Study of the cells
question
Histology
answer
study of tissues
question
Embryology
answer
study of embryos and their development
question
Renal Physiology
answer
concerns kidney function and urine production
question
Neurophysiology
answer
Explains the working of the nervous system
question
Cardiovascular Physiology
answer
examines the operation of the heart and blood vessels
question
Chemical level
answer
atoms and molecules, the simplest level of the structural hierarchy
question
Cellular Level
answer
Cells are made up of molecules
question
Tissue Level
answer
Tissues are groups of similar cells that have a common function.
question
Organ Level
answer
Made up of different types of tissues
question
Organ System Level
answer
a group of organs with similar or common function
question
Organismal level
answer
Largest level of organization. All the systems of the body make up an organism.
question
Maintaining Boundaries
answer
separation between internal and external environments.
question
Movement
answer
Includes the activities promoted by the muscular system.
question
Contractility
answer
the muscle cell's ability to move by shortening
question
Responsiveness
answer
ability to sense and respond to stimuli
question
Digestion
answer
breakdown of ingested foodstuffs to simple molecules that can be absorbed into the blood.
question
Metabolism
answer
all of the chemical processes that build up or break down materials
question
Catabolism
answer
breakdown of molecules
question
Anabolism
answer
synthesis of molecules
question
Excretion
answer
Process by which metabolic wastes are eliminated from the body
question
Reproduction
answer
At the cellular level- division of cells At the organismal level- production of offspring
question
Growth
answer
Increase in size or body part.
question
Survival Needs
answer
nutrients, oxygen, water, body temperature, atmospheric pressure
question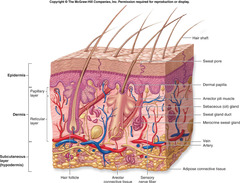
Integumentary System

answer
Forms the external body covering, and protects deeper tissue from injury. Synthesizes vitamin D, and houses cutaneous (pain, pressure, etc.) receptors and sweat and oil glands.
question
Skeletal System
answer
Protects and supports body organs, and provides a framework the muscles use to cause movement. Blood cells are formed within bones. Bones store minerals.
question
Muscular System
answer
Allows manipulation of the environment, locomotion, and facial expression. Maintains posture, and produces heat.
question
Nervous System
answer
As the fast acting control system of the body, it responds to internal and external changes by activating appropriate muscles and glands.
question
Endocrine System
answer
Glands secrete hormones that regulate processes such as growth, reproduction, and nutrient use (metabolism) by body cells.
question
Cardiovascular System
answer
Blood vessels transport blood, which carries oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, wastes etc. The heart pumps blood.
question
Lymphatic System
answer
Picks up fluid leaked from blood vessels and returns it to blood. Disposes of debris in the lymphatic stream. Houses white blood cells (lymphocytes) involved in immunity.
question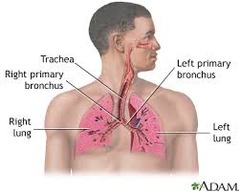
Respiratory System

answer
Keeps blood constantly supplied with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide.
question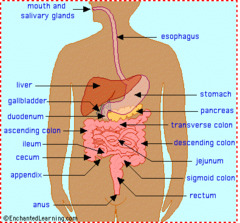
Digestive System

answer
Breaks down food into absorbable units that enter the blood for distribution to body cells. Indigestible foodstuffs are eliminated as feces.
question
Urinary System
answer
Eliminates nitrogenous wastes from the body. Regulates water, electrolyte, and acid-base balance of the blood.
question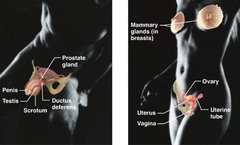
Reproductive System

answer
Overall function is production of offspring.
question
Nutrients
answer
Chemicals for energy and cell building ex: carbohydrates, proteins, fats, minerals, and vitamins
question
Water
answer
Most abundant chemical in the body; provides the watery environment needed for chemical reactions.
question
Homeostasis
answer
ability to maintain relatively stable internal conditions even though the outside world changes continuously.
question
Receptor
answer
is some type of sensor that monitors the environment and responds to changes, called stimuli, by sending information to the control center. Input is sent along afferent pathway to control center.
question
Control Center
answer
determines the set point, which is the level or range at which a variable is to be maintained. It also analyzes the input it receives and determines the appropriate response.
question
Effector
answer
Receives output from control center through the efferent pathway. Provides the means to respond. Response reduces stimulus or enhances it.
question
Oxygen
answer
Essential for release of energy. Tasteless, odorless, colorless gas essential for human respiration
question
Negative Feedback
answer
feedback that reduces the output of a system
question
Positive Feedback
answer
Feedback that tends to magnify a process or increase its output.
question
Homeostatic Imbalance
answer
a disturbance in homeostasis resulting in disease
question
Axial
answer
Makes up the main axis of our body, includes the head, neck, and trunk.
question
Appendicular
answer
Includes the limbs which are attached to the body's Axis
question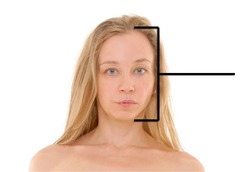
Cephallic

answer
Head
question
Frontal
answer
Forehead
question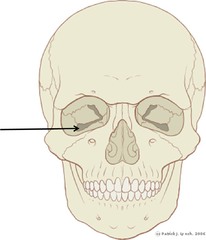
Orbital

answer
Eye
question
Nasal
answer
Nose
question
Buccal
answer
Cheek
question
Otic
answer
Ear
question
Oral
answer
Mouth
question
Mental
answer
Chin
question
Occipital
answer
back of head
question
Nuchal
answer
back of neck
question
Cervical
answer
Neck
question
Acromial

answer
point of shoulder
question
Brachial
answer
Arm
question
Antecubital
answer
front of elbow
question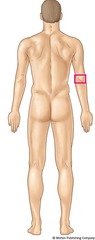
Olecranal

answer
Elbow
question
Antebrachial
answer
Forearm
question
Carpal
answer
Wrist
question
Metacarpal
answer
Hand
question
Palmer
answer
Palm of the hand
question
Pollex
answer
Thumb
question
Digital
answer
Fingers or toes
question
Thoracic
answer
pertaining to the chest
question
Sternal
answer
Sternum
question
Axillary
answer
Armpit
question
Mammary
answer
breast
question
Anterior
answer
Ventral, located towards the front of the body
question
Posterior
answer
Dorsal, back of the body
question
Scapular
answer
shoulder blade
question
vertebral
answer
spine
question
Lumbar
answer
lower back
question
Sacral
answer
Tailbone
question
Gluteal
answer
Buttock
question
Perineal
answer
Region between the anus and external genitalia
question
Umbilical
answer
central region near the navel
question
Inguinal
answer
groin
question
Pubic
answer
genital region
question
Coxal
answer
Hip
question
Femoral
answer
Thigh
question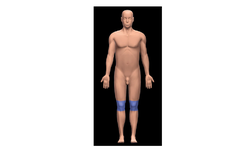
Patellar

answer
Knee
question
Popliteal
answer
Back of knee
question
Crural
answer
shin
question
Sural
answer
calf
question
Fibular
answer
lateral (side) part of leg
question
Manus
answer
pertaining to the hand
question
Pedal
answer
Pertaining to the foot
question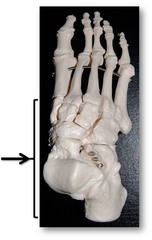
Tarsal

answer
ankle
question
calcaneal
answer
heel
question
Metatarsal
answer
top of foot
question
plantar
answer
sole of foot
question
Hallux
answer
big toe
question
Superior
answer
cranial, above, higher on the body, nearer to the head
question
Inferior
answer
caudal, lower on the body, farther from the head
question
Medial
answer
Toward the midline of the body
question
Lateral
answer
Away from the midline of the body
question
Intermediate
answer
between a more medial and a more lateral structure. ex: the collar bone is intermediate between the breastbone and shoulder.
question
Proximal
answer
Nearer to the trunk of the body. Closer to the point of attachment Ex: elbow is _________ to wrist
question
Distal
answer
Farther from the trunk of the body Farther from the point of attachment Ex: knee is _______to thigh
question
Superficial
answer
external, toward or at the body surface
question
Deep

answer
Away from the body surface; more internal
question
Sagittal Plane
answer
vertical division of the body into right and left portions
question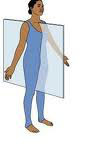
Midsagittal plane

answer
divides body into equal left and right parts
question
Parasagittal plane
answer
vertical plane that divides into UNEQUAL left and right parts
question
Frontal plane
answer
coronal, vertically divide the body into anterior and posterior parts
question
Transverse plane
answer
A horizontal plane that divides the body into superior and inferior sectionsD
question
Dorsal body cavity
answer
cavity that protects the fragile nervous system organs, has 2 subdivisions; cranial cavity and vertebral cavity
question
Ventral body cavity
answer
cavity that contains the structures within the chest and abdomen
question
Cranial Cavity
answer
cavity that contains the brain
question
vertebral Cavity
answer
cavity that contains spinal cord
question
thoracic cavity
answer
cavity housing lungs and heart
question
abdominopelvic cavity
answer
Continuous cavity formed by the abdominal and pelvic cavities
question
Pleural Cavity
answer
the cavity between the lungs and the wall of the chest
question
Mediastinum
answer
area between the lungs containing the heart, aorta, venae cavae, esophagus, and trachea
question
Pericardial Cavity
answer
The cavity within the mediastinum that houses the heart
question
Pelvic Cavity
answer
cavity that contains urinary bladder, reproductive organs, and rectum
question
Serosa
answer
thin, double-layered membranes that cover surfaces in ventral body cavity.
question
parietal serosa
answer
part of the membrane lining the cavity walls
question
visceral serosa
answer
part of the membrane that covers/lines the organ.
question
serous fluid
answer
In the body, the serous membranes are separated by a thin, slitlike layer of lubricating fluid.
question
umbilical region
answer
The centermost region, which includes the umbilicus
question
epigastric region
answer
Located superior to the umbilical region
question
hypogastric region
answer
inferior to the umbilical region, pubic region.
question
right iliac region
answer
located lateral to the hypogastric region
question
left iliac region
answer
located lateral to the hypogastric region
question
right lumbar region
answer
located lateral to the umbilical region
question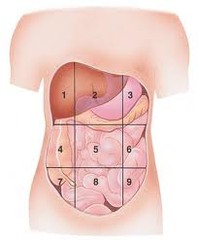
left lumbar region

answer
located lateral to the umbilical region
question
right hypochondriac region
answer
lateral to the epigastric region
question
left hypochondriac region
answer
lateral to the epigastric region



