Dermatology 1: Papules, Plaques, and Pustules – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion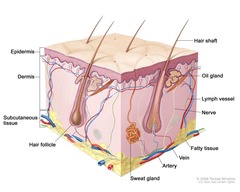

answer
Skin Anatomy
question
Color Shape Configuration Texture Size Location Palpable
answer
Descriptive Factors of Rashes/Lesions
question
When/where did it start? Is this the first episode? Itchy, burning, painful? Spreading? Pattern? Change in size, shape, color, location of lesions? Bleeding? Provoking, alleviating, exacerbating factors? PMHx: asthma, allergies, sensitivities Medications Travel history Environmental exposures Family history
answer
Derm History
question
assessment of respiratory and cardiac stress (anaphylaxis)
answer
ROS must include!
question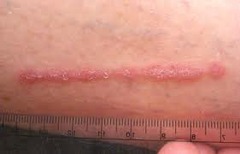
straight line i.e. contact dermatitis, lichen striatus (poison ivy)

answer
Linear lesions (configuration)
question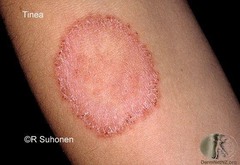
rings with central clearing i.e. ring worm (tinea)

answer
Annular lesions (configuration)
question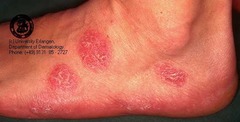
circular or coin-shape i.e. nummular eczema

answer
Nummular lesions (configuration)
question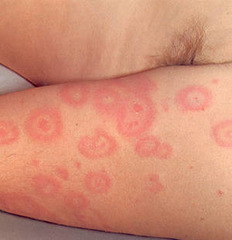
rings with central duskiness i.e. erythema multiforme, lyme disease

answer
Target (bull's eye) lesions (configuration)
question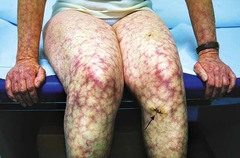
lacy or networked pattern (fishnets) i.e. livedo reticularis

answer
Reticulated lesions (configuration)
question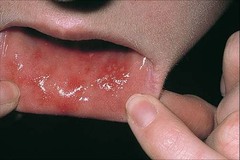
grouped papules or vesicles arranged like a herpes simplex infection i.e. shingles

answer
Herpetiform (configuration)
question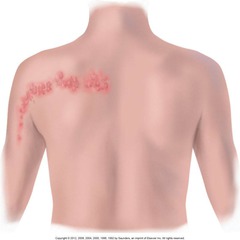
clustered in a dermatomal distribution like herpes zoster

answer
Zosteriform (configuration)
question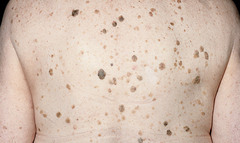
irregular, pebbly, or rough surface i.e. warts and seborrheic keratoses

answer
Verrucous lesions (texture)
question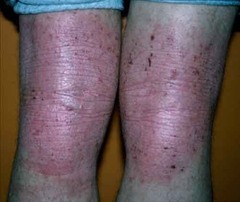
thickening of the skin with accentuation of normal skin markings, results from repeated scratching or rubbing i.e. psoriasis

answer
Lichenification (texture)
question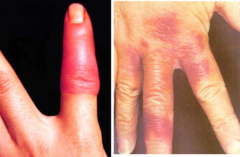
deep thickening of the skin, hard/resistant feel i.e. cellulitis

answer
Induration (texture)
question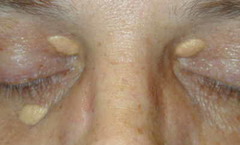
yellowish, waxy lesions, usually benign, idiopathic i.e. lipid disorders, commonly on eyelids

answer
Xanthomas (texture)
question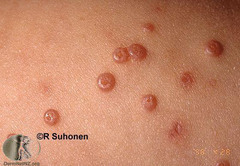
central indentation, usually viral i.e. molluscum contagiosum

answer
Umbilicated (texture)
question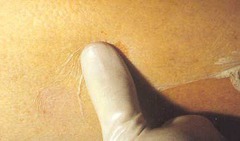
epidermal exfoliation that occurs with gentle lateral pressure on seemingly uninvolved skin, seen in TEN (toxicepidermal necrosis) and pemphigus vulgaris i.e. touch skin with pressure, epidermis peels

answer
Nikolsky sign
question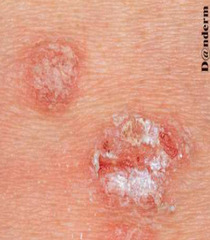
pinpoint bleeding after a scale is removed from plaques in psoriasis

answer
Auspitz sign
question
development of lesions within areas of trauma, psoriasis, lichen planus i.e. think vitiligo occurs at areas of trauma
answer
Koebner phenomenon
question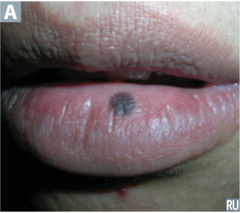
flat, non-palpable usually ;1cm in diameter i.e. freckles, port-wine stains

answer
Macule
question
large macule, flat greater than 1cm

answer
Patch
question
elevated or raised usually ;1cm rounded, flat-topped, umbilicated caused by hyper-proliferation of cells in the epidermis or superficial dermis i.e. warts, insect bites, mole

answer
Papule
question
palpable, elevated ;1cm in diameter caused by proliferation of epidermal and superficial dermal cells i.e. psoriasis

answer
Plaques
question
firm papules that extend into the epidermis, dermis, or subcutaneous tissue pigmented caused by proliferation of the mid to deep dermal cells i.e. lipomas, cysts

answer
Nodules
question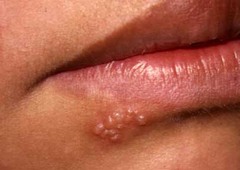
small, fluid-filled papules, aka blisters ;1cm in diameter i.e. herpes

answer
Vesicles
question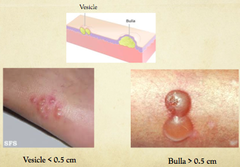
large, fluid-filled vesicles or blisters ;1cm in diameter i.e. burns, allergic contact dermatitis, bullous impetigo

answer
Bullae
question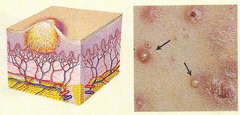
vesicles that contain pus usually infected i.e. folliculitis, acne

answer
Pustules
question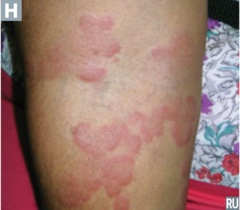
aka wheals or hives elevated pruritic and erythematous lesions caused by local edema i.e. drug, hypersensitivity reactions

answer
Urticaria
question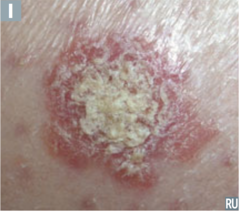
accumulation of horny epithelium i.e. psoriasis, seborrheic dermatitis

answer
Scale
question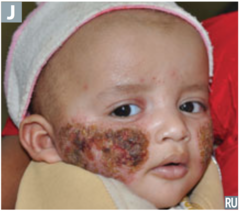
aka scabs dried serum, blood, or pus i.e. impetigo

answer
Crust
question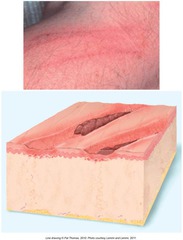
loss of part of epidermis (usually from scratching) -open areas heal without scarring *excoriations- linear

answer
Erosions
question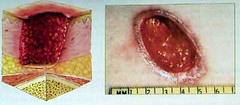
complete loss of epidermis and part of dermis due to venous stasis, trauma *heal with scarring i.e. decubitis ulcers, infections

answer
Ulcers
question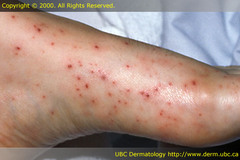
non-blanching punctate foci of hemorrhage can be wet or dry i.e. indicative of systemic or hematologic disorders -platelet abnormalities, vasculitis, RMSF

answer
Petechiae
question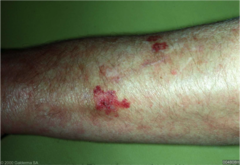
large area of hemorrhage, can be called ecchymosis or bruising maybe palpable -hallmark of leukocytoclastic vasculitis -localized hemorrhage under the skin may indicate co-agulopathy

answer
Purpura
question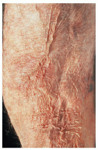
thinning of skin caused by sun exposure, age, long term steroids

answer
Atrophy
question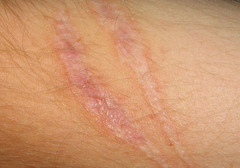
areas of fibrosis that replace normal skin after trauma can lead to keloids (hypertrophic scars that extend beyond the wound margin)

answer
Scars
question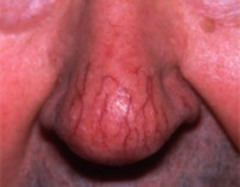
small foci of permanently dilated blood vessels usually occur in areas of sun damage found in numerous systemic diseases

answer
Telangiectasis
question
inflammation of the superficial dermis/epidermis
answer
Dermatitis
question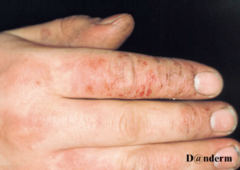
contact dermatitis: papular and itchy rash *can be caused by soaps, detergents, cleaners (localized) Dx: no specific test, arrive by history Tx: identify etiology, topical cortisone cream for pain/itching, PO diphenhydramine (Claritin)

answer
Irritant Dermatitis
question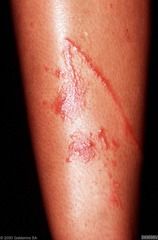
contact dermatitis: more itchy than painful, can have blisters/vesicles on an erythematous base *caused by contact to an allergen (nickel, soaps, perfumes, cosmetics, poison ivy/oak) Dx: KOH to r/o tinea, patch testing to identify chemicals, skin biopsy to exclude tinea, psoriasis or cutaneous lymphoma Tx: identification and removal of allergen, corticosteroids (PO and topical), and anti-histamines

answer
Allergic Dermatitis
question
xerosis, scaly, patchy, cracked skin leading to lichenification unexplained intense pruritis morphology changes depending on age hereditary aggravated by what the person is wearing, stress, anxiety, or dryness worse in winter months
answer
Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema)
question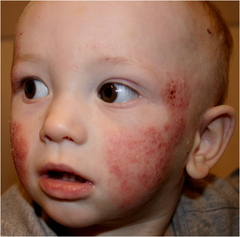
dry, scaly, itchy skin scalp and face (*cheeks) rubbing against bedding, carpeting, and other things in order to scratch the itch, trouble sleeping want to prevent secondary infections

answer
Infant Eczema
question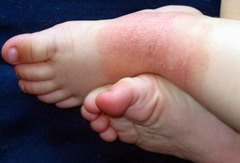
itchy rash beginning at the creases of the elbows or knees, neck, wrists, ankles, and/or crease between the buttocks and legs

answer
Child Eczema
question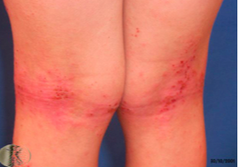
creases of the elbows, knees, and nape of neck especially noticeable on the neck and face and hands causes scaly skin, more scaly then in children or infants

answer
Adult Eczema
question
5 minute luke warm baths followed by liberal application of moisturizer (petroleum or aquaphor) adding emulsifying oils to baths helps (prepares skin for moisturizer) topical steroids in ointment formulation-start with hydrocortisone 1% bid to lesions, can increase strength -typically increase FREQUENCY and then DOSE, then a whole new drug anti-histamines: atarax or diphenhydramine (benadryl) immunomodulators: tacrolimus (black-box warning) soft-clothing, avoid wool products, sleeping in cool temps, humidifier, wash clothing in mild detergents, avoidance of trigger foods (peanuts, eggs, seafood, soy, cow milk, tomatoes, oranges)
answer
Atopic Dermatitis Treatment
question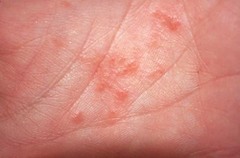
type of eczema pruritic vesicular eruptions on the fingers, palms, and soles "tapioca-like" appearance without surrounding erythema Tx: high dose topical steroids and cold compresses

answer
Dyshidrosis
question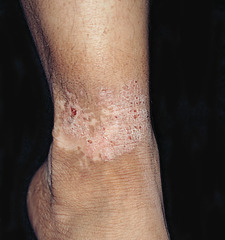
chronic, itchy, inflamed skin caused by a cycle of scratching/rubbing causing more scratching "one or more slightly erythematous, scaly, well-demarcated, lichenified, firm, rough plaques with exaggerated skin lines are noted" Tx: avoid scratching, topical steroids, anti-histamines

answer
Lichen Simplex Chronicus
question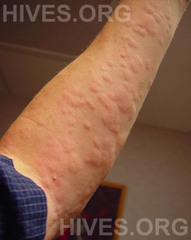
urticaria appear as blanching, pruritic, palpable wheals with erythema and edema involving the dermis and epidermis allergic reaction resulting in histamine release extremely itchy and may result in angioedema Tx: anti-histamines (diphenhydramine or hydroxyzine); check ABC's --> listen to heart and lungs

answer
Hives
question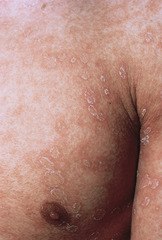
acute, self-limiting (possibly viral) mildly inflammatory, oval, papulosquamous lesions on the trunk and proximal extremities starts with a "herald patch" which is single, oval/round, sharply demarcated, pink or salmon in color on the chest, back, or neck characteristic rash follows in a centrifugal or top down pattern a few days later in a classic "christmas tree" pattern Tx: reassurance, can try anti-histamines if itching is severe but usually not necessary, goes away on its own but can take up to 3 weeks

answer
Pityriasis Rosea
question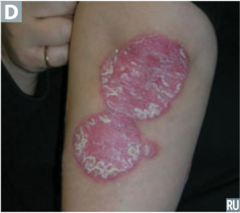
inherited skin disorder (family history) of increased epidermal cell turnover and thickening of the epidermis erythematous papules and plaques with thick silvery scales common on the elbows, knees, and feet four types

answer
Psoriasis
question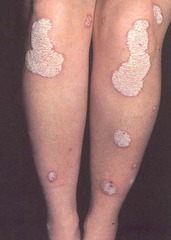
symmetrically distributed plaques involving the scalp, extensor elbows, knees, and back

answer
Plaque psoriasis
question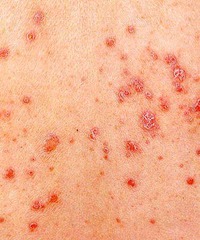
abrupt appearance of multiple small psoriatic lesions

answer
Guttate psoriasis
question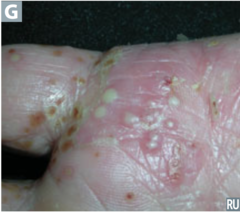
most sever form of psoriasis characterized by erythema, scaling, and sheets of superficial pustule with erosions

answer
Pustular psoriasis
question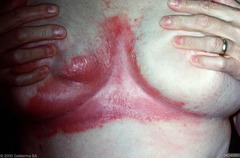
refers to a presentation involving the intertriginous (under breasts, groin) areas

answer
Inverse psoriasis
question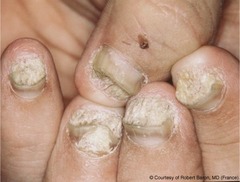
pitting with color changes and crumbling of the nail

answer
Nail psoriasis
question
diagnosis is made clinically and occasionally with a skin biopsy UV light (dec. the cell turnover) or high potency corticosteroids hospitalized in severe cases for a tar ointment or methotrexate
answer
Psoriasis Treatment
question
skin test: RAST (radio-allergosorbant test) skin biopsy d/c offending drug/food if anaphylaxis: H1 antagonists- (anti-histamines, diphenhydramine, cetrizine) H2 antagonists- (ranitidine and cimetidine) steroid burst- (short and intense) tapering- (wean off to prevent adrenal insufficiency)
answer
Hives treatment
question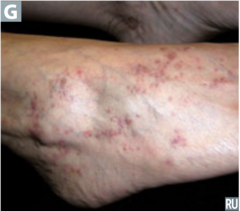
cell-mediated immune response; unknown etiology found with other co-diseases of altered immunity (UC, vitiligo, myasthenia gravis, hep c) hypertrophic, pruritic lichen type lesions on flexor surfaces (wrists) of extremities which spread over the course of weeks involve mucous membranes (painful) actinic, annular, atrophic, linear, etc. Tx: resolve within 8-12 months but can try topical steroids

answer
Lichen Planus
question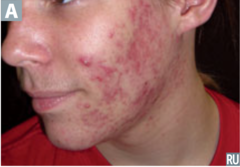
obstruction of sebaceous follicles (oil glands) self limiting, often found in teenagers and young adults manifests as open/closed comedones usually on the face, chest, back causes: stressful events (hormone changes), friction acne, oil based cosmetics retention hyperkeratosis, increased sebum production, inflammation, propionbacterium acne within the follicle Tx: mild cleansers, non-comedogenic moisturizers, diet, topical anti-inflammatory agents +/- topical oral antibiotics

answer
Acne Vulgaris
question
retinoids: comedolytic and anti-inflammatory, help normalize hyperproliferation and hyperkeratinization thus decreasing comedomes -cause sun-sensitivity, qd, taken with oral contraceptive antibiotics: anti-microbial, may have anti-inflammatory properties -clindamycin (topical) -benzoyl peroxide cleansers -minocycline (oral)
answer
Acne vulgaris (topicals)
question
Isotretinoin (accutane): can't get pregnant antibiotics: doxycycline and minocycline hormones: estrogen, oral contraceptives, spironolactone (washes out K+ causing hercitism)
answer
Acne Vulgaris (systemic)
question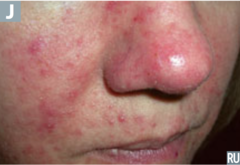
acneiform disorder of middle aged and older adults chronic vascular dilation of central face (nose, cheeks, eyelids, and forehead) susceptible to spicy foods, alcohol, temperature extremes, and emotional reactions Dx: flushing, non-transient erythema, papules and postules, telangiectasia) Tx: topical antibiotics or benzoyl peroxide are the initial treatments of choice -tretinoin cream (papular and pustular lesions unresponsive to other treatments) comes and goes

answer
Rosacea
question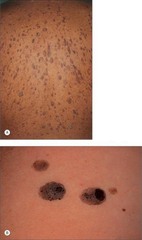
most common benign tumor in older adults over proliferation of epidermal cells (getting old) painless, thickened, acanthotic lesions with an irregular verrucous surface, brown to black in color, with greasy appearance ***Leser-Trelat sign: characterized by the abrupt appearance of multiple tumors that increase their size and number could be malignant if rapid especially GI tract

answer
Seborrheic Keratosis
question
usually none needed ammonium lactate (lac hydrin) and alpha hydroxy acids reduce height of lesion, freezing with liquid nitrogen, curettage Work up and refer stat if Leser-Trelat sign present
answer
Seborrheic keratosis (treatment)



