8. Pulmonary EOR: ARDS, FBA, TB, Lung cancer – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
A potential complication of DKA treatment where fluid overload decreases plasma oncotic pressure and favoring a fluid shift across the pulmonary capillary membrane
answer
acute respiratory distress syndrome protein rich pulmonary edema
question
The most common cause of ARDS is...?
answer
sepsis Other causes include trauma, aspiration pneumonia and dkq fluid overload in treatment
question
DX of ARDS requires these three things:
answer
1. refractory PaO2/FIo2 ration that is not responsive to 100% O2 2. b/l pull infiltrates on car 3. Absence of cariogenic pulm edema
question
Symptoms of ADRS
answer
begins 12-24 hours after event. dyspnea, tachypnea, red or pink sputum, diffuse crackles, cyanosis
question
A key treatment of ARDS IS
answer
1. TREATING UNDERLYING CAUSE 2. POSITIVE end expiratory pressure ventilation
question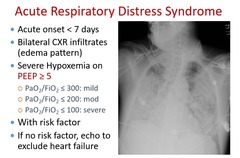
What are likely findings on CXR of ARDS?

answer
Bilateral opacities consistent with pulmonary edema must be present
question
What is the main DDX for ARDS?
answer
Cardiogenic pulmonary edema is the primary alternative that needs to be excluded. This may require diagnostic testing (eg, brain natriuretic peptide [BNP] levels, echocardiography, and/or right heart catheterization)
question
TX and dx of for foreign body aspiration is?
answer
bronchoscopy
question
___________should be suspected in children who have sudden onset of lower respiratory symptoms, or those who do not respond to standard management of other suspected etiologies such as pneumonia, asthma, or croup.
answer
Foreign body aspiration (FBA)
question
For high suspicion of FBA in a stable patient, the first step in dx is...?
answer
evaluation is to perform plain radiography of the chest
question
T/F Most foreign bodies are radiolucent on imaging and require direct visualization, usually bronchoscopy for diagnosis
answer
T
question
Match FBA bronchoscopy: flexible bronchoscopy rigid bronchoscopy children adults
answer
children -rigid bronchoscopy adults - flexible bronchoscopy
question
Acid fast stain erobic rod...
answer
mycobacterium tuberculosis
question
Transmission of TB is through...?
answer
respiratory droplet
question
What are goon complexes?
answer
calcified nodules in the lungs due to macrophages and t lymphocytes
question
High risk of TB?
answer
immigrants jailed population prison drug users elderly and nursing home
question
The skin PPD test becomes positive when?
answer
1-2 months after exposure
question
If the body doesn't contain the primary TB then its called?
answer
active TB (progressive primary)
question
What are some symptoms of TB
answer
progressive cough +- hemoptysis
question
SX of TB?
answer
fevers, chills, nights sweats, anorexia, weight loss, chest pain,
question
Reactivation TB affects what part of lungs on CXR?
answer
apices
question
T/F Acid fast sputum confirms diagnosis of TB
answer
F it supports. DX is definitively by culture
question
Primary TB will show what on CXR?
answer
hilar lad, homogeneous infiltrates, cavitations
question
Positive skin test TB reactions: 1. HIV, close + contacts 2. Immigrants, healthcare workers 3. normal population
answer
1. HIV, close + close contacts ;=5 2. Immigrants, healthcare workers ;=10 3. normal population ;=15
question
How long should active TB patients be isolated?
answer
for at lease two weeks of treatment
question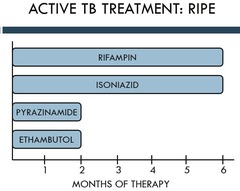
What are the four drugs for for active TB?

answer
INH RIF PZA ethambutol for eight weeks, continue rif/inh for 18 weeks
question
Main SE of INH?
answer
hepatitis/hepatotoxicty
question
T/F Anti-TB meds aren't generally started in the ED
answer
T
question
If someone is suspected of TB or active TB person is admitted what should be done?
answer
respiratory precautions. negative pressure room
question
This TB med causes orange body fluids, hepatitis and flu like symptoms?
answer
rifampin
question
This TB med can cause optic neuritis (red-green vision loss)?
answer
Ethambutol
question
This vaccine is available for TB in endemic areas but is not used in US
answer
bacille palmette guerin (BCG)
question
Two types of bronchogenic neoplasm? MC type?
answer
1) NON-small cell carcinoma = 85% =local spread -adenocarcioma= m/c in smokers & women & nonsmokers = spread peripheral -SCC- typically central spread; associated w/ inc ca, cavity lesions, and pancoast syndrome -large cell (anapestic) - peripheral- VERY aggressive -bronchoalveolar = BEST prognosis = interstital lung pattern **surgery tx FIRST line 2) small cell (OAT cell) carcinoma (SCLC) = met early on, inc chance if smoker, typically central and very aggressive **SCLC is m/c associated w/ paraneoplastic syndrome ***chemo and/or radiation
question
Which bronchogenic carcinoma has the best prognosis, amenable to surgery? Small Cell Non-Small Cell (Adeno, Sqamous, Large)
answer
Non small cell small cell (oat) is very aggressive and not responsive to surgery
question
Which type of bronchogenic cancer is associated with non smokers and spreads peripherally? Small Cell Non-Small Cell (Adeno, Sqamous, Large)
answer
adenocarcinoma
question
These two lung cancers are centrally growing?
answer
small squamous
question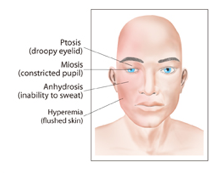
What is a pan coast tumor?

answer
squamous tumor at the apex of lung that leads to pain and horner's syndrome Miosis (constriction) Anhydrous Ptosis
question
Which pneumonia? ear pain; bulls myringitis + resp symptoms
answer
mycoplasma pneumonia
question
FBA swallowed by adults is most likely to lodge where?
answer
LES
question
FBA swallowed by children is most likely to lodge where?
answer
proximal esophagus at cricopharngeal narrowing
question
Which FBA aspiration just be removed immediately
answer
button batteries
question
The preferred method of FB removal is mostly
answer
endoscopy
question
Stridor on inspiration suggest
answer
Obstruction above the vocal chords
question
Stridor in exhale or mixed inhale/exhale
answer
Obstruction below vocal chords
question
FBA occurs on which side of the lungs more commonly
answer
right side
question
Which of the following TB are contagious: 1. primary TB 2. Chronic latent 3. Secondary (reactivation)
answer
1. primary TB - contagious 2. Chronic latent -NOT CONTAGIOUS 3. Secondary (reactivation) -contagious
question
This TB drug can cause liver tox
answer
PXA



