thyroid disease and their anesthetic considerations – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answers
question
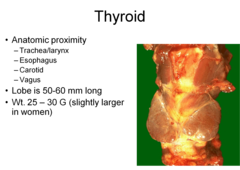
thyroid, size, location

answer
highly vascular 5th-1st thoracic lobes are connected by an isthmus
question
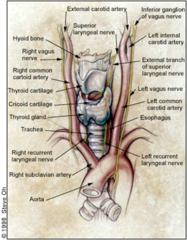
anatomy of thyroid

answer
-recurrent laryngeal, inferior laryngeal artery and inferior laryngeal vein branches off vagus, dips off into chest and back into gland. supplys all lryngeal muscles except the crycothyroid membran which is supplied by superior laryngeal nerve.
question
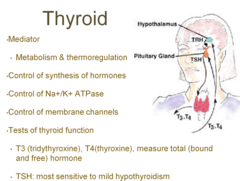
what is the functional purpose of the thyroid

answer
it essentially increase the metabolic rate, increases proteins synthesis, neural maturation, and increased sensbility to catacolimenes.
question
what is elevated in hyperthyroidism?
answer
T4 (thyroxine), this is low in hypothyroid
question
what is higher in hypothyroidism?
answer
TSH- this is the moste sensitive to mild hypothyroidism
question
Hallmark signs of hyperthyriod and hypothyroid SVR, HR, EF, CO, Blood Volume
answer
HYPERTHYROID: decrease SVR, increased HR, increased EF, increased CO, increased blood volume HYPOTHYROID: increased SVR, decreased HR, decreased EF, decreased CO, decreased Blood volume
question
Hyperthyroidism
answer
multinodule goiter from graves disease is common amiodorone is rich in iodine and can cause iodine incued thyrotixicosis
question
why do you get bulging of the eyes in graves disease
answer
because with hyperthyroidism antibodie bind in retro-orbital area casing swelling the eyes
question
signs of hyperthyroidism
answer
red swollen skin
question
treatment of hyperthyroidism
answer
Thioura deritives: methimazole, propythiouracil, (inhibit iodine, so thyroid cannot make thyoid hormone)
question

hyperthyroid systemic effects

answer
Life threating Tachycardia - hyperpyrexia - CHF - dehydration - shock - full bounding pulse - hypertension - atrial fibrillation - sweating, tremor - vomiting and diarrhea - confusion - agitation delirium - coma - metabolic acidosis can cause cardiovascular collapse, want to normalize thyroid function before surgery, can take 6-8 weeks to attain euthyroidism.
question
what is the drug of choice for induction for people with thyroid storm risk?
answer
Thiopental. avoid sympathetic nervous sytem stimulates: pavulon, ketamine, ephedrine. protect patients eyes, and this disorder does not increase MAC.
question
treatment of thyroid storm?
answer
oxygen electrolyte imbalance inderal-esmolol-potassium iodine-cortisol
question

Management of anesthesia for thyroid patients

answer
-Normalize thyroid function prior to surgery -Pre-medicate -Induction agent of choice (thiopental if available) -Avoid sympathetic stimulants -Atrial fibrillation is present in 10-20% of pt Assessment of fluid and electrolyte balance -Airway assessment -Substernal goiters - Tracheoesophageal compression
question
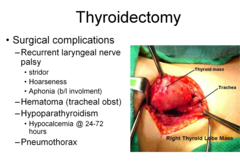
thyroidectomy

answer
want to monitr CA++ for 24-72 hours after surgery
question
hypothyroidism
answer
hashimots is the most common
question
what is the differnce between primary and secondary hyothyroidsim
answer
primary is more comone
question
hypthyroid s/s
answer
untreated in children can lead to mental retardation and stunted growth
question

Myxedema coma

answer
from hypothyroidism. this is medical emergency with 50% mortality. rare, does not effect MAC, the temperature regulations of these patients may effect the MAC of anesthesia
question
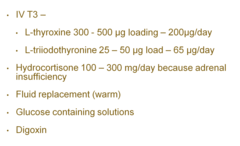
treatment of myxedema coma?
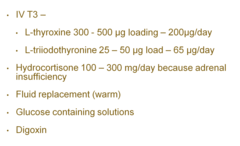
answer
may want to give hydrocortisone
question
other complications of hypothyroidism
answer
Neurologic changes Renal changes decreased glomerular filtration rate - decreased creatinine clearance - decreased free-water excretion Miscellaneous changes Decreased factors VIII & IX - decreased cholesterol Concomitant adrenal insufficiency Ileus & gastroparesis SIADH
question
anesthetic management of hypothyroidism
answer
sensitive to drugs, may need RSI, fluid, difficult weaning -Hypothermia -Anemia -Hypoglycemia -Adrenal insufficiency (hydrocortisone) -Induction with ketamine or other hypnotic -Consider RSI MAINTENANCE ANESTHESIA -Minimize use of volatile anesthetics -Decreased cardiac output (take longer to get off) -Controlled ventilation - Maintain muscle relaxation -Avoid hypothermia -Postoperative respiratory depression -Consider adrenal insufficiency in refractory hypotension and give hydrocortisone
question
Parathyroid
answer
Calcium -GI absorption 0.5-1.0 g/day (duodenum/jejunum) -Body reservoir of 1000 grams -Total serum calcium 8.8-10.4 mg/dL -40-50% (ionized), 40% protein bound (nonionized), 10-20% chelated nonionized -Normal renal excretion of 300-400 mg/day (maximum of 500 mg/day)
question
parathyroid hormone
answer
it is stimulated by high levels of phosphate and low levels of magnesium and low serum ca+
question
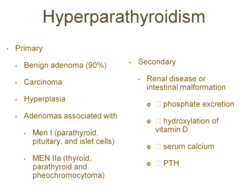
hyperparathyroidsim

answer
all are decreased. can be associated with adenomas -Serum calcium above 11-12 mg/dL Concentration >14 may be life threatening -Generalized weakness -Renal: calculi, polyuria, polydipsia -Cardiac: HTN, short QT, prolonged PR -Skeletal: pain & pathologic fractures -Hematologic: anemia -CNS: somnolence. Psychosis, decreased pain
question
early signs of hyperparathyroidism
answer
sedation vomiting, hypotonia, myasthenia gravis resemblense, systemic hypertension
question
hyperparathyroidism therapy
answer
Thiazides will increase CA+ reabsorption
question

anesthetic considerations for hyperparathyoidism

answer
- can treat with calcium channel blocker -hypophosphate may leave calcium unopposed so make sure phsophate is adequate
question

hypoparathyroidism

answer
low calcium -Hypocalcemia -Ionized calcium < 4.5 mEq/L -Prolonged QT with normal PR -Hyperposphatemia Therapy Acutely: calcium infusion Chronically: Oral calcium - Vitamin D supplements chvosticks sign is with low calcium
question
how much calcium is in calcium chloride and gluconate
answer
27mg/ml of calium in chloride 9mg/ml of calcium in gluconate
question

anesthetic management of hypoparathyroidism

answer
stridor, tetany, monitor muscle block
question
adrenal gland
answer
Arterial blood supply -Abdominal aorta Renal arteries Phrenic arteries -Venous drainage Left gland: renal vein Right gland: inferior vena cava medulla is what secretes: NE, EPI, DOPA Glomerus: aldosterone
question

Glucocorticoids

answer
ACTH regulates their secreation, this is like cortisol reguate homeostais sympathetic response enhancement
question
Mineralcorticoids
answer
regulates extracellular fluid volume through like aldosterone function. Aldosterone accounts for 95% of mineral corticoid activity, conserves sodium and maintains normal potassium levels
question
What is the hallmark for Acute atoic ACTH syndrome?
answer
Hypokalemia and hypertension. this is because acth controls both minercorticoids and glucocorticoids aldosterone gets rid of K+ and holds onto NA thus retaining water
question
clinical featurs of glucocorticoid excess? (eg. cushings)
answer
muscle weakness, crazy, renal stones, fat deposits, rotund belly, hypokalemia
question

Cushings disease

answer
A. 24 hour urine for free cortisol B. High dose decadron suppression test, distinguish between cushing and ectopic syndrome (the steriods will inhibit ACTH) -If A and B normal (cushing's is excluded) -If Cushing's is confirmed, then etiologic diagnosis needs to be done -? plasma ACTH concentration suggests a pituitary tumor -If tumor suspected, obtain MRI
question
anesthetic management of cushings disease (increased acth)
answer
want short acting dilators, patients may need blood pressure support when tumro has been removed. GIVE STRESS DOSE STEROIDS for hypophysectomy or Adrenalectomy
question

Glucocorticoid deficiency (addisons disease)

answer
Two types: primary and secondary Primary: addisones, bilateral adreal distruction cannot produce glucocorticoids 2nd: hypothalmus or decreased acthTwo types: primary and secondary
question
clinical signs and symptoms of addisons
answer
-Hyperpigmentation -Postural and supine hypotension -Asthenia -Muscle weakness -Anorexia & malaise -Abdominal pain & vomiting -Diarrhea or constipation & wt. loss -Salt craving -Myalgias & arthralgias -Mental status changes Steroid treatment shuts down acth production, so the most common cause of insufficent hormone response, this is because of negative feedback, so the body will not ask for more steroids by activating adrenals. <5mg/day of prednisone do not display signs of adrenal insufiicency.
question

******dignosis of addisons****** what is the triad for diagnosis? ON TEST!!!

answer
HYPONATREMIA-HYPERKALEMIA-HYPOGLYCEMIA GIVE STRESS DOSE STEROIDS
question
secondary adrenocortical insufficiency
answer
acth is not released
question

Mineralcorticoid Excess

answer
there is a lot of sodium retention and loss of K
question

Conn's disease

answer
Primary aldosteronism hypertension-Hypokalemic want to replace potassium and give diuretic
question
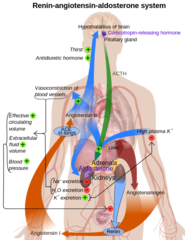
explain the renin angiotensin aldosterone system

answer
When blood volume is low, juxtaglomerular cells in the kidneys secrete renin directly into circulation. Plasma renin then carries out the conversion of angiotensinogen released by the liver to angiotensin I.[2] Angiotensin I is subsequently converted to angiotensin II by the enzyme angiotensin converting enzyme found in the lungs. Angiotensin II is a potent vaso-active peptide that causes blood vessels to constrict, resulting in increased blood pressure. Angiotensin II also stimulates the secretion of the hormone aldosterone from the adrenal cortex. Aldosterone causes the tubules of the kidneys to increase the reabsorption of sodium and water into the blood. This increases the volume of fluid in the body, which also increases blood pressure.
question
anesthetic management of hyperaldosteronism (excess mineralcorticoids Conn's disease)
answer
Restrict sodium and adminster spirolactone possibly adminster potassium, stress dose cortisone infusion.
question
mineralocorticoid deficiency (hypoaldosteronism)
answer
Low aldosterone will have low na high K Hypovolemia
question

Pheochromocytoma

answer
-#1Norepinephrine alone or in combination with epi -Epinephrine -Hyperglycemia and glucosuria -Dopamine -Centrally = Inhibits prolactin secretion Peripherally: -Small amount = renal vasodilation -Moderate = vasodilation of mesenteric and coronary vessels and peripheral vasoconstriction
question
*******Pheochromocytoma triad of symptoms**********
answer
measure urine catacholimines TRIAD ON TEST: HYPERTENSION, DIAPHORESIS, AND H/A
question
clonidine test for pheo reveals?
answer
clonidine will not effect blood pressure if pheo is present
question

hypertension response in pheychromocytoma

answer
this can cause dilated cardiomyopathy and CHF
question

what do you treat a pheochromocytoma with first?

answer
always use beta first, never want uninhibited alpha. if you used a beta blocker first then you may depress the heard and output and not be able to overcome the SVR
question

what medications wuld you want to avoid giving to a pheo?

answer
AVOID MORPHINE! Avoid morphine, because it causes histamine release causing vasodilation promting more catacholine release, tumor manipulation can cause bonkers
question

induction considerations with pheochromocytoma

answer
Morpine, atricurium avoid Droperidrol, metoprolcimde avoid Start off hyperglycemic, release insulin in the absenbce of alpha stimulation
question

anesthetic maintance with pheo

answer
Prepare for hypotension after tumor revmoval with phenylephrine
question
Post operative considerations with pheochroma?
answer
1.Hypotension and tachycardia 2.Hypoglycemia 3.Hypertension



