First Aid: Examples of Each Hypersensitivity and Blood Transfusion rxns – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Type 1 Hypersensitivity examples (2)
answer
1. Allergic and Atopic Disorders (e.g. rhinitis, hay fever, eczema, hives, asthma) 2. anaphlyaxis (e.g. bee sting, some food/drug allergies)
question
Type 1 Hypersensitivity presentation
answer
immediate anaphylatic atopic
question
Type 2 Hypersensitivity examples
answer
1. Acute hemolytic transfusion reactions 2. autoimmune hemolytic anemia 3. bullous pemphigoid 4. erythroblastosis fetalis 5. good pasture syndrome 6. graves disease 7. guillain-barre syndrome 8. idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura 9. myasthenia gravis 10. pemphigus vulgaris 11. penicious anemia 12. rheumatic fever
question
guillain-barre syndrome
answer
an acute form of polyneuritis, often preceded by a respiratory infection, causing weakness and often paralysis of the limbs.
question
polyneuritis
answer
any disorder that affects the peripheral nerves collectively.
question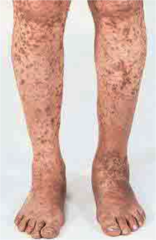
idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura

answer
Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) is a disorder that can lead to easy or excessive bruising and bleeding. The bleeding results from unusually low levels of platelets
question
Type 2 hypersensitivity reaction
answer
disease tends to be specific to tissue or site where antigen is found;
question
define autoimmune hemolytic anemia
answer
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia is a group of disorders characterized by a malfunction of the immune system that produces autoantibodies, which attack red blood cells as if they were substances foreign to the body. Some people have no symptoms, and other people are tired, short of breath, and pale.
question
type 3 hypersensitivity examples
answer
1. Arthus rxn 2. SLE 3. polyarteritis nodosa 4. post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis 5. serum sickness
question
type 3 hypersensitivity presentation
answer
can be associated with vasculitis and systemic manifestations;
question
type 4 hypersensitivity presentation
answer
1. contact dermatatis 2. graft vs host disease 3. multiple sclerosis 4.PPD (test for M.tuberculosis)
question
type 4 hypersensitivity presentation
answer
response is delayed and doesn't involve antibodies
question
Blood transfusion rxn: Allegic rxn
answer
pathogenesis: type 1 hypersensitivity rxn against plasma proteins in transfused blood; presentation: utrica, wheezing, coughing, etc
question
What do you treat allegic rxn relating to a blood transfusion rxns?
answer
antihistamines
question
What do you treat anaphylatic rxn with?
answer
epinephrine
question
What is the pathogenesis of the an anaphylatic rxn?
answer
severe allergic rxn IgA deficient individuals must receive blood products without IgA.
question
What is the clinical presentation of an anaphylatic rxn? (5)
answer
dyspnea, bronchospasm, hypotension, respiratory arrest, shock;
question
Febrile Nonhemolytic transfusion rxn
answer
type 2 hypersensitivity rxn; host antibodies against HLA antigens and WBCs
question
Febrile nonhemolytic transfusion rxn: Clinical presentation (4)
answer
headaches chills flushing fever
question
Acute hemolytic transfusion rxn (4)
answer
type 2 hypersensitivity rxn; intravascular hemolysis (ABO blood group incompatibility) or extravascular hemolysis
question
Intravascular hemolysis
answer
ABO blood group incompability
question
Extravascular hemolysis
answer
Host antibody rxn against foreign antigen or donor RBCs
question
clinical presentation of acute hemolytic transfusion rxn (7)
answer
1.fever 2.hypotension 3.tachypnea 4.tachycardia 5.flank pain 6. hemoglobinuria (intravascular hemolysis) 7. jaundice (extravascular hemolysis)
question
jaundice is the result of...
answer
extravascular hemolysis
question
hemoglobinuria is the result of...
answer
intravascular hemolysis
question
tachypnea
answer
abnormally rapid breathing;
question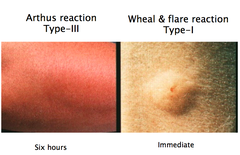
What is arthus rxn caused by?

answer
swelling and inflammation following a tetanus vaccine
question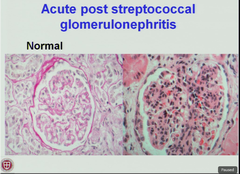
post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis

answer
kidney disease that develops 10 to 14 days after a skin or throat infection. it is not caused by the bacteria itself, but by the body's infection fighting (immune) system. the main symptoms are blood in your child's wee (urine) and swollen ankles or puffy eyes.



