Congenital Anomalies of the Retina – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Only when opaque (mechanical problem)
answer
Do myelinated retinal nerve fibers cause vision loss?
question
Myelinated nerve fibers
answer
In which condition may vessels be partially or completely obscured: myelinated nerve fibers or ischemic events?
question
*Plasia - increased NUMBER of cells; pigment in RPE has been dispersed (see clumping of cells)* *Trophy - increased SIZE of cells; cells don't nourish receptor layer well enough to give you good vision*
answer
*Hyperplasia vs hypertrophy*
question
Normally infectious Possibly trauma
answer
What causes hyperplasia?
question
Mechanical (stretch) or trophic (growth factors) signals (think of it like your muscles getting bigger when you work out - the cells get bigger; they don't increase in number)
answer
What causes hypertrophy?
question
-plasia
answer
Which causes reduced acuity: -plasia or -trophy?
question
-trophy (relative scotoma)
answer
Which causes scotoma: -plasia or -trophy?
question
Maybe, but no treatment
answer
Does CHRPE have associated field loss?
question
Bilateral CHRPE, typically "bear tracks" Autosomal dominant Intestinal polyps typically progress to adenocarcinoma (bowel cancer; if seen in kid, basically 100% chance)
answer
Gardner's syndrome
question
Hyperpigmented - dark brown to black
answer
CHRPE: color
question
Geographic/sharp
answer
CHRPE: borders
question
Lacunae
answer
CHRPE: associated findings
question
Flat
answer
CHRPE: elevation
question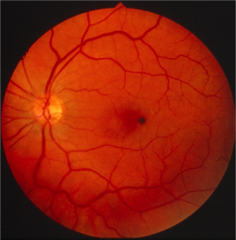
Recurrent toxoplasmosis

answer
Hx of toxo
question
Collection of melanocytes (benign "melanoma")
answer
Nevus definition
question
Typically under 2 DD Can be up to 5 DD
answer
Choroidal nevi: size
question
Fuzzy, indistinct
answer
Choroidal nevi: borders
question
Gray to green May be amelanotic (yellow to brown)
answer
Choroidal nevi: color
question
Drusen
answer
Choroidal nevi: associated findings
question
Moderate hypo-reflectivity
answer
Choroidal nevi: B scan
question
Flat to slightly elevated
answer
Choroidal nevi: elevation
question
Well-demarcated
answer
Choroidal osteoma: borders
question
Pale yellow
answer
Choroidal osteoma: color
question
Hyper-reflective
answer
Choroidal osteoma: B scan
question
Melanoma
answer
Most common primary tumor of the eye
question
Uveal melanoma
answer
Most common primary malignant intraocular tumor in caucasians
question
Caucasians Men 55-60
answer
Uveal melanoma: demographics
question
Liver 5-7 months
answer
What is the most common site for extraocular metastasis from ciliary body and choroidal melanoma, and what is the prognosis?
question
Failure of RPE function; *degeneration of RPE* (Pigment in choroid is displacing the fluid that is leaking from vessels used to nourish RPE)
answer
What does it mean when you see drusen?
question
Good with nevi because it means the lesion has been around a long time and hasn't grown (benign)
answer
When is it relatively good to see drusen?
question
Increasing Most > 10 DD at diagnosis
answer
Choroidal malignant melanoma: size
question
Fuzzy, indistinct
answer
Choroidal malignant melanoma: borders
question
Significantly elevated
answer
Choroidal malignant melanoma: elevation
question
*Lipofuscin* (look more orange than drusen) Sentinel vessel
answer
Choroidal malignant melanoma: associated findings
question
*Acoustically hollow* (hypo-reflective) Dome-shaped
answer
Choroidal malignant melanoma: B scan
question
Full body MRI Blood work Check for metastasis
answer
Choroidal malignant melanoma: treatment
question
*Choroidal melanoma*
answer
*What would you suspect if you observe a large conjunctival blood vessel?*
question
-Cancer center for evaluation of mass -Full body MRI or CT (focus on liver) -Complete physical -Blood workup including CBC and liver function studies
answer
If it is melanoma, how do you refer?
question
Removal of contents of the eye (leave sclera intact)
answer
Evisceration
question
Removal of the eye, including the globe (leave the rest of the orbital contents, including bones, muscles, fat, and conjunctiva)
answer
Enucleation
question
Removal of all orbital contents, including muscles, lacrimal gland system, optic nerve, and varying parts of the bone (may or may not remove eyelids)
answer
Exenteration
question
Benign vascular lesion ("vascular birthmarks")
answer
What is a haemangioma?
question
Diameter, height, ultrasonographic hollowness, extrascleral extension
answer
What can you learn from B-scan ultrasonography?
question
Diameter, monitoring for growth
answer
What can you learn from digital photography?
question
Useful for documentation, not so much diagnosis Drusen stain, melanomas have pooling
answer
What can you learn from FA?
question
Least aggressive, best outcome
answer
Uveal melanoma prognosis: spindle cell A
question
More aggressive than spindle cell A
answer
Uveal melanoma prognosis: spindle cell B
question
Most aggressive, high malignancy
answer
Uveal melanoma prognosis: epithelioid
question
Intermediate prognosis
answer
Uveal melanoma prognosis: mixed cell
question
*Ciliary body melanoma* *(sentinel vessel)*
answer
*What would you suspect if you observe a single large vessel that seems to disappear into the conjunctiva?*
question
*Iris melanoma*
answer
*Of the three types of uveal melanomas, which type is the rarest?*
question
*Ciliary body melanoma* More likely to be composed of epithelioid melanoma cells, larger at time of detection, highly malignant
answer
*Of the three types of uveal melanomas, which type has the poorest prognosis?*
question
Solid, acoustically dark mass
answer
How does ciliary body melanoma appear on B-scan?
question
Low risk of dying in 5 years (just photograph and follow - no treatment)
answer
COMS findings: small tumors
question
Equal mortality rates between enucleation and iodine-125 brachytherapy (neither treatment is likely to increase or decrease mortality rates)
answer
COMS findings: medium tumors
question
Equal mortality rates between radiation (PERT) + enucleation and enucleation alone
answer
COMS findings: large tumors
question
YERVOY (ipilimumab)
answer
What is the only treatment that may be effective against metastatic choroidal melanomas?
question
*DIFFUSE choroidal hemangioma*
answer
*What is congenital anomaly associated with Sturge-Weber syndrome?*
question
Nevus = benign, not optic nerve Melanoma = malignant Melanocytoma = benign, optic nerve
answer
What's the difference between a nevus, a melanoma, and a melanocytoma?
question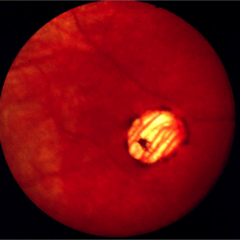
ON coloboma (otherwise looks like hypertrophic RPE with lacunae)

answer
This patient has a keyhole pupil
question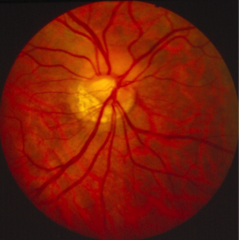
Tilted disc

answer
Tilted disc or oblique insertion?
question
Tilted disc

answer
Tilted disc or oblique insertion?
question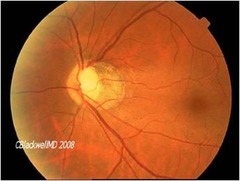
Oblique insertion

answer
Tilted disc or oblique insertion?
question
(most to least important) 1. Gestational age 2. Weighted oxygen 3. Intraventricular hemorrhage 4. Sepsis 5. Birth weight (particularly ; 3.5 lbs)
answer
Risk factors for retinopathy of prematurity
question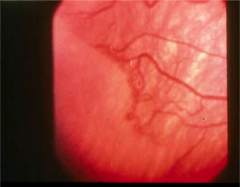
ROP stage 1 (line of demarcation separates the more nasal vascular zone from the more temporal avascular zone)

answer
What is this stage of ROP?
question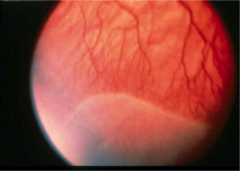
ROP stage 2 (line of demarcation becomes a ridge that protrudes into the vitreous - histological evidence of an A/V shunt)

answer
What is this stage of ROP?
question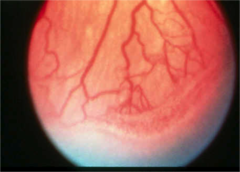
ROP stage 3 (neovascularization, as a result of anoxia, occurs along the ridge)

answer
What is this stage of ROP?
question
Scarring and fibrosis can occur when the neovascularization extends into the vitreous
answer
Describe ROP stage 4 (he didn't have an actual picture)
question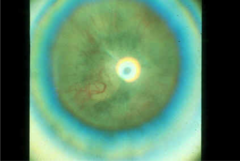
ROP stage 5 (total retinal detachment)

answer
What is this stage of ROP?



