Pharmacology – Treatment of Hyperlipidemia – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Goal for Treatment of Hyperlipidemias:
answer
- prevent the consequences of atherosclerosis, including heart attacks, angina, peripheral arterial disease, ischemic stroke
question
Drugs for Treatment of Hyperlipidemias:
answer
1. HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors - Statins 2. Resins 3. Ezetimibe 4. Niacin 5. Fibrates
question
Risk Factors for CVD
answer
1. Age: Male > 45 years, Female > 55 years 2. Family History of premature CHD: 1st degree relative - Male < 55 years or Female < 65 year before 1st CHD even occurs 3. Current Cigarette Smoking 4. HTN 5. Low HDL 6. Obesity
question
Lipoproteins
answer
Macromolecular complexes in the blood that transport lipids
question
Apolipoproteins
answer
Proteins on the surface of lipoproteins; they play critical roles in the regulation of lipoprotein metabolism and uptake into cells
question
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL)
answer
Cholesterol-rich lipoprotein whose regulated uptake by hepatocytes and other cells requires functional LDL receptors; an elevated LDL concentration is associated with atherosclerosis
question
High-density lipoprotein (HDL)
answer
Cholesterol-rich lipoprotein that transports cholesterol from the tissues to the liver; a low concentration is associated with atherosclerosis
question
Very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL)
answer
Triglyceride- and cholesterol-rich lipoprotein secreted by the liver that transports triglycerides to the periphery; precursor of LDL
question
HMG-CoA reductase
answer
3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase; the enzyme that catalyzes the rate-limiting step in cholesterol biosynthesis
question
Lipoprotein lipase (LPL)
answer
- Breaks down endogenous triglycerides into glycerol and fatty acids; responsible for releasing free fatty acids from TGs from chylomicrons → VLDLs → IDLs → LDLs - found primarily along endothelial lining - Apolipoprotein C-II is a co-factor - free fatty acids are taken up into cells
question
Proliferator-activated receptor-alpha (PPAR-alpha)
answer
- Member of a family of nuclear transcription regulators that participate in the regulation of metabolic processes; target of the fibrate drugs and omega-3 fatty acids
question
Hyperlipoproteinemia: Pathogenesis
answer
- elevated concentrations of certain plasma lipoproteins, especially LDLs, that participate in cholesterol transport - strongly associated with premature or accelerated development of *atherosclerosis* - *Low HDL* levels also associated with increased risk of atherosclerosis. - In some families, hypertriglyceridemia is similarly correlated with atherosclerosis.
question
Familial ligand-defective Apo B
answer
- *problem with ApoB -> LDL can't bind to receptor* - LDL is increased - most prevalent genetic mutation (2-3%)
question
Lp(a) hyperlipoproteinemia
answer
LDL increased
question
Lp(a)
answer
- has *Apo A* affiliation - interferes with clotting and can increase cholesterol
question
Familial dysbetalipoproteinemia
answer
- increased levels of VLDL remnants and chylomicron remnants - deficiency in *apoE*
question
Familial hypercholesterolemia
answer
- LDL significantly increased - *defect in LDL receptors prevents uptake of LDL* - *Heterozygous:* cholesterol level > 400mg/dL, die at 40 yrs - *Homozygous:* cholesterol level >800, die at 10 yrs without treatment - must treat with drugs that don't work via LDL receptor, such as Niacin
question
Regulation of plasma lipoprotein levels
answer
- involves a complex interplay of dietary fat intake, hepatic processing, and utilization in peripheral tissues. - *Primary disturbances* in regulation occur in a number of *genetic* conditions involving mutations in apolipoproteins, their receptors, transport mechanisms, and lipid-metabolizing enzymes. - *Secondary disturbances* are associated with a Western *diet,* many endocrine conditions, and diseases of the liver or kidneys.
question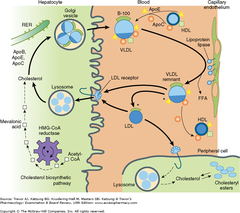
Metabolism of lipoproteins of hepatic origin

answer
- The heavy arrows show the primary pathways. *Nascent VLDL* are secreted via the Golgi apparatus. They acquire additional *apoC* lipoproteins and *apoE* from *HDL.* VLDL is converted to *VLDL remnants* by lipolysis via *lipoprotein lipase* associated with capillaries in peripheral tissue supplies. In the process, *C apolipoproteins* and a portion of *apoE* are given *back* to *HDL.* Some of the VLDL remnants are converted to *LDL* by further *loss of triglycerides and loss of apoE.* - A major pathway for *LDL degradation* involves the *endocytosis of LDL by LDL receptors* in the liver and the peripheral tissues, for which *apoB-100 is the ligand.* (Dark color denotes cholesteryl esters; light color, triglycerides; the asterisk denotes a functional ligand for LDL receptors; triangles indicate apoE; circles and squares represent C apolipoproteins.)
question
Diet treatment strategy
answer
- first method of management, may be enough to lower levels to safe range - Diet designed to *reduce the total intake of cholesterol and saturated fats* (primary dietary factors that contribute to elevated levels of plasma lipoproteins) - Because *alcohol raises triglyceride and VLDL levels,* it should be avoided by patients with hypertriglyceridemia
question
Drugs that are most effective at lowering LDL cholesterol
answer
- HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors / statins - resins - ezetimibe - niacin
question
Drugs that are most effective at lowering triglyceride and VLDL concentrations and raising HDL cholesterol concentrations
answer
- fibric acid derivatives (eg, gemfibrozil) - niacin - marine omega-3 fatty acids
question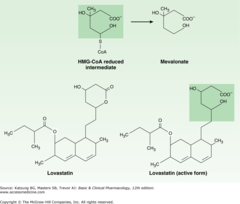
Statins

answer
- structural analogs of HMG-CoA that competitively inhibit the enzyme, HMG-CoA Reductase - Top: The HMG-CoA intermediate that is the immediate precursor of mevalonate, a critical compound in the synthesis of cholesterol. - Bottom: The structure of lovastatin and its active form, showing similarity to the normal HMG-CoA intermediate
question
Which statins are prodrugs?
answer
Lovastatin and simvastatin
question
Which statins are active as given?
answer
atorvastatin, fluvastatin, pravastatin, and rosuvastatin
question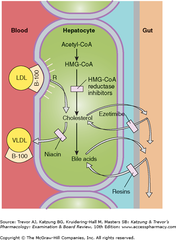
HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors: MOA and Effects

answer
- Although the *inhibition of hepatic cholesterol synthesis* contributes a small amount to the total serum cholesterol-lowering effect of these drugs, a much greater effect derives from the response to a reduction in a tightly regulated hepatic pool of cholesterol. - The liver compensates by *increasing the number of high-affinity LDL receptors,* which clear LDL and VLDL remnants from the blood. - also have direct anti-atherosclerotic effects, and have been shown to prevent bone loss.
question
HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors: Effects
answer
- Since cholesterol is not made anymore, VLDL secretion and TGs decrease, liver increases LDL receptors - result: decreased risk of second heart attack - men: decreased mortality and decreased CV events in men who've never had one - women: decreased CV events - can prevent strokes - questionable for cancer prevention
question
Other Actions of Statins
answer
1. stabilizes plaques 2. coronary vasodilator 3. decreases inflammation by decreasing C-reactive protein 4. decreases LDL oxidation (minor role) 5. works on diabetics to decrease mortality
question
HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors: Toxicity
answer
- *Mild elevations of serum aminotransferases* are common but are not often associated with hepatic damage. - Patients with preexisting liver disease may have more severe reactions; Asians have higher risk of toxicity - *increase in creatine kinase* (released from skeletal muscle) is noted in about 10% of patients; in a few, *severe muscle pain* and even *rhabdomyolysis* may occur as a result of decreased muscle integrity - may be *teratogenic,* so these drugs should be avoided in pregnancy (stops growth of baby) - may lead to *breast cancer* in women - *complete memory loss* is now an FDA warning - can *increase blood glucose* in diabetics
question
Rhabdomyolysis
answer
- possible toxicity from statins - muscle destruction -> material from muscle cell accumulates in the kidney -> damage -> death
question
HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors: Drug Interactions
answer
- 1st and 2nd generations: metabolized by the CYP450 system; drugs or foods, like grapefruit juice, that inhibit CYP450 activity increase the risk of hepatotoxicity and myopathy. - others mainly metabolized in the bile, so not many drug interactions
question
Pitavastatin, Livalo
answer
- *NEW* statin drug that might be the *best at increasing HDL* - better at reducing cholesterol - longer half-life than older statins
question
Enterohepatic Circulation of Bile Salts
answer
- Synthesized by the liver → bile ducts → duodenum → emulsify fats → fat broken down by lipases → bile salt acts as carriers to transport fatty acids back into enteric cells - Bile salts are taken back up into the liver from blood (portal vein)
question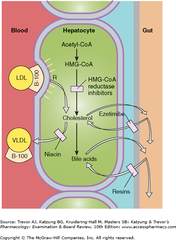
Bile acid-binding Resins: MOA

answer
- Normally, over 90% of bile acids, which are metabolites of cholesterol, are reabsorbed in the GI tract and returned to the liver for reuse. - Examples: cholestyramine, colestipol, and colesevelam - these are large nonabsorbable polymers that *bind bile acids* and similar steroids in the intestine and *prevent their absorption*
question
Bile acid-binding Resins: Effects
answer
- *Prevent the recycling of bile acids* and therefore divert hepatic cholesterol to *synthesis of new bile acids,* resulting in a reduction in the amount of cholesterol collected in a tightly regulated pool. This leads to a compensatory *increase in the synthesis of high-affinity LDL receptors,* which in turn *increases the removal of LDL from the blood.* - cause a modest reduction in LDL but have *little effect on HDL or TG.* In some patients with genetic predisposition for high TG and cholesterol, resins increase TGs and VLDL. - simultaneously *increases cholesterol synthesis* (opposite of statins)
question
Bile acid-binding Resins: Clinical Use
answer
- used in patients with hypercholesterolemia - also been used to reduce pruritus (itching) in patients with cholestasis and bile salt accumulation
question
Bile acid-binding Resins: Toxicity
answer
- bloating, constipation, and an unpleasant gritty taste. - *safe for pregnant women* because they're not absorbed into circulation - take with meals - *Impairs absorption of:* 1. *vitamins* - like vitamin K, dietary folates 2. *drugs* - such as thiazide diuretics, warfarin, pravastatin, fluvastatin
question
Colesevelam
answer
- Bile acid resin - cholestyramine/colestipol - decreased drug binding - encapsulated
question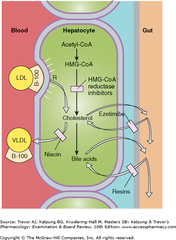
Ezetimibe: MOA

answer
- *prodrug* converted in the liver to the *active glucuronide* form. - active metabolite *inhibits a transporter that mediates GI uptake of cholesterol and phytosterols* - Therefore, *prevents absorption of dietary cholesterol and cholesterol that is excreted in bile* -> also reduces the cholesterol in the tightly regulated hepatic pool. - leads to a compensatory *increase in the synthesis of high-affinity LDL receptors,* which in turn, *increases the removal of LDL* from the blood. - inhibits Neiman-Pick-like protein
question
phytosterols
answer
- plant sterols that normally enter GI epithelial cells but then are immediately transported back into the intestinal lumen - transport blocked by Ezetimibe
question
phytosterolemia
answer
- rare genetic disorder that results from impaired export of phytosterols - treated by Ezetimibe
question
Ezetimibe: Effects
answer
- As monotherapy: *reduces LDL* cholesterol by about 18% - Combined with a statin, it is even more effective (says the book, not Greenspan)
question
Ezetimibe: Clinical Use
answer
- used for treatment of hypercholesterolemia and phytosterolemia
question
Ezetimibe: Toxicity
answer
- well tolerated - combined with statins, may increase the risk of hepatic toxicity
question
Ezetimibe: Drug Interactions
answer
- Serum concentrations of the glucuronide form are: 1. increased by fibrates 2. reduced by cholestyramine
question
Vytorin
answer
- combination of *Simvastatin and Ezetimibe* - lowers cholesterol even further, giving the BEST result (says book) - However, a Merck study showed that combination therapy was no different or maybe even WORSE than statin alone
question
Liptuzet
answer
- Combination therapy including *Atorvastatin and Ezetimibe* - made by same company as Vytorin - no data shows it's beneficial to lower CVD - but it does decrease LDL (a little)
question
Niacin, Nicotinic Acid: MOA
answer
- In the liver: *reduces VLDL synthesis -> reduces LDL levels* - In adipose tissue: activates a signaling pathway that *reduces hormone-sensitive lipase* activity and thus decreases plasma fatty acid and TG levels -> LDL formation is reduced -> decreased LDL - In capillary endothelial cells: *Increased clearance of VLDL by lipoprotein lipase* -> reduces plasma TGs even more - reduces the catabolic rate for HDL - decreases circulating fibrinogen and increases tissue plasminogen activator (plasminogen cleaves clots)
question
Niacin: Effects
answer
- Decreases VLDL synthesis, TG, and LDL concentrations - Increases HDL cholesterol - decreases LPA (Apo A + LDL)
question
Niacin: Clinical Use
answer
- treatment of: 1. hypercholesterolemia 2. hypertriglyceridemia 3. low levels of HDL
question
Niacin: Toxicity
answer
1. *Cutaneous flushing;* pretreatment with aspirin or other NSAIDs reduces the intensity (so may be mediated by prostaglandin release). Tolerance to flushing usually develops within a few days 2. *Dose-dependent nausea and abdominal discomfort* 3. *Pruritus* and other skin conditions 4. *Moderate elevations of liver enzymes* and even severe *hepatotoxicity* may occur, primarily with extended-release preparation. 5. *Hyperuricemia* occurs in about 20% of patients, and *carbohydrate tolerance* may be moderately impaired.
question
Niaspan
answer
- safer than Niacin, but it increases blood glucose and increases uric acid - may cause abdominal discomfort - pregnant women should not take it
question
Advicor
answer
- Combination therapy including *Lovastatin and Niacin* - leads to NO CHANGE in CV death - no evidence that addition of Niacin is better than statin alone
question
Simcor
answer
- Combination therapy including *Simvastatin and Niacin* - leads to NO CHANGE in CV death - no evidence that addition of Niacin is better than statin alone
question
Fibric Acid Derivatives: MOA
answer
- Examples: gemfibrozil, fenofibrate - *ligands/agonists for the PPAR-alpha protein* - In adipose tissue: binding causes *increased synthesis of lipoprotein lipase,* which associates with capillary endothelial cells and *enhances clearance of TG-rich lipoproteins* - In the *liver:* 1. stimulate *fatty acid oxidation* -> limits the supply of TGs and decreases VLDL synthesis 2. *increases expression of apoA-I and apoA-II*-> increases HDL levels 3. *decrease expression of apoC-III,* which impedes the clearance of VLDL
question
Fibric Acid Derivatives: Effects
answer
- In most, *lower TG but little or no effect on LDL* - However, can increase LDL in patients with familial combined hyperlipoproteinemia, which is associated with a combined increase in VLDL and LDL.
question
Fibric Acid Derivatives: Clinical Use
answer
- treat *hypertriglyceridemia* - Because these drugs have only a modest ability to reduce LDL cholesterol and can increase LDL cholesterol in some patients, they often are combined with other cholesterol-lowering drugs for treatment of patients with elevated concentrations of both LDL and VLDL.
question
Fibric Acid Derivatives: Toxicity
answer
1. Nausea = most common 2. Skin rashes = common with gemfibrozil. 3. Few patients show decreases in WBC or Hct 4. *Increased risk of cholesterol gallstones* -> use with caution in patients with a history of cholelithiasis 5. In combination with reductase inhibitors: significantly increase the risk of myopathy
question
Fibric Acid Derivatives: Drug Interactions
answer
- can potentiate the action of anticoagulants
question
Combination Therapy
answer
- Because resins interfere with the absorption of certain statins (pravastatin, cerivastatin, atorvastatin, and fluvastatin), these must be given at least 1 h before or 4 h after the resins. -The combination of reductase inhibitors with either fibrates or niacin increases the risk of myopathy.
question
What is the only drug that inhibits cholesterol absorption in the GI?
answer
Ezetimibe
question
Which drug class can actually INCREASE mortality due to it's induction of formation of gallstones?
answer
Fibrates
question
Which fibrate has a better effect on lowering LDL?
answer
Fenofibrate
question
Two facts we know about Lipid-Lowering drugs
answer
1. Statins decrease mortality 2. Niacin decreases mortality
question
Fish Oil
answer
- thought to be a natural remedy to lower TG and affect platelet aggregation - but recent study showed it caused no statistically significant difference in levels
question
Two New Drugs based on Fish Oil
answer
1. Lovaza 2. Vascepa
question
Lovaza
answer
- Rx drug based on fish oil - omega-3-fatty acid ethyl ester - DHA and EPA - turns -> fatty acids in the body - could increase LDL
question
Vascepa
answer
- Rx drug based on fish oil - ethyleicosapentanoic acid - EPA - no DHA - does NOT increase LDL, so works better than Lovaza - works similarly to Niacin
question
Two NEW drugs to treat familial hypercholesterolemia
answer
1. Lomitapide, Juxtapid 2. Mipomersen, Kynamro
question
Lomitapide, Juxtapid
answer
- made by Aegerion - *Inhibits Microsomal TG Transfer Protein, MTP: inhibits transfer of TG from one molecule to a pre-VLDL particle* - for familial hypercholesterolemia *homozygotes* - *decreases VLDL activity* -> direct effect on LDL synthesis - *decreases LPA significantly* - Toxicity: fat remains in liver -> *fatty liver*
question
Mipomersen, Kynamro
answer
- drug to treat familial hypercholesterolemia - made by Genzyme - *Antisense oligonucleotide able to resist endonucleases* - *inhibit Apo B synthesis -> decreases LDL and VLDL* - *decreases LPA significantly* - Toxicity: fat remains in liver -> *fatty liver*



